vDSP Reference
| Framework | Accelerate/vecLib |
| Declared in | vDSP.h |
Overview
This document describes the vDSP portion of the Accelerate framework.
Functions by Task
Single-Vector Absolute Value
The functions in this group compute the absolute value of each element in a vector.
Single-Vector Negation
The functions in this group negates each element in a vector.
Single-Vector Fill or Clear
The functions in this group fills each element in a vector with a specific value or clears each element.
Single-Vector Generation
The functions in this group build vectors with specific generator functions.
-
vDSP_vramp -
vDSP_vrampD -
vDSP_vrampmul -
vDSP_vrampmul_s1_15 -
vDSP_vrampmul_s8_24 -
vDSP_vrampmul2 -
vDSP_vrampmul2_s1_15 -
vDSP_vrampmul2_s8_24 -
vDSP_vrampmuladd -
vDSP_vrampmuladd_s1_15 -
vDSP_vrampmuladd_s8_24 -
vDSP_vrampmuladd2 -
vDSP_vrampmuladd2_s1_15 -
vDSP_vrampmuladd2_s8_24 -
vDSP_vgen -
vDSP_vgenD -
vDSP_vgenp -
vDSP_vgenpD -
vDSP_vtabi -
vDSP_vtabiD
Single-Vector Squaring
The functions in this group computes the square of each element in a vector or the square of the magnitude of each element in a complex vector.
Single-Vector Polar-Rectangular Conversion
The functions in this group convert each element in a vector between rectangular and polar coordinates.
Single-Vector Conversion to Decibel Equivalents
The functions in this group convert power or amplitude values to decibel values.
Single-Vector Fractional Part Extraction
The functions in this group remove the whole-number part of each element in a vector, leaving the fractional part.
Single-Vector Complex Conjugation
The functions in this group find the complex conjugate of values in a vector.
Single-Vector Phase Computation
The functions in this group compute the phase values of each element in a complex vector.
Single-Vector Clipping, Limit, and Threshold Operations
The functions in this group restrict the values in a vector so that they fall within a given range or invert values outside a given range.
-
vDSP_vclip -
vDSP_vclipD -
vDSP_vclipc -
vDSP_vclipcD -
vDSP_viclip -
vDSP_viclipD -
vDSP_vlim -
vDSP_vlimD -
vDSP_vthr -
vDSP_vthrD -
vDSP_vthres -
vDSP_vthresD -
vDSP_vthrsc -
vDSP_vthrscD
Single-Vector Compression
The functions in this group compress the values of a vector.
Single-Vector Gathering
The functions in this group use either indices or pointers stored within one source vector to generate a new vector containing the chosen elements from either a second source vector or from memory.
Single-Vector Reversing
The functions in this group reverse the order of the elements in a vector.
Single-Vector Copying
The functions in this group copy one vector to another vector.
Single-Vector Zero Crossing Search
The functions in this group find a specified number of zero crossings, returning the last crossing found and the number of crossings found.
Single-Vector Operations: Linear Averaging
The functions in this group take a vector that contains the linear averages of values from other vectors and adds an additional vector into those averages.
Single-Vector Linear Interpolation
The functions in this group calculate the linear interpolation between neighboring elements.
Single-Vector Integration
The functions in this group perform integration on the values in a vector.
Single-Vector Sorting
The functions in this group find sort the values in a vector.
Single-Vector Sliding-Window Summing
The functions in this group calculates a sliding-window sum for a vector.
Single-Vector Precision Conversion
The functions in this group convert between single-precision and double-precision floating-point vectors.
Single-Vector Floating-Point to Integer Conversion
The functions in this group convert the values in a vector from floating-point values to integer values of a given size.
-
vDSP_vfix8 -
vDSP_vfix8D -
vDSP_vfix16 -
vDSP_vfix16D -
vDSP_vfix32 -
vDSP_vfix32D -
vDSP_vfixr8 -
vDSP_vfixr8D -
vDSP_vfixr16 -
vDSP_vfixr16D -
vDSP_vfixr32 -
vDSP_vfixr32D -
vDSP_vfixu8 -
vDSP_vfixu8D -
vDSP_vfixu16 -
vDSP_vfixu16D -
vDSP_vfixu32 -
vDSP_vfixu32D -
vDSP_vfixru8 -
vDSP_vfixru8D -
vDSP_vfixru16 -
vDSP_vfixru16D -
vDSP_vfixru32 -
vDSP_vfixru32D
Single-Vector Integer to Floating-Point Conversion
The functions in this group convert integer values of a given size to floating-point vectors.
-
vDSP_vflt8 -
vDSP_vflt8D -
vDSP_vflt16 -
vDSP_vflt16D -
vDSP_vflt32 -
vDSP_vflt32D -
vDSP_vfltu8 -
vDSP_vfltu8D -
vDSP_vfltu16 -
vDSP_vfltu16D -
vDSP_vfltu32 -
vDSP_vfltu32D
Vector-Scalar Addition
These functions add a scalar to each element of a vector.
Vector-Scalar Division
These functions divide each element of a vector by a scalar.
Vector-Scalar Multiplication
These functions multiply a scalar by each element of a vector.
Vector-Scalar Multiply and Add
These functions multiply a scalar with each element of a vector, ten add another scalar.
Vector-to-Vector Bitwise Logical Equivalence
Vector-to-Vector Real Vector Basic Arithmetic
-
vDSP_vadd -
vDSP_vaddD -
vDSP_vsub -
vDSP_vsubD -
vDSP_vam -
vDSP_vamD -
vDSP_vsbm -
vDSP_vsbmD -
vDSP_vaam -
vDSP_vaamD -
vDSP_vsbsbm -
vDSP_vsbsbmD -
vDSP_vasbm -
vDSP_vasbmD -
vDSP_vasm -
vDSP_vasmD -
vDSP_vsbsm -
vDSP_vsbsmD -
vDSP_vmsa -
vDSP_vmsaD -
vDSP_vdiv -
vDSP_vdivD -
vDSP_vdivi -
vDSP_vmul -
vDSP_vmulD -
vDSP_vma -
vDSP_vmaD -
vDSP_vmsb -
vDSP_vmsbD -
vDSP_vmma -
vDSP_vmmaD -
vDSP_vmmsb -
vDSP_vmmsbD
Vector-to-Vector Complex Vector Basic Arithmetic
-
vDSP_zrvdiv -
vDSP_zrvdivD -
vDSP_zrvmul -
vDSP_zrvmulD -
vDSP_zrvsub -
vDSP_zrvsubD -
vDSP_zrvadd -
vDSP_zrvaddD -
vDSP_zvadd -
vDSP_zvaddD -
vDSP_zvcmul -
vDSP_zvcmulD -
vDSP_zvmul -
vDSP_zvmulD -
vDSP_zvsub -
vDSP_zvsubD -
vDSP_zvcma -
vDSP_zvcmaD
Vector-to-Vector Maxima and Minima
Vector-to-Vector Distance Computation
Vector-to-Vector Interpolation
Vector-to-Vector Polynomial Evaluation
Vector-to-Vector Pythagoras Computation
The functions in this group apply Pythagoras’s theorem to vectors.
Vector-to-Vector Extrema Finding
Vector-to-Vector Element Swapping
Vector-to-Vector Merging
Vector-to-Vector Spectra Computation
Vector-to-Vector Coherence Function Computation
Vector-to-Vector Transfer Function Computation
Vector-to-Vector Recursive Filtering on Real Vectors
Calculating Dot Products
-
vDSP_dotpr -
vDSP_dotpr_s1_15 -
vDSP_dotpr_s8_24 -
vDSP_dotprD -
vDSP_dotpr2 -
vDSP_dotpr2_s1_15 -
vDSP_dotpr2_s8_24 -
vDSP_zdotpr -
vDSP_zdotprD -
vDSP_zidotpr -
vDSP_zidotprD -
vDSP_zrdotpr -
vDSP_zrdotprD
Finding Maximums
Finding Minimums
Calculating Means
-
vDSP_meanv -
vDSP_meanvD -
vDSP_meamgv -
vDSP_meamgvD -
vDSP_measqv -
vDSP_measqvD -
vDSP_mvessq -
vDSP_mvessqD -
vDSP_rmsqv -
vDSP_rmsqvD
Summing Vectors
Matrix Multiplication (Real Matrices)
The functions in this group multiply two matrices.
-
vDSP_mmul -
vDSP_mmulD -
vDSP_zmma -
vDSP_zmmaD -
vDSP_zmms -
vDSP_zmmsD -
vDSP_zmmul -
vDSP_zmmulD -
vDSP_zmsm -
vDSP_zmsmD
Matrix Transposition
Matrix and Submatrix Copying
1D Fast Fourier Transforms (Support Functions)
1D Fast Fourier Transforms (In-Place Real)
-
vDSP_fft_zrip -
vDSP_fftm_zrip -
vDSP_fft_zripD -
vDSP_fftm_zripD -
vDSP_fft_zript -
vDSP_fftm_zript -
vDSP_fft_zriptD -
vDSP_fftm_zriptD
1D Fast Fourier Transforms (Out-of-Place Real)
-
vDSP_fft_zrop -
vDSP_fftm_zrop -
vDSP_fft_zropD -
vDSP_fftm_zropD -
vDSP_fft_zropt -
vDSP_fftm_zropt -
vDSP_fft_zroptD -
vDSP_fftm_zroptD
1D Fast Fourier Transforms (In-Place Complex)
-
vDSP_fft_zip -
vDSP_fftm_zip -
vDSP_fft_zipD -
vDSP_fftm_zipD -
vDSP_fft_zipt -
vDSP_fftm_zipt -
vDSP_fft_ziptD -
vDSP_fftm_ziptD
1D Fast Fourier Transforms (Out-of-Place Complex)
-
vDSP_fft_zop -
vDSP_fft_zopD -
vDSP_fftm_zop -
vDSP_fftm_zopD -
vDSP_fft_zopt -
vDSP_fft_zoptD -
vDSP_fftm_zopt -
vDSP_fftm_zoptD -
vDSP_fft3_zop -
vDSP_fft3_zopD -
vDSP_fft5_zop -
vDSP_fft5_zopD
1D Fast Fourier Transforms (Fixed Length)
2D Fast Fourier Transforms (In-Place Complex)
2D Fast Fourier Transforms (Out-of-Place Complex)
2D Fast Fourier Transforms (In-Place Real)
2D Fast Fourier Transforms (Out-of-Place Real)
Discrete Fourier Transforms
These functions calculate a discrete Fourier transform of a specified length on a vector.
-
vDSP_DFT_CreateSetup -
vDSP_DFT_DestroySetup -
vDSP_DFT_Execute -
vDSP_DFT_zop -
vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup -
vDSP_DFT_zrop -
vDSP_DFT_zrop_CreateSetup
Correlation and Convolution
These functions perform correlation and convolution operations on real or complex signals in vDSP.
-
vDSP_conv -
vDSP_convD -
vDSP_zconv -
vDSP_zconvD -
vDSP_wiener -
vDSP_wienerD -
vDSP_desamp -
vDSP_desampD -
vDSP_zrdesamp -
vDSP_zrdesampD
Windowing and Filtering
This section describes the C API for performing filtering operations on real or complex signals in vDSP. It also describes the built-in support for windowing functions such as Blackman, Hamming, and Hann windows.
-
vDSP_blkman_window -
vDSP_blkman_windowD -
vDSP_hamm_window -
vDSP_hamm_windowD -
vDSP_hann_window -
vDSP_hann_windowD -
vDSP_f3x3 -
vDSP_f3x3D -
vDSP_f5x5 -
vDSP_f5x5D -
vDSP_imgfir -
vDSP_imgfirD
Complex Vector Conversion
These functions convert complex vectors between interleaved and split forms.
Functions
vDSP_blkman_window
Creates a single-precision Blackman window.
void vDSP_blkman_window ( float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_FLAG );
Discussion
Represented in pseudo-code, this function does the following:
for (n=0; n < N; ++n) |
{ |
C[n] = 0.42 - (0.5 * cos( 2 * pi * n / N ) ) + (0.08 * cos( 4 * pi * n / N) ); |
} |
vDSP_blkman_window creates a single-precision Blackman window function C, which can be multiplied by a vector using vDSP_vmul. Specify the vDSP_HALF_WINDOW flag to create only the first (n+1)/2 points, or 0 (zero) for a full-size window.
See also vDSP_vmul.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_blkman_windowD
Creates a double-precision Blackman window.
void vDSP_blkman_windowD ( double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_FLAG );
Discussion
Represented in pseudo-code, this function does the following:
for (n=0; n < N; ++n) |
{ |
C[n] = 0.42 - (0.5 * cos( 2 * pi * n / N ) ) + (0.08 * cos( 4 * pi * n / N) ); |
} |
vDSP_blkman_windowD creates a double-precision Blackman window function C, which can be multiplied by a vector using vDSP_vmulD . Specify the vDSP_HALF_WINDOW flag to create only the first (n+1)/2 points, or 0 (zero) for a full-size window.
See also vDSP_vmulD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_conv
Performs either correlation or convolution on two vectors; single precision.
void vDSP_conv ( const float __vDSP_signal[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, const float __vDSP_filter[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideFilter, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenFilter );
Discussion

If filterStride is positive, vDSP_conv performs correlation. If filterStride is negative,it performs convolution and *filtermust point to the last vector element. The function can run in place, but result cannot be in place with filter.
The value of lenFilter must be less than or equal to 2044. The length of vector signal must satisfy two criteria: it must be
equal to or greater than 12
equal to or greater than the sum of
N-1plus the nearest multiple of 4 that is equal to or greater than the value oflenFilter.
Criteria to invoke vectorized code:
The vectors
signalandresultmust be relatively aligned.The value of
lenFiltermust be between 4 and 256, inclusive.The value of
lenResultmust be greater than 36.The values of
signalStrideandresultStridemust be 1.The value of
filterStridemust be either 1 or -1.
If any of these criteria is not satisfied, the function invokes scalar code.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_convD
Performs either correlation or convolution on two vectors; double precision.
void vDSP_convD ( const double __vDSP_signal[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, const double __vDSP_filter[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideFilter, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenFilter );
Discussion

If filterStride is positive, vDSP_convD performs correlation. If filterStride is negative,it performs convolution and *filtermust point to the last vector element. The function can run in place, but result cannot be in place with filter.
The value of lenFilter must be less than or equal to 2044. The length of vector signal must satisfy two criteria: it must be
equal to or greater than 12
equal to or greater than the sum of
N-1plus the nearest multiple of 4 that is equal to or greater than the value oflenFilter.
Criteria to invoke vectorized code:
No Altivec support for double precision. On a PowerPC processor, this function always invokes scalar code.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_create_fftsetup
Builds a data structure that contains precalculated data for use by single-precision FFT functions.
FFTSetup vDSP_create_fftsetup ( vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTRadix __vDSP_radix );
Parameters
- log2n
A base 2 exponent that represents the number of divisions of the complex unit circle and thus specifies the largest power of two that can be processed by a subsequent frequency-domain function. Parameter
log2nmust equal or exceed the largest power of 2 that any subsequent function processes using the weights array.- radix
-
Specifies radix options. Radix 2, radix 3, and radix 5 functions are supported.
Return Value
Returns an FFTSetup structure for use with one-dimensional FFT functions. Returns 0 on error.
Discussion
This function returns a filled-in FFTSetup data structure for use by FFT functions that operate on double-precision vectors. Once prepared, the setup structure can be used repeatedly by FFT functions (which read the data in the structure and do not alter it) for any (power of two) length up to that specified when you created the structure.
If an application performs FFTs with diverse lengths, the calls with different lengths can share a single setup structure (created for the longest length), and this saves space over having multiple structures. However, in some cases, notably single-precision FFTs on 32-bit PowerPC, an FFT routine may perform faster if it is passed a setup structure that was created specifically for the length of the transform.
Parameter log2n is a base-two exponent and specifies that the largest transform length that can processed using the resulting setup structure is 2**log2n (or 3*2**log2n or 5*2**log2n if the appropriate flags are passed, as discussed below). That is, the log2n parameter must equal or exceed the value passed to any subsequent FFT routine using the setup structure returned by this routine.
Parameter radix specifies radix options. Its value may be the bitwise OR of any combination of kFFTRadix2, kFFTRadix3, or kFFTRadix5. The resulting setup structure may be used with any of the routines for which the respective flag was used. (The radix-3 and radix-5 FFT routines have "fft3" and "fft5" in their names. The radix-2 FFT routines have plain "fft" in their names.)
If zero is returned, the routine failed to allocate storage.
The setup structure is deallocated by calling vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Use vDSP_create_fftsetup during initialization. It is relatively slow compared to the routines that actually perform FFTs. Never use it in a part of an application that needs to be high performance.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_create_fftsetupD
Builds a data structure that contains precalculated data for use by double-precision FFT functions.
FFTSetupD vDSP_create_fftsetupD ( vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTRadix __vDSP_radix );
Parameters
- log2n
A base 2 exponent that represents the number of divisions of the complex unit circle and thus specifies the largest power of two that can be processed by a subsequent frequency-domain function. Parameter
log2nmust equal or exceed the largest power of 2 that any subsequent function processes using the weights array.- radix
Specifies radix options. Radix 2, radix 3, and radix 5 functions are supported.
Return Value
Returns an FFTSetupD structure for use with FFT functions, or 0 if there was an error.
Discussion
This function returns a filled-in FFTSetupD data structure for use by FFT functions that operate on double-precision vectors. Once prepared, the setup structure can be used repeatedly by FFT functions (which read the data in the structure and do not alter it) for any (power of two) length up to that specified when you created the structure.
If an application performs FFTs with diverse lengths, the calls with different lengths can share a single setup structure (created for the longest length), and this saves space over having multiple structures. However, in some cases, notably single-precision FFTs on 32-bit PowerPC, an FFT routine may perform faster if it is passed a setup structure that was created specifically for the length of the transform.
Parameter log2n is a base-two exponent and specifies that the largest transform length that can processed using the resulting setup structure is 2**log2n (or 3*2**log2n or 5*2**log2n if the appropriate flags are passed, as discussed below). That is, the log2n parameter must equal or exceed the value passed to any subsequent FFT routine using the setup structure returned by this routine.
Parameter radix specifies radix options. Its value may be the bitwise OR of any combination of kFFTRadix2, kFFTRadix3, or kFFTRadix5. The resulting setup structure may be used with any of the routines for which the respective flag was used. (The radix-3 and radix-5 FFT routines have fft3 and fft5 in their names. The radix-2 FFT routines have plain fft in their names.)
If zero is returned, the routine failed to allocate storage.
The setup structure is deallocated by calling vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Use vDSP_create_fftsetupD during initialization. It is relatively slow compared to the routines that actually perform FFTs. Never use it in a part of an application that needs to be high performance.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_ctoz
Copies the contents of an interleaved complex vector C to a split complex vector Z; single precision.
void vDSP_ctoz ( const DSPComplex __vDSP_C[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideC, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_Z, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideZ, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
The strideC parameter contains an address stride through C. strideZ is an address stride through Z. The value of strideC must be a multiple of 2.
For best performance, C.realp, C.imagp, Z.realp, and Z.imagp should be 16-byte aligned.
See also functionsvDSP_ztoc and vDSP_ztocD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_ctozD
Copies the contents of an interleaved complex vector C to a split complex vector Z; double precision.
void vDSP_ctozD ( const DSPDoubleComplex __vDSP_C[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideC, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_Z, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideZ, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
The strideC parameter contains an address stride through C. strideZ is an address stride through Z. The value of strideC must be a multiple of 2.
For best performance, C.realp, C.imagp, Z.realp, and Z.imagp should be 16-byte aligned.
See also functions vDSP_ztoc and vDSP_ztocD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_deq22
Difference equation, 2 poles, 2 zeros; single precision.
void vDSP_deq22 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector; must have at least
N+2 elements- I
Stride for
A- B
5 single-precision inputs, filter coefficients
- C
Single-precision real output vector; must have at least
N+2 elements- K
Stride for
C- N
Number of new output elements to produce
Discussion
Performs two-pole two-zero recursive filtering on real input vector A. Since the computation is recursive, the first two elements in vector C must be initialized prior to calling vDSP_deq22. vDSP_deq22 creates N new values for vector C beginning with its third element and requires at least N+2 input values from vector A. This function can only be done out of place.
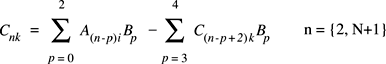
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_deq22D
Difference equation, 2 poles, 2 zeros; double precision.
void vDSP_deq22D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector; must have at least
N+2 elements- I
Stride for
A- B
5 double-precision inputs, filter coefficients
- C
Double-precision real output vector; must have at least
N+2 elements- K
Stride for
C- N
Number of new output elements to produce
Discussion
Performs two-pole two-zero recursive filtering on real input vector A. Since the computation is recursive, the first two elements in vector C must be initialized prior to calling vDSP_deq22D. vDSP_deq22D creates N new values for vector C beginning with its third element and requires at least N+2 input values from vector A. This function can only be done out of place.
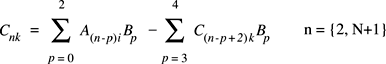
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_desamp
Convolution with decimation; single precision.
void vDSP_desamp ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector, 8-byte aligned; length of
A>= 12- I
Desampling factor
- B
Single-precision input filter coefficients
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- N
Output count
- M
Filter coefficient count
Discussion
Performs finite impulse response (FIR) filtering at selected positions of vector A. desampx can run in place, but C cannot be in place with B. Length of A must be >=(N-1)*I+(nearest multiple of 4 >=M).

