
T3.0 contains generalized hash tables. A table associates a key with a value. make-hash-table is the most general way to make a hash table. In addition, the most common types of tables have been predefined.

(make-hash-tabletype? hash comparator gc? id) procedure
 table
table
make-hash-table creates a table which associates keys to values. Any object may be a key or a value.
(hash-table?object) predicate
 boolean
boolean
hash-table returns true if the object is a hash table.
(table-entrytable key) settable
 object
object
table-entry returns the object associated with the key in the table if there is an entry for key, otherwise returns false.
(walk-tableproc table) procedure
 undefined
undefined
walk-table invokes procedure, a procedure of two arguments, on each key, value association in the table. Note that it is an error to perform any operations on the table while walking it.
The following common table types have been predefined as follows:
(make-table. id) procedure
 table
table
make-table creates a table in which any object can be a key and eqv? is used as the equality predicate on keys.
(table?object) procedure
 boolean
boolean
table? returns true if the object is an eq? table.
(make-string-table. id) procedure
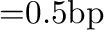 table
table
make-string-table creates a table in which the keys must be strings and string-equal? is used as the equality predicate on keys.
(string-table?object) procedure
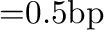 boolean
boolean
string-table? returns true if the object is a string-table.
(make-symbol-table. id) procedure
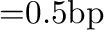 symbol-table
symbol-table
make-symbol-table creates a table in which the keys must be symbols and eq? is used as the equality predicate on keys.
(symbol-table?object) procedure
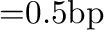 boolean
boolean
symbol-table? returns true if the object is a symbol-table.