| Magazine |
| | Community |
| | Workshop |
| | Tools & Samples |
| | Training |
| | Site Info |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|||||||||
Asynchronous pluggable protocols enable developers to create pluggable protocol handlers, MIME filters, and namespace handlers that work with Microsoft® Internet Explorer version 4.0 and later and a URL moniker. This section covers the pluggable protocol functionally exported by the Urlmon.dll dynamic-link library (DLL). For information on the other APIs exported by the Urlmon.dll, see the Asynchronous and URL Monikers and URL Security Zones sections.
Pluggable protocol handlers can be used to handle a custom Uniform Resource Locator (URL) protocol scheme or filter data for a designated MIME type.
The ability to handle a custom URL protocol scheme using a pluggable protocol handler gives developers the ability to implement new or custom protocol schemes for Internet Explorer 4.0 (and later) and for applications using URL monikers. Existing protocol schemes, such as HTTP and FTP, are handled by the default pluggable protocol handler included with Internet Explorer.
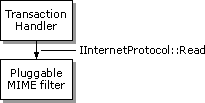
Filtering data for a particular MIME type can be handled by a pluggable MIME filter, which is a unique implementation of a pluggable protocol handler. Unlike standard pluggable protocol handlers and pluggable namespace handlers, which only provide data, pluggable MIME filters both read and provide data. The data is read through the pluggable MIME filter's implementation of the IInternetProtocolSink interface. After the data has been processed, the filtered data is provided to the system through the pluggable MIME filter's implementation of the IInternetProtocol interface.
Let's say that a new protocol scheme has been introduced and your company wants to provide support for users of Internet Explorer 4.0 and later. Pluggable protocols allow you to provide a new protocol handler that will be called for any requests using the new protocol scheme.
Or, say your company wants to design products that will help parents keep their children from reading profanity on the Internet. You could design a pluggable MIME filter, register it to handle the text/* MIME types, and have it replace all profanity with <BEEP> or something similar. Any content that has a matching MIME type, such as a Web page (whose MIME type is usually text/html), will call the pluggable MIME filter and pass the filtered data to the user.
This documentation assumes that you have an understanding of Microsoft® Win32® programming. Also, you should have an understanding of OLE and COM programming and of the format and syntax of a URL. For more information, see RFC 1738, Uniform Resource Locators (URL). You can find this document at ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc1738.txt.
To compile programs that use the functionality provided in Urlmon.dll, make sure the Urlmon.h header file is in the include directory and the Urlmon.lib library file is in the library directory of the C/C++ compiler you use.
A URL follows the syntax described in RFC 1738, which specifies a protocol scheme followed by a scheme-specific portion (<scheme>:<scheme-specific portion>). For example, in the URL http://www.microsoft.com/, "http" is the scheme and "//www.microsoft.com/" is the scheme-specific portion.
The beginning section of the scheme-specific portion of the URL contains the server name. This portion of the URL is often referred to as the URL namespace.
Internet Explorer uses two mechanisms for registering new URL protocol handlers. The first method is to register a URL protocol and its associated application so that all attempts to navigate to a URL using that protocol launch the application (for example, registering applications to handle mailto: or news: URLs). The second method uses the Asynchronous Pluggable Protocols API, which allows you to define new protocols by mapping the protocol scheme to a class.
For information on how to register an application for a particular URL protocol, see Appendix A: Registering an Application to a URL Protocol.
Asynchronous pluggable protocols offer three ways to map a protocol scheme to a class:
Note All asynchronous pluggable protocols must support the BINDF_NO_UI and BINDF_SILENTOPERATION flags.
Interfaces related to asynchronous pluggable protocols
Functions related to asynchronous pluggable protocols
An asynchronous pluggable protocol handler is an apartment-threaded Component Object Model (COM) object that handles any calls made to the protocol scheme that it is registered for. When a client application makes a request, Urlmon looks up the protocol scheme in the registry and creates an instance of the protocol handler registered for that protocol scheme. If the protocol scheme was successfully mapped to the class identifier (CLSID) of a protocol handler, CoCreateInstance is called with that class asking for an IClassFactory interface. An instance of the protocol handler is obtained with IClassFactory::CreateInstance.
To register a custom URL protocol, add a key for the protocol scheme of the custom URL protocol to the registry under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\PROTOCOLS\Handler\protocol_scheme. Under that key, the string value, CLSID, must be set to the CLSID of the protocol handler.
To register the custom protocol scheme example, you would have to add a key named example to the registry under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\PROTOCOLS\Handler. Under the new key, HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\PROTOCOLS\Handler\example, the string value, CLSID, must be assigned the CLSID of the protocol handler. Any URLs with the protocol scheme example: would be handled by the protocol handler associated with the CLSID value.
The protocol handler cannot use any Windows® messaging to switch back to the thread it was instantiated on, since the protocol handler must work on non-GUI threads.
Note All asynchronous pluggable protocols must support the BINDF_NO_UI and BINDF_SILENTOPERATION flags.
Temporary pluggable namespace handlers can be used to handle all URLs using a particular protocol scheme. You can register and unregister a temporary pluggable namespace handler by using the IInternetSession interface.
A pluggable MIME filter is an asynchronous pluggable protocol that receives data through a stream, does some operation on the data, and returns a data stream. The output data might be in a different format from the original stream.
Multiple pluggable MIME filters can be registered either temporarily or permanently. Temporarily registered pluggable MIME filters are called first and in the reverse order in which they were registered. That means the pluggable MIME filters registered last will be called first.
For information on how Internet Explorer 4.0 determines MIME types, see Appendix A: MIME Type Detection in Internet Explorer 4.0.
Note All asynchronous pluggable MIME filters must support the BINDF_NO_UI and BINDF_SILENTOPERATION flags.
Also, pluggable MIME filters are only invoked by Internet Explorer for the resource specified by the URL. The MIME filter will not be invoked for other resources (such as images on an HTML page) that are associated with the resource specified by the URL.
You must register a permanent pluggable MIME filter in the registry with the key HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\PROTOCOLS\Filter\<mime_filter> and with a value for a MIME filter. This value must be a CLSID.
You can register and unregister a temporary pluggable MIME filter by using the IInternetSession interface.
Use the following steps to create an asynchronous pluggable protocol handler:
After the protocol handler is created and added to the registry, it can be used by any application using the functionality provided by Urlmon.dll. The following steps contain the general order of the calls made between Urlmon.dll and your protocol handler when a URL with the protocol scheme you registered your handler for is called:
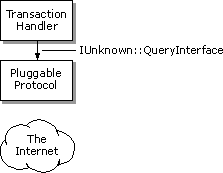
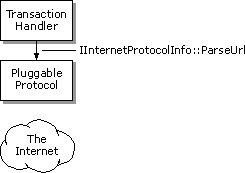
If the protocol handler is being called for an update of a subscription by Internet Explorer 4.0, the pluggable protocol handler's IInternetProtocolInfo::QueryInfo method will also be called with the QUERYOPTION value set to QUERY_USES_CACHE. Only pluggable protocol handlers that use the Internet cache and return TRUE for the QUERY_USES_CACHE flag will be supported by the Internet Explorer subscription mechanism.