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_desampD
Convolution with decimation; double precision.
void vDSP_desampD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector, 8-byte aligned; length of
A>= 12- I
Desampling factor
- B
Double-precision input filter coefficients
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- N
Output count
- M
Filter coefficient count
Discussion
Performs finite impulse response (FIR) filtering at selected positions of vector A. desampx can run in place, but C cannot be in place with B. Length of A must be >=(N-1)*I+(nearest multiple of 4 >=M).

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_destroy_fftsetup
Frees an existing single-precision FFT data structure.
void vDSP_destroy_fftsetup ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup );
Parameters
- setup
Identifies the weights array, and must point to a data structure previously created by
vDSP_create_fftsetup.
Discussion
vDSP_destroy_fftsetup frees an existing weights array. Any memory allocated for the array is released. After the vDSP_destroy_fftsetup function returns, the structure should not be used in any other functions.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_destroy_fftsetupD
Frees an existing double-precision FFT data structure.
void vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup );
Parameters
- setup
Identifies the weights array, and must point to a data structure previously created by
vDSP_create_fftsetupD.
Discussion
vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD frees an existing weights array. Any memory allocated for the array is released. After the vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD function returns, the structure should not be used in any other functions.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_DFT_CreateSetup
Old name for vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup.
vDSP_DFT_Setup vDSP_DFT_CreateSetup ( vDSP_DFT_Setup __vDSP_Previous, vDSP_Length __vDSP_Length );
Discussion
Call vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup instead.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_DFT_DestroySetup
Releases a setup object.
void vDSP_DFT_DestroySetup ( vDSP_DFT_Setup __vDSP_Setup );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Setup
The setup object to destroy (as returned by
vDSP_DFT_CreateSetup,vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup, orvDSP_DFT_zrop_CreateSetup.
Discussion
If this setup object shares memory with other setup objects, that memory is not released until the last object is destroyed.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_DFT_Execute
Calculates the discrete fourier transform for a vector using vDSP_DFT_zop or vDSP_DFT_zrop.
void vDSP_DFT_Execute ( const struct vDSP_DFT_SetupStruct *__vDSP_Setup, const float *__vDSP_Ir, const float *__vDSP_Ii, float *__vDSP_Or, float *__vDSP_Oi );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Setup
A DFT setup object returned by a call to
vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup.- __vDSP_Ir
A vector containing the real part of the input values.
- __vDSP_Ii
A vector containing the imaginary part of the input values.
- __vDSP_Or
A vector where the real part of the results is stored on return.
- __vDSP_Oi
A vector where the imaginary part of the results is stored on return.
Discussion
This function calculates either a real or complex discrete fourier transform, depending on whether the setup object was created with a call to vDSP_DFT_zrop_CreateSetup or vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup.
Note: If the setup was created with vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup, each vector should contain length elements. If it was created with vDSP_DFT_zrop_CreateSetup, each vector should contain length/2 elements.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_DFT_zop
Calculates the discrete fourier transform for a vector (single-precision complex).
void vDSP_DFT_zop ( const struct vDSP_DFT_SetupStruct *__vDSP_Setup, const float *__vDSP_Ir, const float *__vDSP_Ii, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Is, float *__vDSP_Or, float *__vDSP_Oi, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Os, vDSP_DFT_Direction __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Setup
A DFT setup object returned by a call to
vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup.- __vDSP_InputRe
A vector containing the real part of the input values.
- __vDSP_InputIm
A vector containing the imaginary part of the input values.
- __vDSP_InputStride
Stride length within the input vector. For example, passing 2 would cause every second value to be used.
- __vDSP_OutputRe
A vector where the real part of the results is stored on return.
- __vDSP_OutputIm
A vector where the imaginary part of the results is stored on return.
- __vDSP_OutputStride
Stride length within the input vector. For example, passing 2 would cause every second value to be overwritten.
- __vDSP_Direction
vDSP_DFT_FORWARDorvDSP_DFT_INVERSE, indicating whether to perform a forward or inverse transform.
Discussion
The input and output vectors may not overlap, with one exception: if the real and imaginary input vectors are both the same as the corresponding output vector, an in-place algorithm is used.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup
Creates data structures for use with vDSP_DFT_zop.
vDSP_DFT_Setup vDSP_DFT_zop_CreateSetup ( vDSP_DFT_Setup __vDSP_Previous, vDSP_Length __vDSP_Length, vDSP_DFT_Direction __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Previous
An previous result from this function or
NULL.- __vDSP_Length
The length of DFT computations with this object.
Return Value
Returns a DFT setup object.
Discussion
This function is designed to share memory between data structures where possible. You should initially create a setup object with the largest length you expect to use, then pass that object as __vDSP_Previous. By doing so, this setup object can share the underlying data storage with that object, thus reducing the time needed to construct the tables.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_DFT_zrop
Calculates the discrete fourier transform for a vector (single-precision real).
void vDSP_DFT_zrop ( vDSP_DFT_Setup __vDSP_Setup, const float *__vDSP_InputRe, const float *__vDSP_InputIm, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_InputStride, float *__vDSP_OutputRe, float *__vDSP_OutputIm, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OutputStride, vDSP_DFT_Direction __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Setup
A DFT setup object returned by a call to
vDSP_DFT_zrop_CreateSetup.- __vDSP_InputRe
A vector containing the real part of the input values.
- __vDSP_InputIm
A vector containing the imaginary part of the input values.
- __vDSP_InputStride
Stride length within the input vector. For example, passing 2 would cause every second value to be used.
- __vDSP_OutputRe
A vector where the real part of the results is stored on return.
- __vDSP_OutputIm
A vector where the imaginary part of the results is stored on return.
- __vDSP_OutputStride
Stride length within the input vector. For example, passing 2 would cause every second value to be overwritten.
- __vDSP_Direction
vDSP_DFT_FORWARDorvDSP_DFT_INVERSE, indicating whether to perform a forward or inverse transform.
Discussion
The input and output vectors may not overlap unless they are equal, in which case an in-place algorithm is used.
vDSP_DFT_zrop_CreateSetup
Creates data structures for use with vDSP_DFT_zrop.
vDSP_DFT_Setup vDSP_DFT_zrop_CreateSetup ( vDSP_DFT_Setup __vDSP_Previous, vDSP_Length __vDSP_Length, vDSP_DFT_Direction __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Previous
An previous result from this function or
NULL.- __vDSP_Length
The length of DFT computations with this object.
Return Value
Returns a DFT setup object.
Discussion
This function is designed to share memory between data structures where possible. You should initially create a setup object with the largest length you expect to use, then pass that object as __vDSP_Previous. By doing so, this setup object can share the underlying data storage with that object, thus reducing the time needed to construct the tables.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_dotpr
Computes the dot or scalar product of vectors A and B and leaves the result in scalar *C; single precision.
void vDSP_dotpr ( const float __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, float *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- __vDSP_input1
Input vector
A.- __vDSP_stride1
The stride within vector
A. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_input2
Input vector
B.- __vDSP_stride2
The stride within vector
B. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_result
The dot product (on return).
- __vDSP_size
The number of elements (
N).
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
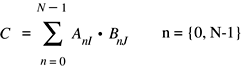
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_dotpr2
Stereo variant of vDSP_dotpr.
void vDSP_dotpr2 ( const float *__vDSP_A0, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_A0Stride, const float *__vDSP_A1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_A1Stride, const float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_BStride, float *__vDSP_C0, float *__vDSP_C1, vDSP_Length __vDSP_Length );
Parameters
- __vDSP_A0
Input vector
A0.- __vDSP_A0Stride
The stride within vector
A0. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_A1
Input vector
A1.- __vDSP_A1Stride
The stride within vector
A1. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_B
Input vector
B.- __vDSP_BStride
The stride within vector
B. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_C0
The dot product of A0 and B (on return).
- __vDSP_C1
The dot product of A1 and B (on return).
- __vDSP_Length
The number of elements.
Discussion
Calculates the dot product of A0 with B, then calculates the dot product of A1 with B. The equation for a single dot product is:
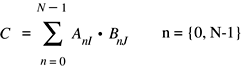
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_dotpr2_s1_15
Vector fixed-point 1.15 format version of vDSP_dotpr2.
void vDSP_dotpr2_s1_15 ( const short int *__vDSP_A0, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_A0Stride, const short int *__vDSP_A1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_A1Stride, const short int *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_BStride, short int *__vDSP_C0, short int *__vDSP_C1, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_A0
Input vector
A0.- __vDSP_A0Stride
The stride within vector
A0. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_A1
Input vector
A1.- __vDSP_A1Stride
The stride within vector
A1. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_B
Input vector
B.- __vDSP_BStride
The stride within vector
B. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_C0
The dot product of A0 and B (on return).
- __vDSP_C1
The dot product of A1 and B (on return).
- __vDSP_Length
The number of elements.
Discussion
Calculates the dot product of A0 with B, then calculates the dot product of A1 with B. The equation for a single dot product is:
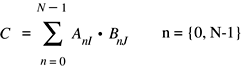
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with one sign bit and 15 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 32768.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_dotpr2_s8_24
Vector fixed-point 8.24 format version of vDSP_dotpr2.
void vDSP_dotpr2_s8_24 ( const int *__vDSP_A0, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_A0Stride, const int *__vDSP_A1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_A1Stride, const int *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_BStride, int *__vDSP_C0, int *__vDSP_C1, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_A0
Input vector
A0.- __vDSP_A0Stride
The stride within vector
A0. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_A1
Input vector
A1.- __vDSP_A1Stride
The stride within vector
A1. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_B
Input vector
B.- __vDSP_BStride
The stride within vector
B. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_C0
The dot product of A0 and B (on return).
- __vDSP_C1
The dot product of A1 and B (on return).
- __vDSP_Length
The number of elements.
Discussion
Calculates the dot product of A0 with B, then calculates the dot product of A1 with B. The equation for a single dot product is:
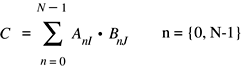
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with eight integer bits (including the sign bit) and 24 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 16777216.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_dotprD
Computes the dot or scalar product of vectors A and B and leaves the result in scalar *C; double precision.
void vDSP_dotprD ( const double __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, double *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
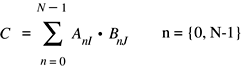
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_dotpr_s1_15
Vector fixed-point 1.15 format version of vDSP_dotpr.
void vDSP_dotpr_s1_15 ( const short int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_AStride, const short int *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_BStride, short int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_A
Input vector
A.- __vDSP_AStride
The stride within vector
A. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_B
Input vector
B.- __vDSP_BStride
The stride within vector
B. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_C
The dot product (on return).
- __vDSP_N
The number of elements.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
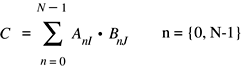
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with one sign bit and 15 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 32768.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_dotpr_s8_24
Vector fixed-point 8.24 format version of vDSP_dotpr.
void vDSP_dotpr_s8_24 ( const int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_AStride, const int *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_BStride, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_A
Input vector
A.- __vDSP_AStride
The stride within vector
A. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_B
Input vector
B.- __vDSP_BStride
The stride within vector
B. For example if stride is 2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_C
The dot product (on return).
- __vDSP_N
The number of elements.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
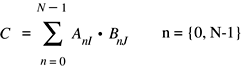
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with eight integer bits (including the sign bit) and 24 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 16777216.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_f3x3
Filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 3x3 kernel; single precision.
void vDSP_f3x3 ( float *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Length __vDSP_rows, vDSP_Length __vDSP_cols, float *__vDSP_filter, float *__vDSP_result );
Discussion
This function filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 3x3 kernel (B) on the input matrix A and storing the resulting image in the output matrix C.
This performs the following operation:

The function pads the perimeter of the output image with a border of zeros of width 1.
B is the 3x3 kernel. M and N are the number of rows and columns, respectively, of the two-dimensional input matrix A. M must be greater than or equal to 3. N must be even and greater than or equal to 4.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_f3x3D
Filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 3x3 kernel; double precision.
void vDSP_f3x3D ( double *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Length __vDSP_rows, vDSP_Length __vDSP_cols, double *__vDSP_filter, double *__vDSP_result );
Discussion
This function filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 3x3 kernel on the input matrix A and storing the resulting image in the output matrix C.
This performs the following operation:

The function pads the perimeter of the output image with a border of zeros of width 1.
B is the 3x3 kernel. M and N are the number of rows and columns, respectively, of the two-dimensional input matrix A. M must be greater than or equal to 3. N must be even and greater than or equal to 4.
Criteria to invoke vectorized code:
A,B, andCmust be 16-byte aligned.Nmust be greater than or equal to 18.
If any of these criteria is not satisfied, the function invokes scalar code.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_f5x5
Filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 5x5 kernel; single precision.
void vDSP_f5x5 ( float *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Length __vDSP_rows, vDSP_Length __vDSP_cols, float *__vDSP_filter, float *__vDSP_result );
Discussion
This function filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 5x5 kernel (B) on the input matrix A and storing the resulting image in the output matrix C.
This performs the following operation:
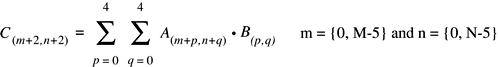
The function pads the perimeter of the output image with a border of zeros of width 2.
B is the 5x5 kernel. M and N are the number of rows and columns, respectively, of the two-dimensional input matrix A. M must be greater than or equal to 5. N must be even and greater than or equal to 6.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_f5x5D
Filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 5x5 kernel; double precision.
void vDSP_f5x5D ( double *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Length __vDSP_rows, vDSP_Length __vDSP_cols, double *__vDSP_filter, double *__vDSP_result );
Discussion
This function filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a 5x5 kernel (B) on the input matrix A and storing the resulting image in the output matrix C.
This performs the following operation:
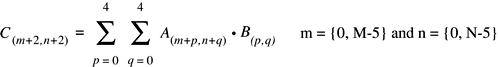
The function pads the perimeter of the output image with a border of zeros of width 2.
B is the 5x5 kernel. M and N are the number of rows and columns, respectively, of the two-dimensional input matrix A. M must be greater than or equal to 5. N must be even and greater than or equal to 6.
Criteria to invoke vectorized code:
A,B, andCmust be 16-byte aligned.Nmust be greater than or equal to 20.
If any of these criteria is not satisfied, the function invokes scalar code.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_FFT16_copv
Performs a 16-element FFT on interleaved complex data.
void vDSP_FFT16_copv ( float *__vDSP_Output, const float *__vDSP_Input, FFTDirection __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Output
A vector-block-aligned output array.
- __vDSP_Input
A vector-block-aligned input array.
- __vDSP_Direction
kFFTDirection_ForwardorkFFTDirection_Inverse, indicating whether to perform a forward or inverse transform.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_FFT16_zopv
Performs a 16-element FFT on split complex data.
void vDSP_FFT16_zopv ( float *__vDSP_Or, float *__vDSP_Oi, const float *__vDSP_Ir, const float *__vDSP_Ii, FFTDirection __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Or
Output vector for real parts.
- __vDSP_Oi
Output vector for imaginary parts.
- __vDSP_Ir
Input vector for real parts.
- __vDSP_Ii
Input vector for imaginary parts.
- __vDSP_Direction
kFFTDirection_ForwardorkFFTDirection_Inverse, indicating whether to perform a forward or inverse transform.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zip
Computes an in-place single-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zip ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the matrix
signal. Specifying 1 forstrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0, parameter
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. If parameterstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for parameter
log2nInColand 6 for parameterlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
direction.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zipD
Computes an in-place double-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zipD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the matrix
signal. Specifying 1 forstrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0, parameter
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. If parameterstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for parameter
log2nInColand 6 for parameterlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
direction.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zipt
Computes an in-place single-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_zipt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the matrix
signal. Specifying 1 forstrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0, parameter
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. If parameterstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- bufferTemp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 16 KB or 4*
n, wherelog2n = log2nInCol + log2nInRow.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for parameter
log2nInColand 6 for parameterlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
direction.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_ziptD
Computes an in-place double-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_ziptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the matrix
signal. Specifying 1 forstrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0, parameter
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. If parameterstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- bufferTemp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 16 KB or 4*
n, wherelog2n = log2nInCol + log2nInRow.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for parameter
log2nInColand 6 for parameterlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
direction.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zop
Computes an out-of-place single-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStrideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix
a. Specifying 1 forsignalStrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- signalStrideInCol
If not 0, this parameter represents the distance between each row of the input /output matrix.
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResultInRow
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInRowspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- strideResultInCol
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInColspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zopD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zopD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInCol, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStrideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix
a. Specifying 1 forsignalStrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- signalStrideInCol
If not 0, this parameter represents the distance between each row of the input /output matrix.
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResultInRow
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInRowspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- strideResultInCol
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInColspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zopt
Computes an out-of-place single-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_zopt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStrideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix
a. Specifying 1 forsignalStrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- signalStrideInCol
If not 0, this parameter represents the distance between each row of the input /output matrix. If parameter signalStrideInCol is 1024, for instance, element 512 equates to element (1,0) of matrix
a, element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResultInRow
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInRowspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- strideResultInCol
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInColspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- bufferTemp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 16 KiB or 4*
n, wherelog2n = log2nInCol + log2nInRow.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zoptD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision complex discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_zoptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInCol, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInCol, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameterslog2nInColandlog2nInRowof the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStrideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix
a. Specifying 1 forsignalStrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- signalStrideInCol
If not 0, this parameter represents the distance between each row of the input /output matrix. If parameter signalStrideInCol is 1024, for instance, element 512 equates to element (1,0) of matrix
a, element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResultInRow
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInRowspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- strideResultInCol
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInColspecifies a stride for input the input /output matrix.- bufferTemp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 16 KB or 4*
n, wherelog2n = log2nInCol + log2nInRow.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zrip
Computes an in-place single-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zrip ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameters log2nInCol andlog2nInRowof the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the input matrix signal. Specifying 1 for
strideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0,
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. IfstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
direction.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.

Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zripD
Computes an in-place double-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zripD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameters log2nInCol andlog2nInRowof the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the input matrix signal. Specifying 1 for
strideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0,
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. IfstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 2 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.

Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
No Altivec/SSE support for double precision. The function always invokes scalar code.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zript
Computes an in-place single-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_zript ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameters log2nInCol andlog2nInRowof the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the input matrix signal. Specifying 1 for
strideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0,
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. IfstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- bufferTemp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory required is discussed below.
- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
direction.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.

Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
The space needed in bufferTemp is at most max(9*nr, nc/2) elements in each of realp and imagp. Here is an example of how to allocate the space:
int nr, nc, tempSize; |
nr = 1 << log2InRow; |
nc = 1 << log2InCol; |
tempSize = max(9*nr, nc/2); |
bufferTemp.realp = (float *) malloc (tempSize * sizeOf(float) ); |
bufferTemp.imagp = (float *) malloc (tempSize * sizeOf(float) ); |
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zriptD
Computes an in-place double-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_zriptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInCol, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the values supplied as parameters log2nInCol andlog2nInRowof the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- strideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of the input matrix signal. Specifying 1 for
strideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- strideInCol
Specifies a column stride for the matrix, and should generally be allowed to default unless the matrix is a submatrix. Parameter
strideInColcan be defaulted by specifying 0. The default column stride equals the row stride multiplied by the column count. Thus, ifstrideInRowis 1 andstrideInColis 0, every element of the input /output matrix is processed. IfstrideInRowis 2 andstrideInColis 0, every other element of each row is processed.If not 0,
strideInColrepresents the distance between each row of the matrix. IfstrideInColis 1024, for instance, complex element 512 of the matrix equates to element (1,0), element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- bufferTemp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory required is discussed below.
- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.

Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
The space needed in bufferTemp is at most max(9*nr, nc/2) elements in each of realp and imagp. Here is an example of how to allocate the space:
int nr, nc, tempSize; |
nr = 1 << log2InRow; |
nc = 1 << log2InCol; |
tempSize = max(9*nr, nc/2); |
bufferTemp.realp = (float *) malloc (tempSize * sizeOf(float) ); |
bufferTemp.imagp = (float *) malloc (tempSize * sizeOf(float) ); |
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zrop
Computes an out-of-place single-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zrop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2norlog2m, whichever is larger, of the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStrideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix signal. Specifying 1 for
signalStrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- signalStrideInCol
If not 0, represents the distance between each row of the input /output matrix. If parameter signalStrideInCol is 1024, for instance, element 512 equates to element (1,0) of matrix
a, element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResultInRow
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
cin the same way thatsignalStrideInRowspecifies strides for input the matrix.- strideResultInCol
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
cin the same way thatsignalStrideInColspecify strides for input the matrix.- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zropD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft2d_zropD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Kr, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Kc, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Ir, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Ic, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nc, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nr, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2norlog2m, whichever is larger, of the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- Kr
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix signal. Specifying 1 for
Krprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- Kc
If not 0, represents the distance between each row of the input /output matrix. If parameter
Kcis 1024, for instance, element 512 equates to element (1,0) of matrixa, element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- ioData2
The complex vector result.
- Ir
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
ioData2in the same way thatKrspecifies strides for input the matrix.- Ic
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
ioData2in the same way thatKcspecify strides for input matrixioData.- log2nc
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2ncmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- log2nr
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2ncand 6 forlog2nr.log2nrmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zropt
Computes an out-of-place single-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_zropt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStrideInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInRow, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResultInCol, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInCol, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nInRow, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2norlog2m, whichever is larger, of the transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStrideInRow
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix
signal. Specifying 1 forsignalStrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- signalStrideInCol
If not 0, represents the distance between each row of matrix
signal. If parametersignalStrideInColis 1024, for instance, element 512 equates to element (1,0) of matrixsignal, element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResultInRow
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
resultin the same way thatsignalStrideInRowspecifies strides for input matrixresult.- strideResultInCol
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
cin the same way thatsignalStrideInColspecify strides for input matrixresult.- bufferTemp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) can be calculated using the algorithm shown below.
- log2nInCol
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2nInColmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- log2nInRow
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2nInColand 6 forlog2nInRow.log2nInRowmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
Here is the bufferTemp size algorithm:
int nr, nc, tempSize; |
nr = 1 << log2InRow; |
nc = 1 << log2InCol; |
if (( (log2InCol-1) < 3 ) || (log2InRow > 9) { |
tempSize = 9 * nr; |
} else { |
tempSize = 17 * nr |
} |
bufferTemp.realp = (float *) malloc (tempSize * sizeOf(float)); |
bufferTemp.imagp = (float *) malloc (tempSize * sizeOf(float)); |
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft2d_zroptD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision real discrete FFT, either from the spatial domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the spatial domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft2d_zroptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Kr, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Kc, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Ir, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_Ic, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nc, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2nr, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2norlog2m, whichever is larger, of the transform function.- ioData
A complex vector input.
- Kr
Specifies a stride across each row of matrix signal. Specifying 1 for
signalStrideInRowprocesses every element across each row, specifying 2 processes every other element across each row, and so forth.- Kc
If not 0, represents the distance between each row of the input /output matrix. If parameter signalStrideInCol is 1024, for instance, element 512 equates to element (1,0) of matrix
a, element 1024 equates to element (2,0), and so forth.- ioData2
The complex vector result.
- Ir
Specifies a row stride for output matrix
ioData2in the same way thatKrspecifies strides for input the matrix.- Ic
Specifies a column stride for output matrix
ioData2in the same way thatKcspecify strides for input matrixioData.- temp
A temporary matrix used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 16 KB or 4*
n, wherelog2n = log2nInCol + log2nInRow.- log2nc
The base 2 exponent of the number of columns to process for each row.
log2ncmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- log2nr
The base 2 exponent of the number of rows to process. For example, to process 64 rows of 128 columns, specify 7 for
log2ncand 6 forlog2nr.log2nrmust be between 3 and 10, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, and must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.Results are undefined for other values of
flag.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, spatial-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_FFT32_copv
Performs a 32-element FFT on interleaved complex data.
void vDSP_FFT32_copv ( float *__vDSP_Output, const float *__vDSP_Input, FFTDirection __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Output
A vector-block-aligned output array.
- __vDSP_Input
A vector-block-aligned input array.
- __vDSP_Direction
kFFTDirection_ForwardorkFFTDirection_Inverse, indicating whether to perform a forward or inverse transform.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_FFT32_zopv
Performs a 32-element FFT on split complex data.
void vDSP_FFT32_zopv ( float *__vDSP_Or, float *__vDSP_Oi, const float *__vDSP_Ir, const float *__vDSP_Ii, FFTDirection __vDSP_Direction );
Parameters
- __vDSP_Or
Output vector for real parts.
- __vDSP_Oi
Output vector for imaginary parts.
- __vDSP_Ir
Input vector for real parts.
- __vDSP_Ii
Input vector for imaginary parts.
- __vDSP_Direction
kFFTDirection_ForwardorkFFTDirection_Inverse, indicating whether to perform a forward or inverse transform.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft3_zop
Computes an out-of-place radix-3 complex Fourier transform, either forward or inverse. The number of input and output values processed equals 3 times the power of 2 specified by parameter log2n; single precision.
void vDSP_fft3_zop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Use
vDSP_create_fftsetup, to initialize this function.kFFTRadix3must be specified in the call tovDSP_create_fftsetup.setupis preserved for reuse.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input vector
signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parametersignalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value ofsignalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride for the result. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal.
log2nmust be between 3 and 15, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft3_zopD
Computes an out-of-place radix-3 complex Fourier transform, either forward or inverse. The number of input and output values processed equals 3 times the power of 2 specified by parameter log2n; double precision.
void vDSP_fft3_zopD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Use
vDSP_create_fftsetupD, to initialize this function.kFFTRadix3must be specified in the call tovDSP_create_fftsetupD.setupis preserved for reuse.- signal
A complex vector input.
- K
Specifies an address stride through the input vector
signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameterK; to process every other element, specify 2. The value ofKshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector result.
- L
Specifies an address stride for the result. The value of
Lshould be 1 for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal.
log2nmust be between 3 and 15, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft5_zop
Computes an out-of-place radix-5 complex Fourier transform, either forward or inverse. The number of input and output values processed equals 5 times the power of 2 specified by parameter log2n; single precision.
void vDSP_fft5_zop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Use
vDSP_create_fftsetup, to initialize this function.kFFTRadix5must be specified in the call tovDSP_create_fftsetup.setupis preserved for reuse.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input vector
signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parametersignalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value ofsignalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride for the result. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal.
log2nmust be between 3 and 15, inclusive.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft5_zopD
Computes an out-of-place radix-5 complex Fourier transform, either forward or inverse. The number of input and output values processed equals 5 times the power of 2 specified by parameter log2n; double precision.
void vDSP_fft5_zopD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Use
vDSP_create_fftsetupD, to initialize this function.kFFTRadix5must be specified in the call tovDSP_create_fftsetupD.setupis preserved for reuse.- signal
A complex vector input.
- K
Specifies an address stride through the input vector
signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameterK; to process every other element, specify 2.- result
The complex vector result.
- L
Specifies an address stride for the result.
- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zip
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zip on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zip ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This function allows you to perform Discrete Fourier Transforms on multiple input signals using a single call. They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride.
The functions compute in-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zipD
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zipD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zipD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n. The value oflog2nmust be between 2 and 12, inclusive.- numFFT
The number of signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This function allows you to perform Discrete Fourier Transforms on multiple signals at once, using a single call. It will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride.
The function computes in-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zipt
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zipt on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zipt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of signalStride should be 1 for best performance.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n. The value oflog2nmust be between 2 and 12, inclusive.- numFFT
The number of different input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The function allows you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. It can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). It will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input/output vector, the parameter signal.
The function computes in-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_ziptD
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_ziptD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_ziptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of signalStride should be 1 for best performance.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n. The value oflog2nmust be between 2 and 12, inclusive.- numFFT
The number of different input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The function allows you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. It can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). It will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input/output vector, the parameter signal.
The function computes in-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zop
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zop on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of signalStride should be 1 for best performance.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The function allows you to perform Discrete Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. It can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). It will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input vector, signal, and single output vector, result.
The function computes out-of-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zopD
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zopD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zopD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetuporvDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of signalStride should be 1 for best performance.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n. The value oflog2nmust be between 2 and 12, inclusive.- numFFT
The number of different input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The function allows you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. It can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). It will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input/output vector, the parameter signal.
The function computes out-of-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zopt
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zopt on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zopt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of signalStride should be 1 for best performance.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n. The value oflog2nmust be between 2 and 12, inclusive.- numFFT
The number of different input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The function allows you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. It can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). It will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input/output vector, the parameter signal.
The function computes out-of-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zoptD
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zoptD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zoptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of signalStride should be 1 for best performance.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.
- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n. The value oflog2nmust be between 2 and 12, inclusive.- numFFT
The number of different input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The function allows you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. It can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). It will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input/output vector, the parameter signal.
The function computes out-of-place complex discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zrip
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zrip on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zrip ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter
signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The function allows you to perform Discrete Fourier Transforms on multiple signals using a single call. They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride.
The functions compute in-place real Discrete Fourier Transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zripD
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zripD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zripD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter
signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The functions allow you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. They can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride.
The functions compute in-place real discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zript
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zript on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zript ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter
signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of different input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The functions allow you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. They can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride.
The functions compute in-place real Discrete Fourier Transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zriptD
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zriptD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zriptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through the input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process in a single input signal. For example, to process 512 elements, specify 9 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The functions allow you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. They can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride.
The functions compute in-place real Discrete Fourier Transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zrop
Performs the same operation as vDSP_fft_zrop on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zrop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.
- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.
- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This function allows you to perform Discrete Fourier Transforms on multiple input signals using a single call. They can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input vector, signal, and a single output vector, result.
The functions compute out-of-place real Discrete Fourier Transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zropD
Performs the same operation as VDSP_fft_zropD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zropD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
signalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This function allows you to perform Discrete Fourier Transforms on multiple input signals using a single call. They can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input vector, the parameter signal.
The functions compute out-of-place real Discrete Fourier Transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zropt
Performs the same operation as VDSP_fft_zropt on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zropt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
signalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The functions allow you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. They can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input vector, the parameter signal.
The functions compute out-of-place real discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup, vDSP_destroy_fftsetup, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fftm_zroptD
Performs the same operation as VDSP_fft_zroptD on multiple signals with a single call.
void vDSP_fftm_zroptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_fftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_resultStride, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_rfftStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_temp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numFFT, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input signals. To process every element of each signal, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
signalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- fftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one input signal and the first element of the next (which is also to length of each input signal, measured in elements).
- result
The complex vector signal output.
- resultStride
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
resultStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- rfftStride
The number of elements between the first element of one result vector and the next in the output vector
result.- temp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
temp.realpandtemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- numFFT
The number of different input signals.
- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
The functions allow you to perform Fourier transforms on a number of different input signals at once, using a single call. They can be used for efficient processing of small input signals (less than 512 points). They will work for input signals of 4 points or greater. Each of the input signals processed by a given call must have the same length and address stride. The input signals are concatenated into a single input vector, the parameter signal.
The functions compute out-of-place real discrete Fourier transforms of the input signals, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD, vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD, and “Using Fourier Transforms”.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zip
Computes an in-place single-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input/output vector signal, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zip ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- stride
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter
stride; to process every other element, specify 2.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
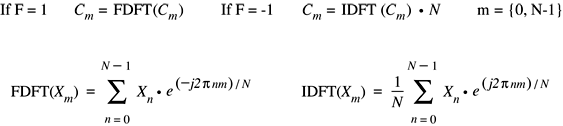
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zipD
Computes an in-place double-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input/output vector signal, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zipD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- stride
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter
stride; to process every other element, specify 2. The value ofstrideshould be 1 for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
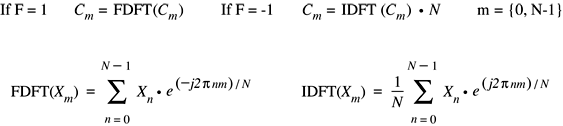
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zipt
Computes an in-place single-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input/output vector signal, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft_zipt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- stride
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter
stride; to process every other element, specify 2.- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
bufferTemp.realpandbufferTemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
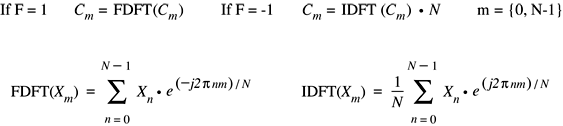
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_ziptD
Computes an in-place double-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input/output vector signal, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse). A buffer is used for intermediate results.
void vDSP_fft_ziptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the earlier call to the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- stride
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector signal. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter
stride; to process every other element, specify 2.- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
bufferTemp.realpandbufferTemp.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
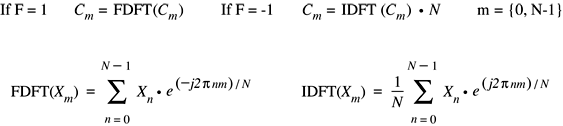
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zop
Computes an out-of-place single-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input vector, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Parameter
strideResultspecifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a signalStride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.
- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
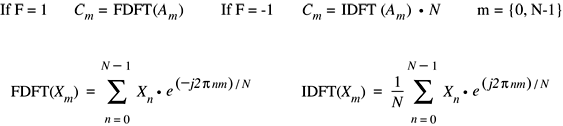
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zopD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input vector, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zopD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetuporvDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Parameter
strideResultspecifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify asignalStrideof 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The values ofsignalStrideandstrideResultshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
strideResultshould be 1 for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
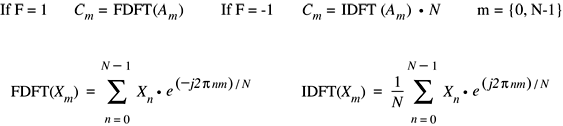
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zopt
Computes an out-of-place single-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input vector, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zopt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector that stores the input and output signal.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Parameter
strideResultspecifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a signalStride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The values of signalStride andstrideResultshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.
- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible, tempBuffer
.realpand tempBuffer.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
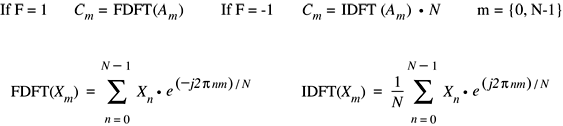
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zoptD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision complex discrete Fourier transform of the input vector, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zoptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Parameter
strideResultspecifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a signalStride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The values of signalStride andstrideResultshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.
- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible, tempBuffer
.realpand tempBuffer.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
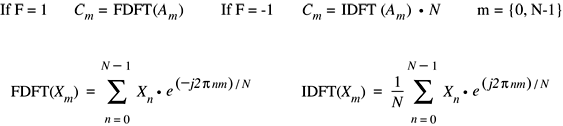
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zrip
Computes an in-place single-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zrip ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- C
A complex input/output vector.
- K
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter
signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameterlog2n.- F
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. You can find more details on the packing format in vDSP Programming Guide. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
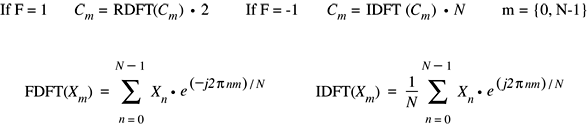
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zripD
Computes an in-place double-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zripD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- C
A complex vector input.
- K
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter
stride; to process every other element, specify 2.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameterlog2n.- F
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
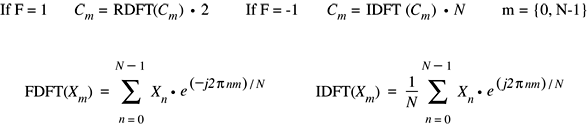
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zript
Computes an in-place single-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zript ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- C
A complex vector input.
- K
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.
- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible, tempBuffer
.realpand tempBuffer.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameterlog2n.- F
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
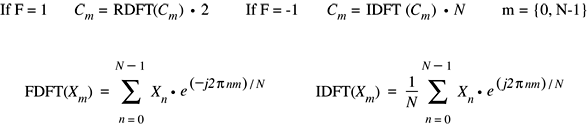
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zriptD
Computes an in-place double-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zriptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_ioData, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- C
A complex vector input.
- K
Specifies an address stride through the input/output vector. To process every element of the vector, specify 1 for parameter
signalStride; to process every other element, specify 2.- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible, tempBuffer
.realpand tempBuffer.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameterlog2n.- F
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
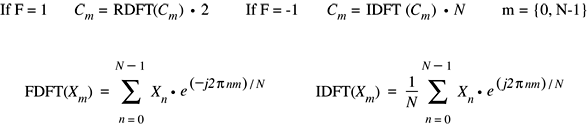
Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zrop
Computes an out-of-place single-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zrop ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
signalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2.
- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output (see vDSP Programming Guide for details on the packing format). Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zropD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zropD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
signalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
strideResultshould be 1 for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements. Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zropt
Computes an out-of-place single-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zropt ( FFTSetup __vDSP_setup, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_direction );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,vDSP_create_fftsetup. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
signalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
strideResultshould be 1 for best performance.- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible, tempBuffer
.realpand tempBuffer.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- direction
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements. Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetup and vDSP_destroy_fftsetup.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_fft_zroptD
Computes an out-of-place double-precision real discrete Fourier transform, either from the time domain to the frequency domain (forward) or from the frequency domain to the time domain (inverse).
void vDSP_fft_zroptD ( FFTSetupD __vDSP_setup, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_bufferTemp, vDSP_Length __vDSP_log2n, FFTDirection __vDSP_flag );
Parameters
- setup
Points to a structure initialized by a prior call to the FFT weights array function,
vDSP_create_fftsetupD. The value supplied as parameterlog2nof the setup function must equal or exceed the value supplied as parameterlog2nof this transform function.- signal
A complex vector signal input.
- signalStride
Specifies an address stride through input vector signal. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
signalStrideshould be 1 for best performance.- result
The complex vector signal output.
- strideResult
Specifies an address stride through output vector result. Thus, to process every element, specify a stride of 1; to process every other element, specify 2. The value of
strideResultshould be 1 for best performance.- bufferTemp
A temporary vector used for storing interim results. The size of temporary memory for each part (real and imaginary) is the lower value of 4*n or 16k for best performance. Or you can simply pass the buffer of size 2^(log2n) for each part (real and imaginary). If possible,
tempBuffer.realpandtempBuffer.imagpshould be 32-byte aligned for best performance.- log2n
The base 2 exponent of the number of elements to process. For example, to process 1024 elements, specify 10 for parameter
log2n.- flag
A forward/inverse directional flag, which must specify
kFFTDirection_Forwardfor a forward transform orkFFTDirection_Inversefor an inverse transform.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Forward transforms read real input and write packed complex output. Inverse transforms read packed complex input and write real output. As a result of packing the frequency-domain data, time-domain data and its equivalent frequency-domain data have the same storage requirements. Real data is stored in split complex form, with odd reals stored on the imaginary side of the split complex form and even reals in stored on the real side.
See also functions vDSP_create_fftsetupD and vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_hamm_window
Creates a single-precision Hamming window.
void vDSP_hamm_window ( float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_FLAG );
Discussion
vDSP_hamm_window creates a single-precision Hamming window function C, which can be multiplied by a vector using vDSP_vmul. Specify the vDSP_HALF_WINDOW flag to create only the first (n+1)/2 points, or 0 (zero) for a full-size window.
See also vDSP_vmul.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_hamm_windowD
Creates a double-precision Hamming window.
void vDSP_hamm_windowD ( double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_FLAG );
Discussion
vDSP_hamm_windowD creates a double-precision Hamming window function C, which can be multiplied by a vector using vDSP_vmulD. Specify the vDSP_HALF_WINDOW flag to create only the first (n+1)/2 points, or 0 (zero) for a full-size window.
See also vDSP_vmulD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_hann_window
Creates a single-precision Hanning window.
void vDSP_hann_window ( float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_FLAG );
Discussion
vDSP_hann_window creates a single-precision Hanning window function C, which can be multiplied by a vector using vDSP_vmul.
The FLAG parameter can have the following values:
vDSP_HANN_DENORMcreates a denormalized window.vDSP_HANN_NORMcreates a normalized window.vDSP_HALF_WINDOWcreates only the first(N+1)/2points.
vDSP_HALF_WINDOW can be ORed with any of the other values (i.e., using the C operator |).
See also vDSP_vmul.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_hann_windowD
Creates a double-precision Hanning window.
void vDSP_hann_windowD ( double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_FLAG );
Discussion
vDSP_hann_window creates a double-precision Hanning window function C, which can be multiplied by a vector using vDSP_vmulD.
The FLAG parameter can have the following values:
vDSP_HANN_DENORMcreates a denormalized window.vDSP_HANN_NORMcreates a normalized window.vDSP_HALF_WINDOWcreates only the first (N+1)/2 points.
vDSP_HALF_WINDOW can ORed with any of the other values (i.e., using the C operator |).
See also vDSP_vmulD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_imgfir
Filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a kernel; single precision.
void vDSP_imgfir ( float *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numRow, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numCol, float *__vDSP_filter, float *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_fnumRow, vDSP_Length __vDSP_fnumCol );
Parameters
- A
A real matrix signal input.
- M
Number of rows in
A.- N
Number of columns in
A.- B
A two-dimensional real matrix containing the filter.
- C
Stores real output matrix.
- P
Number of rows in
B.- Q
Number of columns in
B.
Discussion
The image is given by the input matrix A. It has M rows and N columns.

