Next | Prev | Up | Top | Contents | Index
Serial Port Pin Signal Tables
The serial port on your workstation or server is either a DB-9 (9-pin) or a mini-DIN8 port. In either case, the port is clearly labeled as a serial port. Consult your system Owner's Guide to determine which kind of port your system has. There are two basic printer cable configurations; one for the DB-9 serial ports and one for the mini-DIN8 serial port. Depending on the cables used some serial functionality may be sacrificed due to unconnected wires in the cable. Note that the pinout of the DB-9 connectors is different from that of the full size DIN connectors that may be next to them. These DIN connectors also have different pinouts from the mini-DIN8 connectors used on some systems and documented in this section. The DB-9 and full-sized DIN connectors are connected to the same internal port hardware.
DB-9 Connector Cabling
For most serial printers, use the following cable. This cable uses the normal 3-wire connection and be used as a /dev/ttyd* device. Table 2-2 lists typical DB-9 serial pin assignment, as shown in Figure 2-5.

Figure 2-5 : DB-9 Pin Assignment
Pin Definitions for a DB-9 Serial Cable
| DB-9-Male | Function |
| 1 | Transmit Data |
| 2 | Receive Data |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | Signal Ground |
| 8 | Data Carrier Detect* |
| 9 | |
* Data Carrier Detect is used only with /dev/ttym* devices if the system must notice when the printer powers off. Normally it is not used.
For printers using RTS/CTS hardware flow control, the following pinout allows "full flow control." This cable is required to implement /dev/ttyf* devices. This cable also supports /dev/ttym* devices. Table 2-3 lists the correct pinout for these devices, as shown in Figure 2-6.
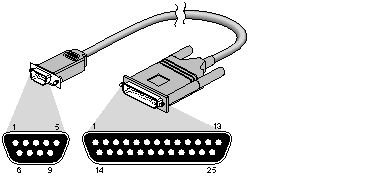
Figure 2-6 : DB-9 to DB-25 RTS/CTS Flow Control Cable
Pin Definitions for a DB-9 to DB-25 RTS/CTS Flow Control Cable
| DB-9-Male | Signal | DB-25-Male | Signal |
| 1 | not used | 1 | not used |
| 2 | Transmit Data | 2 | Receive Data |
| 3 | Receive Data | 3 | Transmit Data |
| 4 | Request to Send* | 4 | Request to Send* |
| 5 | Clear to Send* | 5 | Clear to Send |
| 6 | not used | 6 | not used |
| 7 | Signal Ground | 7 | Signal Ground |
| 8 | Data Carrier Detect | 8 | Data Carrier Detect |
| 9 | Data Terminal Ready | 20 | Data Terminal Ready |
* RTS and CTS are ignored (optional) if using /dev/ttym* but required if using /dev/ttyf*.
Note: This cable can be used with a null modem adapter for printers; however, it is recommended that you use this cable exclusively for modem connections. The IBM pC/AT to modem cable ("off the shelf cable") does not work properly with your workstation. For additional information, see the serial(7) reference page.
Mini-DIN8 Connector Cabling
Many workstations and servers use the mini-DIN8 serial port. Check your system Owner's Guide to see if your system supports this type of connection. Note that the pinout of these mini-DIN8 connectors is different from that of the DIN connectors on larger systems. These larger systems also have DB-9 connectors that are connected to the same internal port hardware.
For most serial printers you should use a commercially available cable, Macintosh SE to ImageWriter1. This cable uses the normal three-wire connection and is used as a /dev/ttyd* device. Table 2-4 lists the pin configuration, as shown in Figure 2-7.
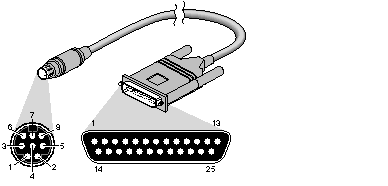
Figure 2-7 : Mini-DIN8 to DB-25 Serial Cable
Pin Definitions for a Mini-DIN8 to DB-25 Serial Cable
| Mini-DIN8-Male | Signal | DB-25-Male | Signal |
| 1 | not used | 1 | not used |
| 2 | not used | 2 | Transmit Data |
| 3 | Transmit Data | 3 | Receive Data |
| 4 | Signal Ground | 4 | Request to Send |
| 5 | Receive Data | 5 | Clear to Send |
| 6 | not used | 8 | Data Carrier Detect* |
| 7 | Data Carrier Detect* | 20 | Data Terminal Ready |
| 8 | Signal Ground | | |
* /dev/ttym* devices should be used with this cable only if the system must notice when the terminal or printer is powered off.
Note: A Macintosh SE cable has other pins connected, but they can be ignored.
Next | Prev | Up | Top | Contents | Index