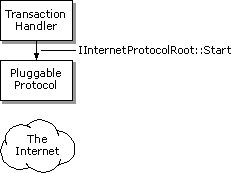

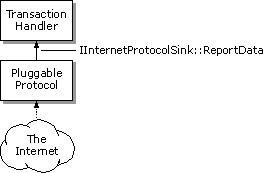
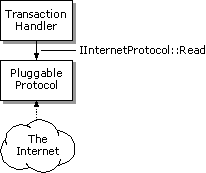

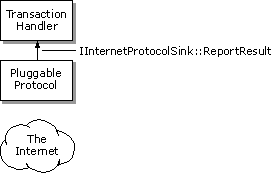
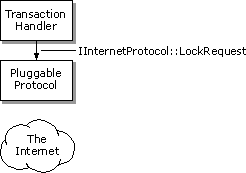
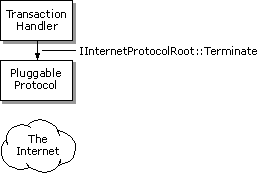
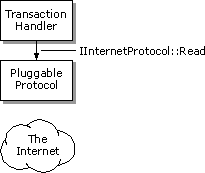
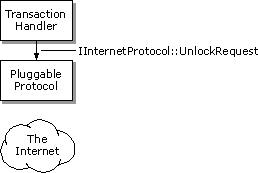
Note Your pluggable protocol handler's IInternetProtocol::Read method might continue to get called even after the method has indicated that all the data has been read. All asynchronous pluggable protocol handlers must be prepared to handle this possibility.
A pluggable MIME filter is essentially an asynchronous pluggable protocol handler that implements an IInternetProtocolSink interface. Urlmon.dll will use the MIME filter's implementation of IInternetProtocolSink to notify the pluggable MIME filter that it has data ready to be filtered.
Also, filters that handle multiple MIME types must register a separate CLSID for each MIME type they handle:
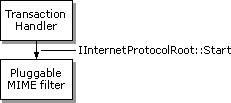

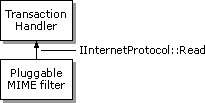

More details will be provided in future versions of this documentation.
The following topic contains content that is related to asynchronous pluggable protocols:
Does this content meet your programming needs? Write us!
© 1998 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Terms of use.