B is the filter kernel. It has P rows and Q columns.
Ensure Q >= P for best performance.
The filtered image is placed in the output matrix C. The function pads the perimeter of the output image with a border of (P-1)/2 rows of zeros on the top and bottom and (Q-1)/2 columns of zeros on the left and right.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_imgfirD
Filters an image by performing a two-dimensional convolution with a kernel; double precision.
void vDSP_imgfirD ( double *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numRow, vDSP_Length __vDSP_numCol, double *__vDSP_filter, double *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_fnumRow, vDSP_Length __vDSP_fnumCol );
Parameters
- A
A complex vector signal input.
- M
Number of rows in input matrix.
- N
Number of columns in input matrix.
- B
A two-dimensional real matrix containing the filter.
- C
Stores real output matrix.
- P
Number of rows in
B.- Q
Number of columns in
B.
Discussion
The image is given by the input matrix A. It has M rows and N columns.

B is the filter kernel. It has P rows and Q columns. For best performance, ensure Q >= P.
The filtered image is placed in the output matrix C. The functions pad the perimeter of the output image with a border of (P-1)/2 rows of zeros on the top and bottom and (Q-1)/2 columns of zeros on the left and right.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxmgv
Vector maximum magnitude; single precision.
void vDSP_maxmgv ( const float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = 0; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
if (*C < abs(A[n*I])) |
*C = abs(A[n*I]); |
Finds the element with the greatest magnitude in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxmgvD
Vector maximum magnitude; double precision.
void vDSP_maxmgvD ( const double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = 0; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
if (*C < abs(A[n*I])) |
*C = abs(A[n*I]); |
Finds the element with the greatest magnitude in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxmgvi
Vector maximum magnitude with index; single precision.
void vDSP_maxmgvi ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A.- C
Output scalar.
- IC
Output scalar index.
- N
Count of values in
A.
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = 0; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
{ |
if (*C < abs(A[n*I])) |
{ |
*C = abs(A[n*I]); |
*IC = n*I; |
} |
} |
Copies the element with the greatest magnitude from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index.If vector A contains more than one instance of the maximum magnitude, *IC contains the index of the first instance.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of 0 in *C, and the value in *IC is undefined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxmgviD
Vector maximum magnitude with index; double precision.
void vDSP_maxmgviD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- IC
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = 0; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
{ |
if (*C < abs(A[n*I])) |
{ |
*C = abs(A[n*I]); |
*IC = n*I; |
} |
} |
Copies the element with the greatest magnitude from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If vector A contains more than one instance of the maximum magnitude, *IC contains the index of the first instance.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of 0 in *C, and the value in *IC is undefined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxv
Vector maximum value; single precision.
void vDSP_maxv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = -INFINITY; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
if (*C < A[n*I]) |
*C = A[n*I]; |
Finds the element with the greatest value in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C. If N is zero (0), this function returns -INFINITY in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxvD
Vector maximum value; double precision.
void vDSP_maxvD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = -INFINITY; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
if (*C < A[n*I]) |
*C = A[n*I]; |
Finds the element with the greatest value in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C. If N is zero (0), this function returns -INFINITY in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxvi
Vector maximum value with index; single precision.
void vDSP_maxvi ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- IC
Output scalar index
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = -INFINITY; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
{ |
if (*C < A[n * I]) |
{ |
*C = A[n * I]; |
*IC = n * I; |
} |
} |
Copies the element with the greatest value from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If vector A contains more than one instance of the maximum value, *IC contains the index of the first instance. If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of -INFINITY in *C and *IC is undetermined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_maxviD
Vector maximum value with index; double precision.
void vDSP_maxviD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- IC
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
*C = -INFINITY; |
for (n = 0; n < N; ++n) |
{ |
if (*C < A[n * I]) |
{ |
*C = A[n * I]; |
*IC = n * I; |
} |
} |
Copies the element with the greatest value from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If vector A contains more than one instance of the maximum value, *IC contains the index of the first instance. If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of -INFINITY in *C and the value in *IC is undefined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_meamgv
Vector mean magnitude; single precision.
void vDSP_meamgv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean of the magnitudes of elements of vector A and stores this value in scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_meamgvD
Vector mean magnitude; double precision.
void vDSP_meamgvD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean of the magnitudes of elements of vector A and stores this value in scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_meanv
Vector mean value; single precision.
void vDSP_meanv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean value of the elements of vector A and stores this value in scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_meanvD
Vector mean value; double precision.
void vDSP_meanvD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean value of the elements of vector A and stores this value in scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_measqv
Vector mean square value; single precision.
void vDSP_measqv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean value of the squares of the elements of vector A and stores this value in scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_measqvD
Vector mean square value; double precision.
void vDSP_measqvD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean value of the squares of the elements of vector A and stores this value in scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN. in *C
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minmgv
Vector minimum magnitude; single precision.
void vDSP_minmgv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Finds the element with the least magnitude in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns +INF in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minmgvD
Vector minimum magnitude; double precision.
void vDSP_minmgvD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Finds the element with the least magnitude in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns +INF in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minmgvi
Vector minimum magnitude with index; single precision.
void vDSP_minmgvi ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- IC
Output scalar index
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Copies the element with the least magnitude from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If vector A contains more than one instance of the least magnitude, *IC contains the index of the first instance.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of +INF in *C and the value in *IC is undefined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minmgviD
Vector minimum magnitude with index; double precision.
void vDSP_minmgviD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- IC
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Copies the element with the least magnitude from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If vector A contains more than one instance of the least magnitude, *IC contains the index of the first instance.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of +INF in *C and the value in *IC is undefined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minv
Vector minimum value.
void vDSP_minv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Finds the element with the least value in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns +INFINITY in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minvD
Vector minimum value; double precision.
void vDSP_minvD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Finds the element with the least value in vector A and copies this value to scalar *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns +INF in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minvi
Vector minimum value with index; single precision.
void vDSP_minvi ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- IC
Output scalar index
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Copies the element with the least value from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If vector A contains more than one instance of the least value, *IC contains the index of the first instance.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of +INF in *C, and the value in *IC is undefined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_minviD
Vector minimum value with index; double precision.
void vDSP_minviD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- IC
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Copies the element with the least value from real vector A to real scalar *C, and writes its zero-based index to integer scalar *IC. The index is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If vector A contains more than one instance of the least value, *IC contains the index of the first instance.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a value of +INF in *C, and the value in *IC is undefined.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mmov
Copies the contents of a submatrix to another submatrix.
void vDSP_mmov ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_NC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_NR, vDSP_Length __vDSP_TCA, vDSP_Length __vDSP_TCC );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input submatrix
- C
Single-precision real output submatrix
- NC
Number of columns in
AandC- NR
Number of rows in
AandC- TCA
Number of columns in the matrix of which
Ais a submatrix- TCC
Number of columns in the matrix of which
Cis a submatrix
Discussion
The matrices are assumed to be stored in row-major order. Thus elements A[i][j] and A[i][j+1] are adjacent. Elements A[i][j] and A[i+1][j] are TCA elements apart.
This function may be used to move a subarray beginning at any point in a larger embedding array by passing for A the address of the first element of the subarray. For example, to move a subarray starting at A[3][4], pass &A[3][4]. Similarly, the address of the first destination element is passed for C
NC may equal TCA, and it may equal TCC. To copy all of an array to all of another array, pass the number of rows in NR and the number of columns in NC, TCA, and TCC.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mmovD
Copies the contents of a submatrix to another submatrix.
void vDSP_mmovD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_NC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_NR, vDSP_Length __vDSP_TCA, vDSP_Length __vDSP_TCC );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input submatrix
- C
Double-precision real output submatrix
- NC
Number of columns in
AandC- NR
Number of rows in
AandC- TCA
Number of columns in the matrix of which
Ais a submatrix- TCC
Number of columns in the matrix of which
Cis a submatrix
Discussion
The matrices are assumed to be stored in row-major order. Thus elements A[i][j] and A[i][j+1] are adjacent. Elements A[i][j] and A[i+1][j] are TCA elements apart.
This function may be used to move a subarray beginning at any point in a larger embedding array by passing for A the address of the first element of the subarray. For example, to move a subarray starting at A[3][4], pass &A[3][4]. Similarly, the address of the first destination element is passed for C
NC may equal TCA, and it may equal TCC. To copy all of an array to all of another array, pass the number of rows in NR and the number of columns in NC, TCA, and TCC.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mmul
Performs an out-of-place multiplication of two matrices; single precision.
void vDSP_mmul ( float *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_aStride, float *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_bStride, float *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_cStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function multiplies an M-by-P matrix (A) by a P-by-N matrix (B) and stores the results in an M-by-N matrix (C).
This performs the following operation:
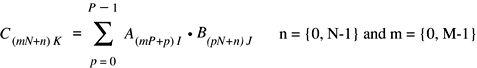
Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B.
Parameter C is the result matrix. K is an address stride through C.
Parameter M is the row count for both A and C. Parameter N is the column count for both B and C. Parameter P is the column count for A and the row count for B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mmulD
Performs an out-of-place multiplication of two matrices; double precision.
void vDSP_mmulD ( double *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_aStride, double *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_bStride, double *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_cStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function multiplies an M-by-P matrix (A) by a P-by-N matrix (B) and stores the results in an M-by-N matrix (C).
This performs the following operation:
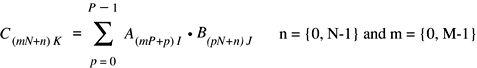
Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B.
Parameter C is the result matrix. K is an address stride through C.
Parameter M is the row count for both A and C. Parameter N is the column count for both B and C. Parameter P is the column count for A and the row count for B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mtrans
Creates a transposed matrix C from a source matrix A; single precision.
void vDSP_mtrans ( float *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_aStride, float *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_cStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Parameter A is the source matrix. I is an address stride through the source matrix.
Parameter C is the resulting transposed matrix. K is an address stride through the result matrix.
Parameter M is the number of rows in C (and the number of columns in A).
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mtransD
Creates a transposed matrix C from a source matrix A; double precision.
void vDSP_mtransD ( double *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_aStride, double *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_cStride, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Parameter A is the source matrix. I is an address stride through the source matrix.
Parameter C is the resulting transposed matrix. K is an address stride through the result matrix.
Parameter M is the number of rows in C (and the number of columns in A).
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mvessq
Vector mean of signed squares; single precision.
void vDSP_mvessq ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean value of the signed squares of the elements of vector A and stores this value in *C. If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C. .
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_mvessqD
Vector mean of signed squares; double precision.
void vDSP_mvessqD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Finds the mean value of the signed squares of the elements of vector A and stores this value in *C. If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_nzcros
Find zero crossings; single precision.
void vDSP_nzcros ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, vDSP_Length __vDSP_B, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Maximum number of crossings to find
- C
Index of last crossing found
- D
Total number of zero crossings found
- N
Count of elements in
A
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

The "function" sign(x) above has the value -1 if the sign bit of x is 1 (x is negative or -0), and +1 if the sign bit is 0 (x is positive or +0).
Scans vector A to locate transitions from positive to negative values and from negative to positive values. The scan terminates when the number of crossings specified by B is found, or the end of the vector is reached. The zero-based index of the last crossing is returned in C. C is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If the zero crossing that B specifies is not found, zero is returned in C. The total number of zero crossings found is returned in D.
Note that a transition from -0 to +0 or from +0 to -0 is counted as a zero crossing.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_nzcrosD
Find zero crossings; double precision.
void vDSP_nzcrosD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, vDSP_Length __vDSP_B, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Maximum number of crossings to find
- C
Index of last crossing found
- D
Total number of zero crossings found
- N
Count of elements in
A
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

The "function" sign(x) above has the value -1 if the sign bit of x is 1 (x is negative or -0), and +1 if the sign bit is 0 (x is positive or +0).
Scans vector A to locate transitions from positive to negative values and from negative to positive values. The scan terminates when the number of crossings specified by B is found, or the end of the vector is reached. The zero-based index of the last crossing is returned in C. C is the actual array index, not the pre-stride index. If the zero crossing that B specifies is not found, zero is returned in C. The total number of zero crossings found is returned in D.
Note that a transition from -0 to +0 or from +0 to -0 is counted as a zero crossing.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_polar
Rectangular to polar conversion; single precision.
void vDSP_polar ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A, must be even- C
Single-precision output vector
- K
Stride for
C, must be even- N
Number of ordered pairs processed
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Converts rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates. Cartesian (x,y) pairs are read from vector A. Polar (rho, theta) pairs, where rho is the radius and theta is the angle in the range [-pi, pi] are written to vector C. N specifies the number of coordinate pairs in A and C.
Coordinate pairs are adjacent elements in the array, regardless of stride; stride is the distance from one coordinate pair to the next.
This function performs the inverse operation of vDSP_rect, which converts polar to rectangular coordinates.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_polarD
Rectangular to polar conversion; double precision.
void vDSP_polarD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A, must be even- C
Double-precision output vector
- K
Stride for
C, must be even- N
Number of ordered pairs processed
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Converts rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates. Cartesian (x,y) pairs are read from vector A. Polar (rho, theta) pairs, where rho is the radius and theta is the angle in the range [-pi, pi] are written to vector C. N specifies the number of coordinate pairs in A and C.
Coordinate pairs are adjacent elements in the array, regardless of stride; stride is the distance from one coordinate pair to the next.
This function performs the inverse operation of vDSP_rectD, which converts polar to rectangular coordinates.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_rect
Polar to rectangular conversion; single precision.
void vDSP_rect ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A, must be even- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C, must be even- N
Number of ordered pairs processed
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Converts polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates. Polar (rho, theta) pairs, where rho is the radius and theta is the angle in the range [-pi, pi] are read from vector A. Cartesian (x,y) pairs are written to vector C. N specifies the number of coordinate pairs in A and C.
Coordinate pairs are adjacent elements in the array, regardless of stride; stride is the distance from one coordinate pair to the next.
This function performs the inverse operation of vDSP_polar, which converts rectangular to polar coordinates.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_rectD
Polar to rectangular conversion; double precision.
void vDSP_rectD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A, must be even- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C, must be even- N
Number of ordered pairs processed
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Converts polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates. Polar (rho, theta) pairs, where rho is the radius and theta is the angle in the range [-pi, pi] are read from vector A. Cartesian (x,y) pairs are written to vector C. N specifies the number of coordinate pairs in A and C.
Coordinate pairs are adjacent elements in the array, regardless of stride; stride is the distance from one coordinate pair to the next.
This function performs the inverse operation of vDSP_polarD, which converts rectangular to polar coordinates.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_rmsqv
Vector root-mean-square; single precision.
void vDSP_rmsqv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
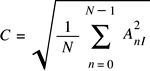
Calculates the root mean square of the elements of A and stores the result in *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_rmsqvD
Vector root-mean-square; double precision.
void vDSP_rmsqvD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
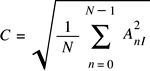
Calculates the root mean square of the elements of A and stores the result in *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns a NaN in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svdiv
Divide scalar by vector; single precision.
void vDSP_svdiv ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input scalar
- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Divides scalar A by each element of vector B, storing the results in vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svdivD
Divide scalar by vector; double precision.
void vDSP_svdivD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input scalar
- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Divides scalar A by each element of vector B, storing the results in vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_sve
Vector sum; single precision.
void vDSP_sve ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Writes the sum of the elements of A into *C. If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_sveD
Vector sum; double precision.
void vDSP_sveD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Writes the sum of the elements of A into *C. If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svemg
Vector sum of magnitudes; single precision.
void vDSP_svemg ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
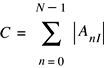
Writes the sum of the magnitudes of the elements of A into *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svemgD
Vector sum of magnitudes; double precision.
void vDSP_svemgD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
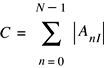
Writes the sum of the magnitudes of the elements of A into *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svesq
Vector sum of squares; single precision.
void vDSP_svesq ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Writes the sum of the squares of the elements of A into *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svesqD
Vector sum of squares; double precision.
void vDSP_svesqD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Writes the sum of the squares of the elements of A into C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svs
Vector sum of signed squares; single precision.
void vDSP_svs ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
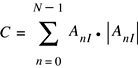
Writes the sum of the signed squares of the elements of A into *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_svsD
Vector sum of signed squares; double precision.
void vDSP_svsD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector.
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output scalar
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
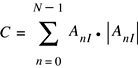
Writes the sum of the signed squares of the elements of A into *C.
If N is zero (0), this function returns 0 in *C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vaam
Vector add, add, and multiply; single precision.
void vDSP_vaam ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, float *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Single-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count ; each vector must have at least
Nelements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies the sum of vectors A and B by the sum of vectors C and D. Results are stored in vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vaamD
Vector add, add, and multiply; double precision.
void vDSP_vaamD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, double *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Double-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count ; each vector must have at least N elements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies the sum of vectors A and B by the sum of vectors C and D. Results are stored in vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vabs
Vector absolute values; single precision.
void vDSP_vabs ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Writes the absolute values of the elements of A into corresponding elements of C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vabsD
Vector absolute values; double precision.
void vDSP_vabsD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Writes the absolute values of the elements of A into corresponding elements of C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vabsi
Integer vector absolute values.
void vDSP_vabsi ( int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Integer input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Integer output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Writes the absolute values of the elements of A into corresponding elements of C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vadd
Adds vector A to vector B and leaves the result in vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_vadd ( const float __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vaddD
Adds vector A to vector B and leaves the result in vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_vaddD ( const double __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vam
Adds vectors A and B, multiplies the sum by vector C, and leaves the result in vector D; single precision.
void vDSP_vam ( const float __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, const float __vDSP_input3[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride3, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vamD
Adds vectors A and B, multiplies the sum by vector C, and leaves the result in vector D; double precision.
void vDSP_vamD ( const double __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, const double __vDSP_input3[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride3, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vasbm
Vector add, subtract, and multiply; single precision.
void vDSP_vasbm ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, float *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Single-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count ; each vector must have at least
Nelements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies the sum of vectors A and B by the result of subtracting vector D from vector C. Results are stored in vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vasbmD
Vector add, subtract, and multiply; double precision.
void vDSP_vasbmD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, double *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Double-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count ; each vector must have at least N elements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies the sum of vectors A and B by the result of subtracting vector D from vector C. Results are stored in vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vasm
Vector add and scalar multiply; single precision.
void vDSP_vasm ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input scalar
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count ; each vector must have at least N elements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies the sum of vectors A and B by scalar C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vasmD
Vector add and scalar multiply; double precision.
void vDSP_vasmD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input scalar
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count ; each vector must have at least N elements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies the sum of vectors A and B by scalar C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vavlin
Vector linear average; single precision.
void vDSP_vavlin ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real input-output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count ; each vector must have at least N elements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Recalculates the linear average of input-output vector C to include input vector A. Input scalar B specifies the number of vectors included in the current average.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vavlinD
Vector linear average; double precision.
void vDSP_vavlinD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real input-output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count ; each vector must have at least N elements
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Recalculates the linear average of input-output vector C to include input vector A. Input scalar B specifies the number of vectors included in the current average.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vclip
Vector clip; single precision.
void vDSP_vclip ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: low clipping threshold
- C
Single-precision real input scalar: high clipping threshold
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Elements of A are copied to D while clipping elements that are outside the interval [B, C] to the endpoints.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vclipc
Vector clip and count; single precision.
void vDSP_vclipc ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_NLOW, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_NHI );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: low clipping threshold
- C
Single-precision real input scalar: high clipping threshold
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count of elements in
AandD- NLOW
Number of elements that were clipped to
B- NHI
Number of elements that were clipped to
C
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Elements of A are copied to D while clipping elements that are outside the interval [B, C] to the endpoints.
The count of elements clipped to B is returned in *NLOW, and the count of elements clipped to C is returned in *NHI
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vclipcD
Vector clip and count; double precision.
void vDSP_vclipcD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_NLOW, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_NHI );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: low clipping threshold
- C
Double-precision real input scalar: high clipping threshold
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count of elements in
AandD- NLOW
Number of elements that were clipped to
B- NHI
Number of elements that were clipped to
C
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Elements of A are copied to D while clipping elements that are outside the interval [B, C] to the endpoints.
The count of elements clipped to B is returned in *NLOW, and the count of elements clipped to C is returned in *NHI
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vclipD
Vector clip; double precision.
void vDSP_vclipD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: low clipping threshold
- C
Double-precision real input scalar: high clipping threshold
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Elements of A are copied to D while clipping elements that are outside the interval [B, C] to the endpoints.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vclr
Vector clear; single precision.
void vDSP_vclr ( float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
All elements of vector C are set to zeros.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vclrD
Vector clear; double precision.
void vDSP_vclrD ( double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
All elements of vector C are set to zeros.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vcmprs
Vector compress; single precision.
void vDSP_vcmprs ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Compresses vector A based on the nonzero values of gating vector B. For nonzero elements of B, corresponding elements of A are sequentially copied to output vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vcmprsD
Vector compress; double precision.
void vDSP_vcmprsD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
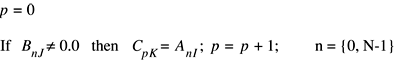
Compresses vector A based on the nonzero values of gating vector B. For nonzero elements of B, corresponding elements of A are sequentially copied to output vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdbcon
Vector convert power or amplitude to decibels; single precision.
void vDSP_vdbcon ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, unsigned int __vDSP_F );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: zero reference
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
- F
Power (0) or amplitude (1) flag
Discussion
Performs the following operation. α is 20 if F is 1, or 10 if F is 0.
Converts inputs from vector A to their decibel equivalents, calculated in terms of power or amplitude according to flag F. As a relative reference point, the value of input scalar B is considered to be zero decibels.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdbconD
Vector convert power or amplitude to decibels; double precision.
void vDSP_vdbconD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, unsigned int __vDSP_F );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: zero reference
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
- F
Power (0) or amplitude (1) flag
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
The Greek letter alpha equals 20 if F = 1, and 10 if F = 0.
Converts inputs from vector A to their decibel equivalents, calculated in terms of power or amplitude according to flag F. As a relative reference point, the value of input scalar B is considered to be zero decibels.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdist
Vector distance; single precision.
void vDSP_vdist ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Computes the square root of the sum of the squares of corresponding elements of vectors A and B, and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdistD
Vector distance; double precision.
void vDSP_vdistD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Computes the square root of the sum of the squares of corresponding elements of vectors A and B, and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdiv
Vector divide; single precision.
void vDSP_vdiv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Divides elements of vector B by corresponding elements of vector A, and stores the results in corresponding elements of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdivD
Vector divide; double precision.
void vDSP_vdivD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Divides elements of vector B by corresponding elements of vector A, and stores the results in corresponding elements of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdivi
Vector divide; integer.
void vDSP_vdivi ( int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Integer input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Integer input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Integer output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Divides elements of vector A by corresponding elements of vector B, and stores the results in corresponding elements of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vdpsp
Vector convert double-precision to single-precision.
void vDSP_vdpsp ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Creates single-precision vector C by converting double-precision inputs from vector A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_venvlp
Vector envelope; single precision.
void vDSP_venvlp ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector: high envelope
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector: low envelope
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
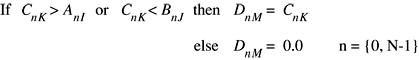
Finds the extrema of vector C. For each element of C, the corresponding element of A provides an upper-threshold value, and the corresponding element of B provides a lower-threshold value. If the value of an element of C falls outside the range defined by these thresholds, it is copied to the corresponding element of vector D. If its value is within the range, the corresponding element of vector D is set to zero.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_venvlpD
Vector envelope; double precision.
void vDSP_venvlpD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector: high envelope
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector: low envelope
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
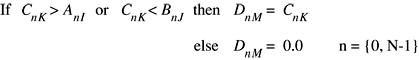
Finds the extrema of vector C. For each element of C, the corresponding element of A provides an upper-threshold value, and the corresponding element of B provides a lower-threshold value. If the value of an element of C falls outside the range defined by these thresholds, it is copied to the corresponding element of vector D. If its value is within the range, the corresponding element of vector D is set to zero.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_veqvi
Vector equivalence, 32-bit logical.
void vDSP_veqvi ( int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Integer input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Integer input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Integer output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Outputs the bitwise logical equivalence, exclusive NOR, of the integers of vectors A and B. For each pair of input values, bits in each position are compared. A bit in the output value is set if both input bits are set, or both are clear; otherwise it is cleared.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfill
Vector fill; single precision.
void vDSP_vfill ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Sets each element of vector C to the value of A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfillD
Vector fill; double precision.
void vDSP_vfillD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Sets each element of vector C to the value of A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfilli
Integer vector fill.
void vDSP_vfilli ( int *__vDSP_A, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Integer input scalar
- C
Integer output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Sets each element of vector C to the value of A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfix16
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to signed 16-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfix16 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfix16D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to signed 16-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfix16D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfix32
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to signed 32-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfix32 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfix32D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to signed 16-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfix32D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfix8
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to signed 8-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfix8 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfix8D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to signed 8-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfix8D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixr16
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to signed 16-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixr16 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixr16D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to signed 16-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixr16D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixr32
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to signed 32-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixr32 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixr32D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to signed 32-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixr32D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixr8
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to signed 8-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixr8 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixr8D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to signed 8-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixr8D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixru16
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to unsigned 16-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixru16 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixru16D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to unsigned 16-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixru16D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixru32
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to unsigned 32-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixru32 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixru32D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to unsigned 32-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixru32D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixru8
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to unsigned 8-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixru8 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixru8D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to unsigned 8-bit integer values, rounding towards nearest integer.
void vDSP_vfixru8D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixu16
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to unsigned 16-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfixu16 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixu16D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to unsigned 16-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfixu16D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned short *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixu32
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to unsigned 32-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfixu32 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixu32D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to unsigned 32-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfixu32D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixu8
Converts an array of single-precision floating-point values to unsigned 8-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfixu8 ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfixu8D
Converts an array of double-precision floating-point values to unsigned 8-bit integer values, rounding towards zero.
void vDSP_vfixu8D ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, unsigned char *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vflt16
Converts an array of signed 16-bit integers to single-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vflt16 ( short *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vflt16D
Converts an array of signed 16-bit integers to double-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vflt16D ( short *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vflt32
Converts an array of signed 32-bit integers to single-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vflt32 ( int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vflt32D
Converts an array of signed 32-bit integers to double-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vflt32D ( int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vflt8
Converts an array of signed 8-bit integers to single-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vflt8 ( char *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vflt8D
Converts an array of signed 8-bit integers to double-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vflt8D ( char *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfltu16
Converts an array of unsigned 16-bit integers to single-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vfltu16 ( unsigned short *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfltu16D
Converts an array of unsigned 16-bit integers to double-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vfltu16D ( unsigned short *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfltu32
Converts an array of unsigned 32-bit integers to single-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vfltu32 ( unsigned int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfltu32D
Converts an array of unsigned 32-bit integers to double-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vfltu32D ( unsigned int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfltu8
Converts an array of unsigned 8-bit integers to single-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vfltu8 ( unsigned char *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfltu8D
Converts an array of unsigned 8-bit integers to double-precision floating-point values.
void vDSP_vfltu8D ( unsigned char *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Source vector.
- __vDSP_I
Source vector stride length.
- __vDSP_C
Destination vector.
- __vDSP_K
Destination vector stride length.
- __vDSP_N
Number of elements in vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfrac
Vector truncate to fraction; single precision.
void vDSP_vfrac ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
The "function" truncate(x) is the integer farthest from 0 but not farther than x. Thus, for example, vDSP_vFrac(-3.25) produces the result -0.25.
Sets each element of vector C to the signed fractional part of the corresponding element of A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vfracD
Vector truncate to fraction; double precision.
void vDSP_vfracD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
The "function" truncate(x) is the integer farthest from 0 but not farther than x. Thus, for example, vDSP_vFrac(-3.25) produces the result -0.25.
Sets each element of vector C to the signed fractional part of the corresponding element of A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgathr
Vector gather; single precision.
void vDSP_vgathr ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- B
Integer vector containing indices
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Uses elements of vector B as indices to copy selected elements of vector A to sequential locations in vector C. Note that 1, not zero, is treated as the first location in the input vector when evaluating indices. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgathra
Vector gather, absolute pointers; single precision.
void vDSP_vgathra ( float **A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Pointer input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Uses elements of vector A as pointers to copy selected single-precision values from memory to sequential locations in vector C. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgathraD
Vector gather, absolute pointers; double precision.
void vDSP_vgathraD ( double **A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Pointer input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Uses elements of vector A as pointers to copy selected double-precision values from memory to sequential locations in vector C. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgathrD
Vector gather; double precision.
void vDSP_vgathrD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- B
Integer vector containing indices
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Uses elements of vector B as indices to copy selected elements of vector A to sequential locations in vector C. Note that 1, not zero, is treated as the first location in the input vector when evaluating indices. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgen
Vector tapered ramp; single precision.
void vDSP_vgen ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input scalar: base value
- B
Single-precision real input scalar: end value
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates ramped vector C with element zero equal to scalar A and element N-1 equal to scalar B. Output values between element zero and element N-1 are evenly spaced and increase or decrease monotonically.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgenD
Vector tapered ramp; double precision.
void vDSP_vgenD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input scalar: base value
- B
Double-precision real input scalar: end value
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates ramped vector C with element zero equal to scalar A and element N-1 equal to scalar B. Output values between element zero and element N-1 are evenly spaced and increase or decrease monotonically.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgenp
Vector generate by extrapolation and interpolation; single precision.
void vDSP_vgenp ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count for
C- M
Count for
AandB
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
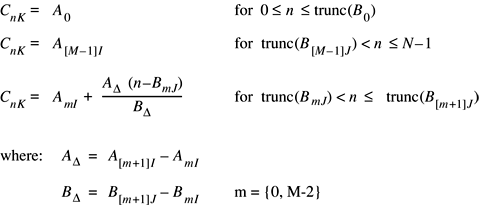
Generates vector C by extrapolation and linear interpolation from the ordered pairs (A,B) provided by corresponding elements in vectors A and B. Vector B provides index values and should increase monotonically. Vector A provides intensities, magnitudes, or some other measurable quantities, one value associated with each value of B. This function can only be done out of place.
Vectors A and B define a piecewise linear function, f(x):
In the interval [-infinity, trunc(
B[0*J]], the function is the constantA[0*I].In each interval (trunc(
B[m*J]), trunc(B[(m+1)*J])], the function is the line passing through the two points (B[m*J],A[m*I]) and (B[(m+1)*J],A[(m+1)*I]). (This is for each integer m, 0 <= m <M-1.)In the interval (
B[(M-1)*J], infinity], the function is the constantA[(M-1)*I].For 0 <= n <
N,C[n*K] = f(n).
This function can only be done out of place.
Output values are generated for integral indices in the range zero through N - 1, deriving output values by interpolating and extrapolating from vectors A and B. For example, if vectors A and B define velocity and time pairs (v, t), vDSP_vgenp writes one velocity to vector C for every integral unit of time from zero to N - 1.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vgenpD
Vector generate by extrapolation and interpolation; double precision.
void vDSP_vgenpD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count for
C- M
Count for
AandB
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
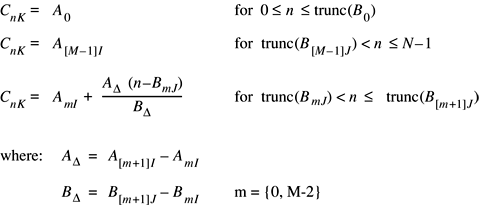
Generates vector C by extrapolation and linear interpolation from the ordered pairs (A,B) provided by corresponding elements in vectors A and B. Vector B provides index values and should increase monotonically. Vector A provides intensities, magnitudes, or some other measurable quantities, one value associated with each value of B. This function can only be done out of place.
Vectors A and B define a piecewise linear function, f(x):
In the interval [-infinity, trunc(
B[0*J]], the function is the constantA[0*I].In each interval (trunc(
B[m*J]), trunc(B[(m+1)*J])], the function is the line passing through the two points (B[m*J],A[m*I]) and (B[(m+1)*J],A[(m+1)*I]). (This is for each integer m, 0 <= m <M-1.)In the interval (
B[(M-1)*J], infinity], the function is the constantA[(M-1)*I].For 0 <= n <
N,C[n*K] = f(n).
This function can only be done out of place.
Output values are generated for integral indices in the range zero through N - 1, deriving output values by interpolating and extrapolating from vectors A and B. For example, if vectors A and B define velocity and time pairs (v, t), vDSP_vgenp writes one velocity to vector C for every integral unit of time from zero to N - 1.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_viclip
Vector inverted clip; single precision.
void vDSP_viclip ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Single-precision real input scalar: upper threshold
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Performs an inverted clip of vector A using lower-threshold and upper-threshold input scalars B and C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_viclipD
Vector inverted clip; double precision.
void vDSP_viclipD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Double-precision real input scalar: upper threshold
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Performs an inverted clip of vector A using lower-threshold and upper-threshold input scalars B and C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vindex
Vector index; single precision.
void vDSP_vindex ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- B
Single-precision real input vector: indices
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Uses vector B as zero-based subscripts to copy selected elements of vector A to vector C. Fractional parts of vector B are ignored.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vindexD
Vector index; double precision.
void vDSP_vindexD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- B
Double-precision real input vector: indices
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Uses vector B as zero-based subscripts to copy selected elements of vector A to vector C. Fractional parts of vector B are ignored.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vintb
Vector linear interpolation between vectors; single precision.
void vDSP_vintb ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input scalar: interpolation constant
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Creates vector D by interpolating between vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vintbD
Vector linear interpolation between vectors; double precision.
void vDSP_vintbD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input scalar: interpolation constant
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Creates vector D by interpolating between vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vlim
Vector test limit; single precision.
void vDSP_vlim ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: limit
- C
Single-precision real input scalar
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Compares values from vector A to limit scalar B. For inputs greater than or equal to B, scalar C is written to D . For inputs less than B, the negated value of scalar C is written to vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vlimD
Vector test limit; double precision.
void vDSP_vlimD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: limit
- C
Double-precision real input scalar
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Compares values from vector A to limit scalar B. For inputs greater than or equal to B, scalar C is written to D . For inputs less than B, the negated value of scalar C is written to vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vlint
Vector linear interpolation between neighboring elements; single precision.
void vDSP_vlint ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- B
Single-precision real input vector: integer parts are indices into
Aand fractional parts are interpolation constants- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count for C
- M
Length of A
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Generates vector C by interpolating between neighboring values of vector A as controlled by vector B. The integer portion of each element in B is the zero-based index of the first element of a pair of adjacent values in vector A.
The value of the corresponding element of C is derived from these two values by linear interpolation, using the fractional part of the value in B.
Argument M is not used in the calculation. However, the integer parts of the values in B must be greater than or equal to zero and less than or equal to M - 2.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vlintD
Vector linear interpolation between neighboring elements; double precision.
void vDSP_vlintD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- B
Double-precision real input vector: integer parts are indices into
Aand fractional parts are interpolation constants- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count for C
- M
Length of A
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Generates vector C by interpolating between neighboring values of vector A as controlled by vector B. The integer portion of each element in B is the zero-based index of the first element of a pair of adjacent values in vector A.
The value of the corresponding element of C is derived from these two values by linear interpolation, using the fractional part of the value in B.
Argument M is not used in the calculation. However, the integer parts of the values in B must be greater than or equal to zero and less than or equal to M - 2.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vma
Vector multiply and add; single precision.
void vDSP_vma ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies corresponding elements of vectors A and B, add the corresponding elements of vector C, and stores the results in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmaD
Vector multiply and add; double precision.
void vDSP_vmaD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Multiplies corresponding elements of vectors A and B, add the corresponding elements of vector C, and stores the results in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmax
Vector maxima; single precision.
void vDSP_vmax ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the greater of the corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmaxD
Vector maxima; double precision.
void vDSP_vmaxD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the greater of the corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmaxmg
Vector maximum magnitudes; single precision.
void vDSP_vmaxmg ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the larger of the magnitudes of corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmaxmgD
Vector maximum magnitudes; double precision.
void vDSP_vmaxmgD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the larger of the magnitudes of corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmin
Vector minima; single precision.
void vDSP_vmin ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the lesser of the corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vminD
Vector minima; double precision.
void vDSP_vminD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the lesser of the corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vminmg
Vector minimum magnitudes; single precision.
void vDSP_vminmg ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the smaller of the magnitudes of corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vminmgD
Vector minimum magnitudes; double precision.
void vDSP_vminmgD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each element of output vector C is the smaller of the magnitudes of corresponding values from input vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmma
Vector multiply, multiply, and add; single precision.
void vDSP_vmma ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, float *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Single-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied, corresponding values of C and D are multiplied, and these products are added together and stored in E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmmaD
Vector multiply, multiply, and add; double precision.
void vDSP_vmmaD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, double *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Double-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied, corresponding values of C and D are multiplied, and these products are added together and stored in E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmmsb
Vector multiply, multiply, and subtract; single precision.
void vDSP_vmmsb ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, float *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Single-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied, corresponding values of C and D are multiplied, and the second product is subtracted from the first. The result is stored in E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmmsbD
Vector multiply, multiply, and subtract; double precision.
void vDSP_vmmsbD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, double *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Double-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied, corresponding values of C and D are multiplied, and the second product is subtracted from the first. The result is stored in E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmsa
Vector multiply and scalar add; single precision.
void vDSP_vmsa ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input scalar
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied and the scalar C is added. The result is stored in D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmsaD
Vector multiply and scalar add; double precision.
void vDSP_vmsaD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input scalar
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied and the scalar C is added. The result is stored in D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmsb
Vector multiply and subtract, single precision.
void vDSP_vmsb ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied and the corresponding value of C is subtracted. The result is stored in D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmsbD
Vector multiply and subtract; double precision.
void vDSP_vmsbD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Corresponding elements of A and B are multiplied and the corresponding value of C is subtracted. The result is stored in D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmul
Multiplies vector A by vector B and leaves the result in vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_vmul ( const float __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vmulD
Multiplies vector A by vector B and leaves the result in vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_vmulD ( const double __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vnabs
Vector negative absolute values; single precision.
void vDSP_vnabs ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each value in C is the negated absolute value of the corresponding element in A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vnabsD
Vector negative absolute values; double precision.
void vDSP_vnabsD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Each value in C is the negated absolute value of the corresponding element in A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vneg
Vector negative values; single precision.
void vDSP_vneg ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Each value in C is the negated value of the corresponding element in A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vnegD
Vector negative values; double precision.
void vDSP_vnegD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Each value in C is the negated value of the corresponding element in A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vpoly
Vector polynomial evaluation; single precision.
void vDSP_vpoly ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector: coefficients
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector: variable values
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
- P
Degree of polynomial
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
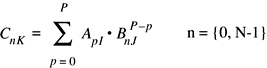
Evaluates polynomials using vector B as independent variables and vector A as coefficients. A polynomial of degree p requires p+1 coefficients, so vector A should contain P+1 values.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vpolyD
Vector polynomial evaluation; double precision.
void vDSP_vpolyD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector: coefficients
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector: variable values
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
- P
Degree of polynomial
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
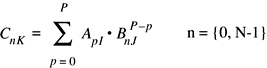
Evaluates polynomials using vector B as independent variables and vector A as coefficients. A polynomial of degree p requires p+1 coefficients, so vector A should contain P+1 values.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vpythg
Vector Pythagoras; single precision.
void vDSP_vpythg ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, float *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Single-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector C from A and squares the differences, subtracts vector D from B and squares the differences, adds the two sets of squared differences, and then writes the square roots of the sums to vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vpythgD
Vector Pythagoras; double precision.
void vDSP_vpythgD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, double *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Double-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector C from A and squares the differences, subtracts vector D from B and squares the differences, adds the two sets of squared differences, and then writes the square roots of the sums to vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vqint
Vector quadratic interpolation; single precision.
void vDSP_vqint ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- B
Single-precision real input vector: integer parts are indices into
Aand fractional parts are interpolation constants- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count for C
- M
Length of A: must be greater than or equal to 3
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
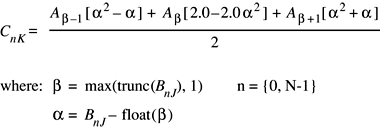
Generates vector C by interpolating between neighboring values of vector A as controlled by vector B. The integer portion of each element in B is the zero-based index of the first element of a triple of adjacent values in vector A.
The value of the corresponding element of C is derived from these three values by quadratic interpolation, using the fractional part of the value in B.
Argument M is not used in the calculation. However, the integer parts of the values in B must be less than or equal to M - 2.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vqintD
Vector quadratic interpolation; double precision.
void vDSP_vqintD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- B
Double-precision real input vector: integer parts are indices into
Aand fractional parts are interpolation constants- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count for C
- M
Length of A: must be greater than or equal to 3
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
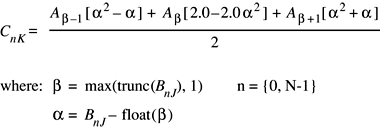
Generates vector C by interpolating between neighboring values of vector A as controlled by vector B. The integer portion of each element in B is the zero-based index of the first element of a triple of adjacent values in vector A.
The value of the corresponding element of C is derived from these three values by quadratic interpolation, using the fractional part of the value in B.
Argument M is not used in the calculation. However, the integer parts of the values in B must be less than or equal to M - 2.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vramp
Build ramped vector; single precision.
void vDSP_vramp ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input scalar: initial value
- B
Single-precision real input scalar: increment or decrement
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates a monotonically incrementing or decrementing vector. Scalar A is the initial value written to vector C. Scalar B is the increment or decrement for each succeeding element.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampD
Build ramped vector; double precision.
void vDSP_vrampD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input scalar: initial value
- B
Double-precision real input scalar: increment or decrement
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates a monotonically incrementing or decrementing vector. Scalar A is the initial value written to vector C. Scalar B is the increment or decrement for each succeeding element.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmul
Builds a ramped vector and multiplies by a source vector.
void vDSP_vrampmul ( const float *__vDSP_I, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, float *__vDSP_Start, const float *__vDSP_Step, float *__vDSP_O, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I
Input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O
The output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This routine calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O[i*OS] = *Start * I[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmul2
Stereo version of vDSP_vrampmul.
void vDSP_vrampmul2 ( const float *__vDSP_I0, const float *__vDSP_I1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, float *__vDSP_Start, const float *__vDSP_Step, float *__vDSP_O0, float *__vDSP_O1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I0
First input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_I1
Second input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vectors. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O0
First output vector.
- __vDSP_O1
Second output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This function calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O0[i*OS] = *Start * I0[i*IS]; |
O1[i*OS] = *Start * I1[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmul2_s1_15
Vector fixed-point 1.15 format version of vDSP_vrampmul2.
void vDSP_vrampmul2_s1_15 ( const short int *__vDSP_I0, const short int *__vDSP_I1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, short int *__vDSP_Start, const short int *__vDSP_Step, short int *__vDSP_O0, short int *__vDSP_O1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I0
First input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_I1
Second input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vectors. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O0
First output vector.
- __vDSP_O1
Second output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This function calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O0[i*OS] = *Start * I0[i*IS]; |
O1[i*OS] = *Start * I1[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with one sign bit and 15 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 32768.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmul2_s8_24
Vector fixed-point 8.24 format version of vDSP_vrampmul2.
void vDSP_vrampmul2_s8_24 ( const int *__vDSP_I0, const int *__vDSP_I1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, int *__vDSP_Start, const int *__vDSP_Step, int *__vDSP_O0, int *__vDSP_O1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I0
First input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_I1
Second input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vectors. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O0
First output vector.
- __vDSP_O1
Second output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This function calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O0[i*OS] = *Start * I0[i*IS]; |
O1[i*OS] = *Start * I1[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with eight integer bits (including the sign bit) and 24 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 16777216.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmuladd
Builds a ramped vector, multiplies it by a source vector, and adds the result to the output vector.
void vDSP_vrampmuladd ( const float *__vDSP_I, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, float *__vDSP_Start, const float *__vDSP_Step, float *__vDSP_O, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I
Input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O
The output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This routine calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O[i*OS] += *Start * I[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmuladd2
Stereo version of vDSP_vrampmuladd.
void vDSP_vrampmuladd2 ( const float *__vDSP_I0, const float *__vDSP_I1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, float *__vDSP_Start, const float *__vDSP_Step, float *__vDSP_O0, float *__vDSP_O1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I0
First input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_I1
Second input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vectors. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O0
First output vector.
- __vDSP_O1
Second output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This function calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O0[i*OS] += *Start * I0[i*IS]; |
O1[i*OS] += *Start * I1[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmuladd2_s1_15
Vector fixed-point 1.15 format version of vDSP_vrampmuladd2.
void vDSP_vrampmuladd2_s1_15 ( const short int *__vDSP_I0, const short int *__vDSP_I1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, short int *__vDSP_Start, const short int *__vDSP_Step, short int *__vDSP_O0, short int *__vDSP_O1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I0
First input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_I1
Second input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vectors. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O0
First output vector.
- __vDSP_O1
Second output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This function calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O0[i*OS] += *Start * I0[i*IS]; |
O1[i*OS] += *Start * I1[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with one sign bit and 15 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 32768.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmuladd2_s8_24
Vector fixed-point 8.24 format version of vDSP_vrampmuladd2.
void vDSP_vrampmuladd2_s8_24 ( const int *__vDSP_I0, const int *__vDSP_I1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, int *__vDSP_Start, const int *__vDSP_Step, int *__vDSP_O0, int *__vDSP_O1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I0
First input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_I1
Second input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vectors. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O0
First output vector.
- __vDSP_O1
Second output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This function calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O0[i*OS] += *Start * I0[i*IS]; |
O1[i*OS] += *Start * I1[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with eight integer bits (including the sign bit) and 24 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 16777216.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmuladd_s1_15
Vector fixed-point 1.15 format version of vDSP_vrampmuladd.
void vDSP_vrampmuladd_s1_15 ( const short int *__vDSP_I, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, short int *__vDSP_Start, const short int *__vDSP_Step, short int *__vDSP_O, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I
Input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O
The output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This routine calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O[i*OS] += *Start * I[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with one sign bit and 15 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 32768.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmuladd_s8_24
Vector fixed-point 8.24 format version of vDSP_vrampmuladd.
void vDSP_vrampmuladd_s8_24 ( const int *__vDSP_I, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, int *__vDSP_Start, const int *__vDSP_Step, int *__vDSP_O, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I
Input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O
The output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This routine calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O[i*OS] += *Start * I[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with eight integer bits (including the sign bit) and 24 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 16777216.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmul_s1_15
Vector fixed-point 1.15 format version of vDSP_vrampmul.
void vDSP_vrampmul_s1_15 ( const short int *__vDSP_I, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, short int *__vDSP_Start, const short int *__vDSP_Step, short int *__vDSP_O, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I
Input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O
The output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This routine calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O[i*OS] = *Start * I[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with one sign bit and 15 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 32768.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrampmul_s8_24
Vector fixed-point 8.24 format version of vDSP_vrampmul.
void vDSP_vrampmul_s8_24 ( const int *__vDSP_I, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_IS, int *__vDSP_Start, const int *__vDSP_Step, int *__vDSP_O, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_OS, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- __vDSP_I
Input vector, multiplied by the ramp function.
- __vDSP_IS
Stride length in input vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is used.- __vDSP_Start
The initial value for the ramp function. Modified on return to hold the next value (including accumulated errors) so that the ramp function can be continued smoothly.
- __vDSP_Step
The value to increment each subsequent value of the ramp function by.
- __vDSP_O
The output vector.
- __vDSP_OS
Stride length in output vector. For example, if
__vDSP_ISis2, every second element is modified.- __vDSP_N
The number of elements to modify.
Discussion
This routine calculates the following:
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { |
O[i*OS] = *Start * I[i*IS]; |
*Start += *Step; |
} |
The elements are fixed-point numbers, each with eight integer bits (including the sign bit) and 24 fraction bits. A value in this representation can be converted to floating-point by dividing it by 16777216.0.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrsum
Vector running sum integration; single precision.
void vDSP_vrsum ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_S, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- S
Single-precision real input scalar: weighting factor
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Integrates vector A using a running sum from vector C. Vector A is weighted by scalar S and added to the previous output point. The first element from vector A is not used in the sum.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrsumD
Vector running sum integration; double precision.
void vDSP_vrsumD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_S, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- S
Double-precision real input scalar: weighting factor
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Integrates vector A using a running sum from vector C. Vector A is weighted by scalar S and added to the previous output point. The first element from vector A is not used in the sum.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrvrs
Vector reverse order, in place; single precision.
void vDSP_vrvrs ( float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- C
Single-precision real input-output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Reverses the order of vector C in place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vrvrsD
Vector reverse order, in place; double precision.
void vDSP_vrvrsD ( double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- C
Double-precision real input-output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Reverses the order of vector C in place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsadd
Vector scalar add; single precision.
void vDSP_vsadd ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Adds scalar B to each element of vector A and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsaddD
Vector scalar add; double precision.
void vDSP_vsaddD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Adds scalar B to each element of vector A and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsaddi
Integer vector scalar add.
void vDSP_vsaddi ( int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_B, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Integer input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Integer input scalar
- C
Integer output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Adds scalar B to each element of vector A and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsbm
Vector subtract and multiply; single precision.
void vDSP_vsbm ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector B from vector A and then multiplies the differences by vector C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsbmD
Vector subtract and multiply; double precision.
void vDSP_vsbmD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Double for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector B from vector A and then multiplies the differences by vector C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsbsbm
Vector subtract, subtract, and multiply; single precision.
void vDSP_vsbsbm ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, float *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Single-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector B from A, subtracts vector D from C, and multiplies the differences. Results are stored in vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsbsbmD
Vector subtract, subtract, and multiply; double precision.
void vDSP_vsbsbmD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, double *__vDSP_E, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real input vector
- L
Stride for
D- E
Double-precision real output vector
- M
Stride for
E- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector B from A, subtracts vector D from C, and multiplies the differences. Results are stored in vector E.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsbsm
Vector subtract and scalar multiply; single precision.
void vDSP_vsbsm ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real input scalar
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector B from vector A and then multiplies each difference by scalar C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsbsmD
Vector subtract and scalar multiply; double precision.
void vDSP_vsbsmD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real input scalar
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Subtracts vector B from vector A and then multiplies each difference by scalar C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsdiv
Vector scalar divide; single precision.
void vDSP_vsdiv ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Divides each element of vector A by scalar B and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsdivD
Vector scalar divide; double precision.
void vDSP_vsdivD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Divides each element of vector A by scalar B and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsdivi
Integer vector scalar divide.
void vDSP_vsdivi ( int *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, int *__vDSP_B, int *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Integer input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Integer input scalar
- C
Integer output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Divides each element of vector A by scalar B and stores the result in the corresponding element of vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsimps
Simpson integration; single precision.
void vDSP_vsimps ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
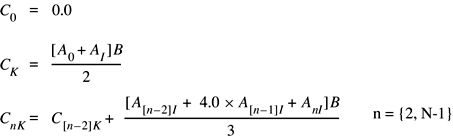
Integrates vector A using Simpson integration, storing results in vector C. Scalar B specifies the integration step size. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsimpsD
Simpson integration; double precision.
void vDSP_vsimpsD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
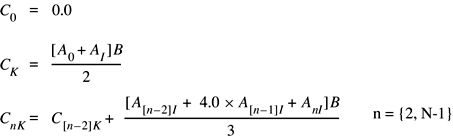
Integrates vector A using Simpson integration, storing results in vector C. Scalar B specifies the integration step size. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsma
Vector scalar multiply and vector add; single precision.
void vDSP_vsma ( const float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, const float *__vDSP_B, const float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and then adds the products to vector C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsmaD
Vector scalar multiply and vector add; double precision.
void vDSP_vsmaD ( const double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, const double *__vDSP_B, const double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and then adds the products to vector C. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsmsa
Vector scalar multiply and scalar add; single precision.
void vDSP_vsmsa ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real input scalar
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and then adds scalar C to each product. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsmsaD
Vector scalar multiply and scalar add; double precision.
void vDSP_vsmsaD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real input scalar
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and then adds scalar C to each product. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsmsb
Vector scalar multiply and vector subtract; single precision.
void vDSP_vsmsb ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar
- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and then subtracts vector C from the products. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsmsbD
Vector scalar multiply and vector subtract; double precision.
void vDSP_vsmsbD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar
- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and then subtracts vector C from the products. Results are stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsmul
Multiplies vector signal1 by scalar signal2 and leaves the result in vector result; single precision.
void vDSP_vsmul ( const float __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float *__vDSP_input2, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsmulD
Multiplies vector signal1 by scalar signal2 and leaves the result in vector result; double precision.
void vDSP_vsmulD ( const double __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double *__vDSP_input2, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsort
Vector in-place sort; single precision.
void vDSP_vsort ( float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_OFLAG );
Parameters
- C
Single-precision real input-output vector
- N
Count
- OFLAG
Flag for sort order: 1 for ascending, -1 for descending
Discussion
Performs an in-place sort of vector C in the order specified by parameter OFLAG.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsortD
Vector in-place sort; double precision.
void vDSP_vsortD ( double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_OFLAG );
Parameters
- C
Double-precision real input-output vector
- N
Count
- OFLAG
Flag for sort order: 1 for ascending, -1 for descending
Discussion
Performs an in-place sort of vector C in the order specified by parameter OFLAG.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsorti
Vector index in-place sort; single precision.
void vDSP_vsorti ( float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_List_addr, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_OFLAG );
Parameters
- C
Single-precision real input vector
- IC
Integer output vector. Must be initialized with the indices of vector
C, from 0 toN-1.- List_addr
Temporary vector. This is currently not used and NULL should be passed.
- N
Count
- OFLAG
Flag for sort order: 1 for ascending, -1 for descending
Discussion
Leaves input vector C unchanged and performs an in-place sort of the indices in vector IC according to the values in C. The sort order is specified by parameter OFLAG.
The values in C can then be obtained in sorted order, by taking indices in sequence from IC.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsortiD
Vector index in-place sort; double precision.
void vDSP_vsortiD ( double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_IC, vDSP_Length *__vDSP_List_addr, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, int __vDSP_OFLAG );
Parameters
- C
Double-precision real input vector
- IC
Integer output vector. Must be initialized with the indices of vector
C, from 0 toN-1.- List_addr
Temporary vector. This is currently not used and NULL should be passed.
- N
Count
- OFLAG
Flag for sort order: 1 for ascending, -1 for descending
Discussion
Leaves input vector C unchanged and performs an in-place sort of the indices in vector IC according to the values in C. The sort order is specified by parameter OFLAG.
The values in C can then be obtained in sorted order, by taking indices in sequence from IC.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vspdp
Vector convert single-precision to double-precision.
void vDSP_vspdp ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Creates double-precision vector C by converting single-precision inputs from vector A. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsq
Computes the squared values of vector input and leaves the result in vector result; single precision.
void vDSP_vsq ( const float __vDSP_input[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInput, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsqD
Computes the squared values of vector signal1 and leaves the result in vector result; double precision.
void vDSP_vsqD ( const double __vDSP_input[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInput, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vssq
Computes the signed squares of vector signal1 and leaves the result in vector result; single precision.
void vDSP_vssq ( const float __vDSP_input[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInput, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vssqD
Computes the signed squares of vector signal1 and leaves the result in vector result; double precision.
void vDSP_vssqD ( const double __vDSP_input[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideInput, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsub
Subtracts vector signal1 from vector signal2 and leaves the result in vector result; single precision.
void vDSP_vsub ( const float __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, float __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vsubD
Subtracts vector signal1 from vector signal2 and leaves the result in vector result; double precision.
void vDSP_vsubD ( const double __vDSP_input1[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, double __vDSP_result[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vswap
Vector swap; single precision.
void vDSP_vswap ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input-output vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input-output vector
- J
Stride for
B- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Exchanges the elements of vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vswapD
Vector swap; double precision.
void vDSP_vswapD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input-output vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input-output vector
- J
Stride for
B- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Exchanges the elements of vectors A and B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vswsum
Vector sliding window sum; single precision.
void vDSP_vswsum ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count of output points
- P
Length of window
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Writes the sliding window sum of P consecutive elements of vector A to vector C, for each of N possible starting positions of the P-element window in vector A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vswsumD
Vector sliding window sum; double precision.
void vDSP_vswsumD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count of output points
- P
Length of window
Discussion
Performs the following operation:

Writes the sliding window sum of P consecutive elements of vector A to vector C, for each of N possible starting positions of the P-element window in vector A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vtabi
Vector interpolation, table lookup; single precision.
void vDSP_vtabi ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_S1, float *__vDSP_S2, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- S1
Single-precision real input scalar: scale factor
- S2
Single-precision real input scalar: base offset
- C
Single-precision real input vector: lookup table
- M
Lookup table size
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Evaluates elements of vector A for use as offsets into vector C. Vector C is a zero-based lookup table supplied by the caller that generates output values for vector D. Linear interpolation is used to compute output values when offsets do not evaluate integrally. Scale factor S1 and base offset S2 map the anticipated range of input values to the range of the lookup table and are typically assigned values such that:
floor(F * minimum input value + G) = 0 |
floor(F * maximum input value + G) = M-1 |
Input values that evaluate to zero or less derive their output values from table location zero. Values that evaluate beyond the table, greater than M-1, derive their output values from the last table location. For inputs that evaluate integrally, the table location indexed by the integral is copied as the output value. All other inputs derive their output values by interpolation between the two table values surrounding the evaluated input.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vtabiD
Vector interpolation, table lookup; double precision.
void vDSP_vtabiD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_S1, double *__vDSP_S2, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- S1
Double-precision real input scalar: scale factor
- S2
Double-precision real input scalar: base offset
- C
Double-precision real input vector: lookup table
- M
Lookup table size
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Evaluates elements of vector A for use as offsets into vector C. Vector C is a zero-based lookup table supplied by the caller that generates output values for vector D. Linear interpolation is used to compute output values when offsets do not evaluate integrally. Scale factor S1 and base offset S2 map the anticipated range of input values to the range of the lookup table and are typically assigned values such that:
floor(F * minimum input value + G) = 0 |
floor(F * maximum input value + G) = M-1 |
Input values that evaluate to zero or less derive their output values from table location zero. Values that evaluate beyond the table, greater than M-1, derive their output values from the last table location. For inputs that evaluate integrally, the table location indexed by the integral is copied as the output value. All other inputs derive their output values by interpolation between the two table values surrounding the evaluated input.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vthr
Vector threshold; single precision.
void vDSP_vthr ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates vector C by comparing each input from vector A with scalar B. If an input value is less than B, B is copied to C; otherwise, the input value from A is copied to C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vthrD
Vector threshold; double precision.
void vDSP_vthrD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates vector C by comparing each input from vector A with scalar B. If an input value is less than B, B is copied to C; otherwise, the input value from A is copied to C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vthres
Vector threshold with zero fill; single precision.
void vDSP_vthres ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates vector C by comparing each input from vector A with scalar B. If an input value is less than B, zero is written to C; otherwise, the input value from A is copied to C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vthresD
Vector threshold with zero fill; double precision.
void vDSP_vthresD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates vector C by comparing each input from vector A with scalar B. If an input value is less than B, zero is written to C; otherwise, the input value from A is copied to C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vthrsc
Vector threshold with signed constant; single precision.
void vDSP_vthrsc ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Single-precision real input scalar
- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates vector D using the plus or minus value of scalar C. The sign of the output element is determined by comparing input from vector A with threshold scalar B. For input values less than B, the negated value of C is written to vector D. For input values greater than or equal to B, C is copied to vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vthrscD
Vector threshold with signed constant; double precision.
void vDSP_vthrscD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: lower threshold
- C
Double-precision real input scalar
- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
D- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
Creates vector D using the plus or minus value of scalar C. The sign of the output element is determined by comparing input from vector A with threshold scalar B. For input values less than B, the negotiated value of C is written to vector D. For input values greater than or equal to B, C is copied to vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vtmerg
Tapered merge of two vectors; single precision.
void vDSP_vtmerg ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Performs a tapered merge of vectors A and B. Values written to vector C range from element zero of vector A to element N-1 of vector B. Output values between these endpoints reflect varying amounts of their corresponding inputs from vectors A and B, with the percentage of vector A decreasing and the percentage of vector B increasing as the index increases.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vtmergD
Tapered merge of two vectors; double precision.
void vDSP_vtmergD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Performs a tapered merge of vectors A and B. Values written to vector C range from element zero of vector A to element N-1 of vector B. Output values between these endpoints reflect varying amounts of their corresponding inputs from vectors A and B, with the percentage of vector A decreasing and the percentage of vector B increasing as the index increases.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vtrapz
Vector trapezoidal integration; single precision.
void vDSP_vtrapz ( float *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input scalar: step size
- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
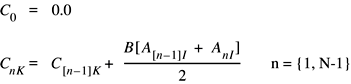
Estimates the integral of vector A using the trapezoidal rule. Scalar B specifies the integration step size. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_vtrapzD
Vector trapezoidal integration; double precision.
void vDSP_vtrapzD ( double *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input scalar: step size
- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
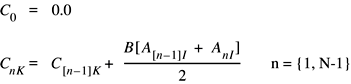
Estimates the integral of vector A using the trapezoidal rule. Scalar B specifies the integration step size. This function can only be done out of place.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_wiener
Wiener-Levinson general convolution; single precision.
void vDSP_wiener ( vDSP_Length __vDSP_L, float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_F, float *__vDSP_P, int __vDSP_IFLG, int *__vDSP_IERR );
Parameters
- L
Input filter length
- A
Single-precision real input vector: coefficients
- C
Single-precision real input vector: input coefficients
- F
Single-precision real output vector: filter coefficients
- P
Single-precision real output vector: error prediction operators
- IFLG
Not currently used, pass zero
- IERR
Error flag
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
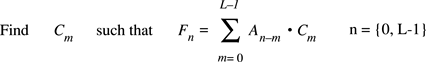
solves a set of single-channel normal equations described by:
B[n] = C[0] * A[n] + C[1] * A[n-1] +, . . . ,+ C[N-1] * A[n-N+1] |
for n = {0, N-1} |
where matrix A contains elements of the symmetric Toeplitz matrix shown below. This function can only be done out of place.
Note that A[-n] is considered to be equal to A[n].
vDSP_wiener solves this set of simultaneous equations using a recursive method described by Levinson. See Robinson, E.A., Multichannel Time Series Analysis with Digital Computer Programs. San Francisco: Holden-Day, 1967, pp. 43-46.
|A[0] A[1] A[2] ... A[N-1] | |C[0] | |B[0] | |
|A[1] A[0] A[1] ... A[N-2] | |C[1] | |B[1] | |
|A[2] A[1] A[0] ... A[N-3] | * |C[2] | = |B[2] | |
| ... ... ... ... ... | | ... | | ... | |
|A[N-1]A[N-2]A[N-3] ... A[0] | |C[N-1]| |B[N-1]| |
Typical methods for solving N equations in N unknowns have execution times proportional to N3, and memory requirements proportional to N2. By taking advantage of duplicate elements, the recursion method executes in a time proportional to N2 and requires memory proportional to N. The Wiener-Levinson algorithm recursively builds a solution by computing the m+1 matrix solution from the m matrix solution.
With successful completion,vDSP_wiener returns zero in error flag IERR. If vDSP_wiener fails, IERR indicates in which pass the failure occurred.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_wienerD
Wiener-Levinson general convolution; double precision.
void vDSP_wienerD ( vDSP_Length __vDSP_L, double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_F, double *__vDSP_P, int __vDSP_IFLG, int *__vDSP_IERR );
Parameters
- L
Input filter length
- A
Double-precision real input vector: coefficients
- C
Double-precision real input vector: input coefficients
- F
Double-precision real output vector: filter coefficients
- P
Double-precision real output vector: error prediction operators
- IFLG
Not currently used, pass zero
- IERR
Error flag
Discussion
Performs the following operation:
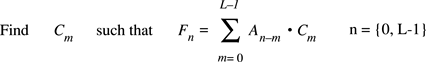
solves a set of single-channel normal equations described by:
B[n] = C[0] * A[n] + C[1] * A[n-1] +, . . . ,+ C[N-1] * A[n-N+1] |
for n = {0, N-1} |
where matrix A contains elements of the symmetric Toeplitz matrix shown below. This function can only be done out of place.
Note that A[-n] is considered to be equal to A[n].
vDSP_wiener solves this set of simultaneous equations using a recursive method described by Levinson. See Robinson, E.A., Multichannel Time Series Analysis with Digital Computer Programs. San Francisco: Holden-Day, 1967, pp. 43-46.
|A[0] A[1] A[2] ... A[N-1] | |C[0] | |B[0] | |
|A[1] A[0] A[1] ... A[N-2] | |C[1] | |B[1] | |
|A[2] A[1] A[0] ... A[N-3] | * |C[2] | = |B[2] | |
| ... ... ... ... ... | | ... | | ... | |
|A[N-1]A[N-2]A[N-3] ... A[0] | |C[N-1]| |B[N-1]| |
Typical methods for solving N equations in N unknowns have execution times proportional to N3, and memory requirements proportional to N2. By taking advantage of duplicate elements, the recursion method executes in a time proportional to N2 and requires memory proportional to N. The Wiener-Levinson algorithm recursively builds a solution by computing the m+1 matrix solution from the m matrix solution.
With successful completion,vDSP_wiener returns zero in error flag IERR. If vDSP_wiener fails, IERR indicates in which pass the failure occurred.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zaspec
Computes an accumulating autospectrum; single precision.
void vDSP_zaspec ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- C
Input-output vector
- N
Real output count
Discussion
vDSP_zaspec multiplies single-precision complex vector A by its complex conjugates, yielding the sums of the squares of the complex and real parts: (x + iy) (x - iy) = (x*x + y*y). The results are added to real single-precision input-output vector C. Vector C must contain valid data from previous processing or should be initialized according to your needs before calling vDSP_zaspec.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zaspecD
Computes an accumulating autospectrum; double precision.
void vDSP_zaspecD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *A, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- C
Input-output vector
- N
Real output count
Discussion
vDSP_zaspecD multiplies double-precision complex vector A by its complex conjugates, yielding the sums of the squares of the complex and real parts: (x + iy) (x - iy) = (x*x + y*y). The results are added to real double-precision input-output vector C. Vector C must contain valid data from previous processing or should be initialized according to your needs before calling vDSP_zaspec.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zcoher
Coherence function of two signals; single precision.
void vDSP_zcoher ( float *__vDSP_A, float *__vDSP_B, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, float *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Discussion
Computes the single-precision coherence function D of two signals. The inputs are the signals' autospectra, real single-precision vectors A and B, and their cross-spectrum, single-precision complex vector C.

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zcoherD
Coherence function of two signals; double precision.
void vDSP_zcoherD ( double *__vDSP_A, double *__vDSP_B, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, double *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Discussion
Computes the double-precision coherence function D of two signals. The inputs are the signals' autospectra, real double-precision vectors A and B, and their cross-spectrum, double-precision complex vector C.

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zconv
Performs either correlation or convolution on two complex vectors; single precision.
void vDSP_zconv ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_filter, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideFilter, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenFilter );
Discussion
A is the input vector, with stride I, and C is the output vector, with stride K and length N.
B is a filter vector, with stride I and length P. If Jis positive,the function performs correlation. If Jis negative, it performs convolution and Bmust point to the last element in the filter vector. The function can run in place, but Ccannot be in place with B.

The value of N must be less than or equal to 512.
Criteria to invoke vectorized code:
Both the real parts and the imaginary parts of vectors
AandCmust be relatively aligned.The values of
IandKmust be 1.
If any of these criteria is not satisfied, the function invokes scalar code.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zconvD
Performs either correlation or convolution on two complex vectors; double precision.
void vDSP_zconvD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_signal, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_signalStride, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_filter, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideFilter, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_lenFilter );
Discussion
A is the input vector, with stride I, and C is the output vector, with stride K and length N.
B is a filter vector, with stride I and length P. If J is positive, the function performs correlation. If J is negative, it performs convolution and B must point to the last element in the filter vector. The function can run in place, but C cannot be in place with B.

The value of N must be less than or equal to 512.
Criteria to invoke vectorized code:
No Altivec support for double precision. On a PowerPC processor, this function always invokes scalar code.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zcspec
Accumulating cross-spectrum on two complex vectors; single precision.
void vDSP_zcspec ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- B
Single-precision complex input vector
- C
Single-precision complex input-output vector
- N
Count
Discussion
Computes the cross-spectrum of complex vectors A and B and then adds the results to complex input-output vector C. Vector C should contain valid data from previous processing or should be initialized with zeros before callingvDSP_zcspec.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zcspecD
Accumulating cross-spectrum on two complex vectors; double precision.
void vDSP_zcspecD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *A, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- B
Double-precision complex input vector
- C
Double-precision complex input-output vector
- N
Count
Discussion
Computes the cross-spectrum of complex vectors A and B and then adds the results to complex input-output vector C. Vector C should contain valid data from previous processing or should be initialized with zeros before calling vDSP_zcspecD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zdotpr
Calculates the complex dot product of complex vectors A and B and leaves the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zdotpr ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
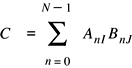
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zdotprD
Calculates the complex dot product of complex vectors A and B and leaves the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zdotprD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
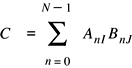
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zidotpr
Calculates the conjugate dot product (or inner dot product) of complex vectors A and B and leave the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zidotpr ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zidotprD
Calculates the conjugate dot product (or inner dot product) of complex vectors A and B and leave the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zidotprD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmma
Multiplies two complex matrices, then adds a third complex matrix; out-of-place; single precision.
void vDSP_zmma ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_d, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_l, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B, adds the product to M-by-N matrix C, and stores the result in M-by-N matrix D; single precision.
This performs the following operation:

Parameters A and C are the matrixes to be multiplied, and C the matrix to be added. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B. K is an address stride through C. L is an address stride through D.
Parameter D is the result matrix.
Parameter M is the row count for A, C and D. Parameter N is the column count of B, C, and D. Parameter P is the column count of A and the row count of B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmmaD
Multiplies two complex matrices, then adds a third complex matrix; out-of-place; double precision.
void vDSP_zmmaD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_d, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_l, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B, adds the product to M-by-N matrix C, and stores the result in M-by-N matrix D; double precision.
This performs the following operation:

Parameters A and C are the matrixes to be multiplied, and C the matrix to be added. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B. K is an address stride through C. L is an address stride through D.
Parameter D is the result matrix.
Parameter M is the row count for A, C and D. Parameter N is the column count of B, C, and D. Parameter P is the column count of A and the row count of B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmms
Multiplies two complex matrices, then subtracts a third complex matrix; out-of-place; single precision.
void vDSP_zmms ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_d, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_l, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B , subtracts M-by-N matrix C from the product, and stores the result in M-by-N matrix D.
This performs the following operation:
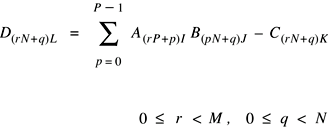
Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied, and C the matrix to be subtracted. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B. K is an address stride through C. L is an address stride through D.
Parameter D is the result matrix.
Parameter M is the row count for A, C and D. Parameter N is the column count of B, C, and D. Parameter P is the column count of A and the row count of B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmmsD
Multiplies two complex matrices, then subtracts a third complex matrix; out-of-place; double precision.
void vDSP_zmmsD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_d, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_l, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B, subtracts M-by-N matrix C from the product, and stores the result in M-by-N matrix D.
This performs the following operation:
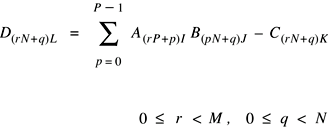
Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied, and C the matrix to be subtracted. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B. K is an address stride through C. L is an address stride through D.
Parameter D is the result matrix.
Parameter M is the row count for A, C and D. Parameter N is the column count of B, C, and D. Parameter P is the column count of A and the row count of B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmmul
Multiplies two matrices of complex numbers; out-of-place; single precision.
void vDSP_zmmul ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B and stores the results in an M-by-N matrix C.
This performs the following operation:
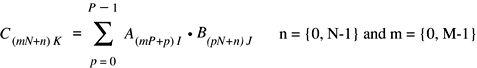
Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B.
Parameter C is the result matrix. K is an address stride through C.
Parameter M is the row count for both A and C. Parameter N is the column count for both B and C. Parameter P is the column count for A and the row count for B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmmulD
Multiplies two matrices of complex numbers; out-of-place; double precision.
void vDSP_zmmulD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B and stores the results in an M-by-N matrix C.
This performs the following operation:
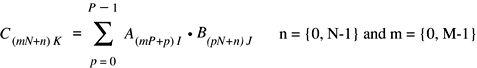
Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied. I is an address stride through A. J is an address stride through B.
Parameter C is the result matrix. K is an address stride through C.
Parameter M is the row count for both A and C. Parameter N is the column count for both B and C. Parameter P is the column count for A and the row count for B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmsm
Subtracts the product of two complex matrices from a third complex matrix; out-of-place; single precision.
void vDSP_zmsm ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_d, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_l, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B, subtracts the product from M-by-P matrix C, and stores the result in M-by-P matrix D.
This performs the following operation:

Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied, and C is the matrix from which the product is to be subtracted. aStride is an address stride through A. bStride is an address stride through B. cStride is an address stride through C. dStride is an address stride through D.
Parameter D is the result matrix.
Parameter M is the row count for A, C and D. Parameter N is the column count of B, C, and D. Parameter P is the column count of A and the row count of B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zmsmD
Subtracts the product of two complex matrices from a third complex matrix; out-of-place; double precision.
void vDSP_zmsmD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_a, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_i, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_b, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_j, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_c, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_k, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_d, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_l, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_P );
Discussion
This function performs an out-of-place complex multiplication of an M-by-P matrix A by a P-by-N matrix B, subtracts the product from M-by-P matrix C, and stores the result in M-by-P matrix D.
This performs the following operation:

Parameters A and B are the matrixes to be multiplied, and parameter C is the matrix from which the product is to be subtracted. aStride is an address stride through A. bStride is an address stride through B. cStride is an address stride through C. dStride is an address stride through D.
Parameter D is the result matrix.
Parameter M is the row count for A, C and D. Parameter N is the column count of B, C, and D. Parameter P is the column count of A and the row count of B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrdesamp
Complex/real downsample with anti-aliasing; single precision.
void vDSP_zrdesamp ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector.
- I
Complex decimation factor.
- B
Filter coefficient vector.
- C
Single-precision complex output vector.
- N
Length of output vector.
- M
Length of real filter vector.
Discussion
Performs finite impulse response (FIR) filtering at selected positions of input vector A.
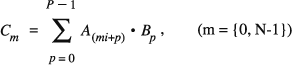
Length of A must be at least (N+M-1)*i. This function can run in place, but C cannot be in place with B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrdesampD
Complex/real downsample with anti-aliasing; double precision.
void vDSP_zrdesampD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N, vDSP_Length __vDSP_M );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector.
- I
Complex decimation factor.
- B
Filter coefficient vector.
- C
Double-precision complex output vector.
- N
Length of output vector.
- M
Length of real filter vector.
Discussion
Performs finite impulse response (FIR) filtering at selected positions of input vector A.
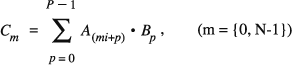
Length of A must be at least (N+M-1)*i. This function can run in place, but C cannot be in place with B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrdotpr
Calculates the complex dot product of complex vector A and real vector B and leaves the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zrdotpr ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrdotprD
Calculates the complex dot product of complex vector A and real vector B and leaves the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zrdotprD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvadd
Adds real vector B to complex vector A and leaves the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zrvadd ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvaddD
Adds real vector B to complex vector A and leaves the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zrvaddD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for A
- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for B
- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for C
- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvdiv
Divides complex vector A by real vector B and leaves the result in vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zrvdiv ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvdivD
Divides complex vector A by real vector B and leaves the result in vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zrvdivD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:

Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvmul
Multiplies complex vector A by real vector B and leaves the result in vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zrvmul ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvmulD
Multiplies complex vector A by real vector B and leaves the result in vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zrvmulD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvsub
Subtracts real vector B from complex vector A and leaves the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zrvsub ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const float __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zrvsubD
Subtracts real vector B from complex vector A and leaves the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zrvsubD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const double __vDSP_input2[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_ztoc
Copies the contents of a split complex vector A to an interleaved complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_ztoc ( const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_Z, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideZ, DSPComplex __vDSP_C[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation;
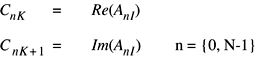
The strideC parameter contains an address stride through C. strideZ is an address stride through Z.
For best performance, C->realp, C->imagp, A->realp, and A->imagp should be 16-byte aligned.
See also vDSP_ctoz and vDSP_ctozD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_ztocD
Copies the contents of a split complex vector A to an interleaved complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_ztocD ( const DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_Z, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideZ, DSPDoubleComplex __vDSP_C[], vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideC, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
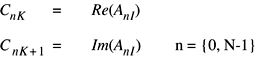
The strideC parameter contains an address stride through C. strideZ is an address stride through Z.
For best performance, C->realp, C->imagp, A->realp, and A->imagp should be 16-byte aligned.
See also vDSP_ctoz and vDSP_ctozD.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_ztrans
Transfer function; single precision.
void vDSP_ztrans ( float *__vDSP_A, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision real input vector
- B
Single-precision complex input vector
- C
Single-precision complex output vector
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
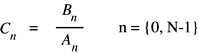
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_ztransD
Transfer function; double precision.
void vDSP_ztransD ( double *__vDSP_A, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision real input vector
- B
Double-precision complex input vector
- C
Double-precision complex output vector
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
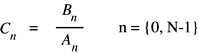
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvabs
Complex vector absolute values; single precision.
void vDSP_zvabs ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for C
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvabsD
Complex vector absolute values; double precision.
void vDSP_zvabsD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for C
- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvadd
Adds complex vectors A and B and leaves the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zvadd ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex output count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvaddD
Adds complex vectors A and B and leaves the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zvaddD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvcma
Multiplies complex vector B by the complex conjugates of complex vector A, adds the products to complex vector C, and stores the results in complex vector D; single precision.
void vDSP_zvcma ( const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input3, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride3, const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvcmaD
Multiplies complex vector B by the complex conjugates of complex vector A, adds the products to complex vector C, and stores the results in complex vector D; double precision.
void vDSP_zvcmaD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input3, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride3, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvcmul
Complex vector conjugate and multiply; single precision.
void vDSP_zvcmul ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision complex input vector
- J
Stride for
B- B
Single-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
B- N
Count
Discussion
Multiplies vector B by the complex conjugates of vector A and stores the results in vector B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvcmulD
Complex vector conjugate and multiply; double precision.
void vDSP_zvcmulD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision complex input vector
- J
Stride for
B- B
Double-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
B- N
Count
Discussion
Multiplies vector B by the complex conjugates of vector A and stores the results in vector B.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvconj
Complex vector conjugate; single precision.
void vDSP_zvconj ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Conjugates vector A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvconjD
Complex vector conjugate; double precision.
void vDSP_zvconjD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Conjugates vector A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvdiv
Complex vector divide; single precision.
void vDSP_zvdiv ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision complex input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Divides vector B by vector A.
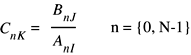
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvdivD
Complex vector divide; double precision.
void vDSP_zvdivD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision complex input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Divides vector B by vector A.
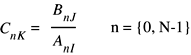
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvfill
Complex vector fill; single precision.
void vDSP_zvfill ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input scalar
- C
Single-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Sets each element in complex vector C to complex scalar A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvfillD
Complex vector fill; double precision.
void vDSP_zvfillD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input scalar
- C
Double-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Sets each element in complex vector C to complex scalar A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmags
Complex vector magnitudes squared; single precision.
void vDSP_zvmags ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Calculates the squared magnitudes of complex vector A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmagsD
Complex vector magnitudes squared; double precision.
void vDSP_zvmagsD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Calculates the squared magnitudes of complex vector A.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmgsa
Complex vector magnitudes square and add; single precision.
void vDSP_zvmgsa ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Adds the squared magnitudes of complex vector A to real vector B and store the results in real vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmgsaD
Complex vector magnitudes square and add; double precision.
void vDSP_zvmgsaD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_B, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_J, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision real input vector
- J
Stride for
B- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Adds the squared magnitudes of complex vector A to real vector B and store the results in real vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmov
Complex vector copy; single precision.
void vDSP_zvmov ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Copies complex vector A to complex vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmovD
Complex vector copy; double precision.
void vDSP_zvmovD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Copies complex vector A to complex vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmul
Multiplies complex vectors A and B and leaves the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zvmul ( const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, const DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size, int __vDSP_conjugate );
Discussion
Pass 1 or -1 for F, for normal or conjugate multiplication, respectively. Results are undefined for other values of F.
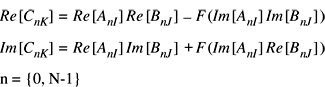
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvmulD
Multiplies complex vectors A and B and leaves the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zvmulD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size, int __vDSP_conjugate );
Discussion
Pass 1 or -1 for F, for normal or conjugate multiplication, respectively. Results are undefined for other values of F.
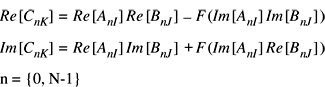
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvneg
Complex vector negate; single precision.
void vDSP_zvneg ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Computes the negatives of the values of complex vector A and puts them into complex vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvnegD
Complex vector negate; double precision.
void vDSP_zvnegD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Computes the negatives of the values of complex vector A and puts them into complex vector C.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvphas
Complex vector phase; single precision.
void vDSP_zvphas ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, float *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Single-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Finds the phase values, in radians, of complex vector A and store the results in real vector C. The results are between -pi and +pi. The sign of the result is the sign of the second coordinate in the input vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvphasD
Complex vector phase; double precision.
void vDSP_zvphasD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, double *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- C
Double-precision real output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Finds the phase values, in radians, of complex vector A and store the results in real vector C. The results are between -pi and +pi. The sign of the result is the sign of the second coordinate in the input vector.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvsma
Complex vector scalar multiply and add; single precision.
void vDSP_zvsma ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision complex input scalar
- C
Single-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Single-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and add the products to vector C. The result is stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvsmaD
Complex vector scalar multiply and add; double precision.
void vDSP_zvsmaD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_D, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_L, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision complex input scalar
- C
Double-precision real input vector
- K
Stride for
C- D
Double-precision real output vector
- L
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
Multiplies vector A by scalar B and add the products to vector C. The result is stored in vector D.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvsub
Subtracts complex vector B from complex vector A and leaves the result in complex vector C; single precision.
void vDSP_zvsub ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex element count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvsubD
Subtracts complex vector B from complex vector A and leaves the result in complex vector C; double precision.
void vDSP_zvsubD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input1, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride1, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_input2, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_stride2, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_result, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_strideResult, vDSP_Length __vDSP_size );
Parameters
- A
Input vector
- I
Address stride for
A- B
Input vector
- J
Address stride for
B- C
Output vector
- K
Address stride for
C- N
Complex element count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvzsml
Complex vector multiply by complex scalar; single precision.
void vDSP_zvzsml ( DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Single-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Single-precision complex input scalar
- C
Single-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_zvzsmlD
Complex vector multiply by complex scalar; double precision.
void vDSP_zvzsmlD ( DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_A, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_I, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_B, DSPDoubleSplitComplex *__vDSP_C, vDSP_Stride __vDSP_K, vDSP_Length __vDSP_N );
Parameters
- A
Double-precision complex input vector
- I
Stride for
A- B
Double-precision complex input scalar
- C
Double-precision complex output vector
- K
Stride for
C- N
Count
Discussion
This performs the following operation:
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hData Types
This document describes the data types used by the vDSP portion of the Accelerate framework.
vDSP_Length
Used for numbers of elements in arrays and indices of elements in arrays. It is also used for the base-two logarithm of numbers of elements.
typedef unsigned long vDSP_Length;
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hvDSP_Stride
Used to hold differences between indices of elements, including the lengths of strides.
typedef long vDSP_Stride;
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hDSPComplex
Used to hold a complex value.
struct DSPComplex {
float real;
float imag;
};
typedef struct DSPComplex DSPComplex;
Discussion
Complex data are stored as ordered pairs of floating-point numbers. Because they are stored as ordered pairs, complex vectors require address strides that are multiples of two.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hDSPSplitComplex
Used to represent a complex number when the real and imaginary parts are stored in separate arrays.
struct DSPSplitComplex {
float *realp;
float *imagp;
};
typedef struct DSPSplitComplex DSPSplitComplex;
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hDSPDoubleComplex
Used to hold a double-precision complex value.
struct DSPDoubleComplex {
double real;
double imag;
};
typedef struct DSPDoubleComplex DSPDoubleComplex;
Discussion
Double complex data are stored as ordered pairs of doiuble-precision floating-point numbers. Because they are stored as ordered pairs, complex vectors require address strides that are multiples of two.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hDSPDoubleSplitComplex
Used to represent a double-precision complex number when the real and imaginary parts are stored in separate arrays.
struct DSPDoubleSplitComplex {
double *realp;
double *imagp;
};
typedef struct DSPDoubleSplitComplex DSPDoubleSplitComplex;
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hFFTSetup
An opaque type that contains setup information for a given FFT transform.
typedef struct OpaqueFFTSetup* FFTSetup;
Discussion
A setup object can be allocated with vDSP_create_fftsetup and destroyed with vDSP_destroy_fftsetup. The setup object includes, among other things, precomputed tables used in computing an FFT of the specified size.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hFFTSetupD
An opaque type that contains setup information for a given double-precision FFT transform.
typedef struct OpaqueFFTSetupD* FFTSetupD;
Discussion
A setup object can be allocated with vDSP_create_fftsetupD and destroyed with vDSP_destroy_fftsetupD. The setup object includes, among other things, precomputed tables used in computing an FFT of the specified size.
Availability
- Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared In
vDSP.hConstants
vDSP Compile-Time Version Information
The version of vDSP (at compile time).
#define vDSP_Version0 268 #define vDSP_Version1 0
Constants
vDSP_Version0The vDSP major version.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.vDSP_Version1The vDSP minor version.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.
vDSP_DFT_Direction
Specifies whether to perform a forward or inverse DFT.
typedef enum {
vDSP_DFT_FORWARD = +1,
vDSP_DFT_INVERSE = -1
} vDSP_DFT_Direction;
Constants
vDSP_DFT_FORWARDSpecifies a forward transform.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.vDSP_DFT_INVERSESpecifies an inverse transform.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.
FFTDirection
Specifies whether to perform a forward or inverse FFT.
enum {
kFFTDirection_Forward = 1,
kFFTDirection_Inverse = -1
};
typedef int FFTDirection;
Constants
kFFTDirection_ForwardSpecifies a forward transform.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.kFFTDirection_InverseSpecifies an inverse transform.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.
FFTRadix
The size of the FFT decomposition.
enum {
kFFTRadix2 = 0,
kFFTRadix3 = 1,
kFFTRadix5 = 2
};
typedef int FFTRadix;
Constants
kFFTRadix2Specifies a radix of 2.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.kFFTRadix3Specifies a radix of 3.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.kFFTRadix5Specifies a radix of 5.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.
Discussion
An FFTRadix value is passed as an argument to vDSP_create_fftsetup or vDSP_create_fftsetupD.
FFTWindow
Specifies the windowing mode for data values in an FFT or reverse FFT.
enum {
vDSP_HALF_WINDOW = 1,
vDSP_HANN_DENORM = 0,
vDSP_HANN_NORM = 2
};
Constants
vDSP_HALF_WINDOWSpecifies that the window should only contain the bottom half of the values (
0to(N+1)/2).Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.vDSP_HANN_DENORMSpecifies a denormalized Hann window.
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.vDSP_HANN_NORMSpecifies a normalized Hann window
Available in iOS 4.0 and later.
Declared in
vDSP.h.
Discussion
Passed as a flag to vDSP_blkman_window or vDSP_blkman_windowD to specify the desired type of window..
Last updated: 2010-03-25