|
Local Info |
ε≥εß≡αµασ≥ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ε ┬α°σ∞ Ωε∞∩ⁿ■≥σ≡σ: ∩≡ε÷σ±ε≡, ∩α∞ ≥ⁿ, WinSock, ∞εΣσ∞√, ±σ≥σΓ√σ Φφ≥σ≡⌠σΘ±√, ≥αßδΦ÷α ∞α≡°≡≤≥Φτα÷ΦΦ Φ ≥.Σ.
╚φ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ∞εµφε τα∩Φ±α≥ⁿ Γ ≥σΩ±≥εΓ√Θ ΦδΦ HTML ⌠αΘδ, Γ±■ ΦδΦ ∩ε ≈α±≥ ∞.
╧≡Φ∞σ≡.
|
|
Connections |
²≥α ≤≥ΦδΦ≥α Γ√Σασ≥ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ε ≥ε∞ ΩαΩΦσ ∩ε≡≥√ ±δ≤°ασ≥ Γα°α ∞α°Φφα Φ ± Ωσ∞ εφα ±εσΣσφΦφα.
╧εΣ Windows XP Σδ ΩαµΣεπε ∩ε≡≥α IP-Tools ∩εΩατ√Γασ≥ ∩≡ε÷σ±± Ωε≥ε≡√Θ Φ±∩εδⁿτ≤σ≥ ∩ε≡≥.
Refresh Σσδασ≥± ΩαµΣ√Θ ≡ατ ∩≡Φ ∩σ≡σΩδ■≈σφΦΦ φα ²≥≤ ±≥≡αφΦ÷≤ ΦδΦ ∩≡Φ Γ√ßε≡σ
∩≤φΩ≥α "Refresh" δεΩαδⁿφεπε ∞σφ■ (Γ√τ√Γασ≥± ∩≡αΓεΘ Ωφε∩ΩεΘ ∞√°Φ).
═α≈Φφα ± Γσ≡±ΦΦ 1.07 σ±≥ⁿ Φ AutoRefresh, α ± Γσ≡±ΦΦ 1.09 IP-Tools ∞εµσ≥
τα∩Φ±√Γα≥ⁿ Γ Log File Γ±σ Φτ∞σφσφΦ Γ ±≥α≥≤±α⌡ ∩ε≡≥εΓ, ∞εµσ≥σ ε±≥αΓΦ≥ⁿ φα φε≈ⁿ Φ ≤≥≡ε∞ ∩ε±∞ε≥≡σ≥ⁿ
≈σ∞ ²≥ε ∩ε φε≈α∞ ταφΦ∞ασ≥± Γα°α ∞α°Φφα Φ ± Ωσ∞ εφα Φτ∞σφ σ≥ ┬α∞.
╩≡ε∞σ ≥επε ┬√ ∞εµσ≥σ Γ√±≥αΓΦ≥ⁿ ⌠Φδⁿ≥≡ ∩ε ≥Φ∩≤ ∩ε≡≥εΓ, ∩ε ±≥α≥≤±≤ ∩ε≡≥εΓ, ∩ε IP αΣ≡σ±α∞.
═α±≥≡εΘΩΦ ≤≥ΦδΦ≥√ φα⌡εΣ ≥± Γ ΣΦαδεπσ "Options" φα ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ "Connections".
╠εµσ≥ ∩ε∞ε≈ⁿ Σδ εßφα≡≤µσφΦ ≥≡ε φεΓ ≥Φ∩α backdoor.
┬ετ∞εµφ√σ τφα≈σφΦ ±≥α≥≤±εΓ TCP ∩ε≡≥εΓ :
| CLOSED | ∩ε≡≥ ταΩ≡√≥ Φ φΦΩαΩ φσ Φ±∩εδⁿτ≤σ≥± . |
| LISTENING | ∩ε≡≥ ε≥Ω≡√≥ Φ µΣσ≥ Γ⌡εΣ ∙Φσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ . |
| SYN_SENT | ∩ε±δαδΦ τα∩≡ε± φα φα ≤±≥αφεΓδσφΦσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ , εµΦΣαφΦσ ∩α≡φεπε τα∩≡ε±α. |
| SYN_RECEIVED | εµΦΣαφΦσ ∩εΣ≥Γσ≡µΣσφΦ ∩ε±δσ ≥επε, ΩαΩ τα∩≡ε± ±εσΣΦφσφΦ ≤µσ ∩≡Φφ ≥ Φ ε≥∩≡αΓδσφ. |
| ESTABLISHED | ±εσΣΦφσφΦσ ≤±≥αφεΓδσφε. |
| CLOSE_WAIT | εµΦΣαφΦσ τα∩≡ε±α φα ταΩ≡√≥Φσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ ±ε ±≥ε≡εφ√ ±Γεσπε ΩδΦσφ≥α. |
| FIN_WAIT_1 | εµΦΣαφΦσ τα∩≡ε±α ε≥ ≈≤µεΘ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞√ TCP, ΦδΦ ∩εΣ≥Γσ≡µΣσφΦ ≡αφσσ ε≥∩≡αΓδσφφεπε τα∩≡ε±α φα ταΩ≡√≥Φσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ . |
| CLOSING | εµΦΣαφΦσ ∩εΣ≥Γσ≡µΣσφΦ ±ε ±≥ε≡εφ√ ≈≤µεΘ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞√ TCP τα∩≡ε±α ε ταΩ≡√≥ΦΦ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ . |
| LAST_ACK | εµΦΣαφΦσ τα∩≡ε±α φα ταΩ≡√≥Φσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ , ≡αφσσ
ε≥∩≡αΓδσφφεπε ≈≤µεΘ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞σ TCP (τα∩≡ε± ΓΩδ■≈αδ ≥αΩµσ ∩εΣ≥Γσ≡µΣσφΦσ ∩εδ≤≈σφΦ ≈≤µεπε τα∩≡ε±α φα ταΩ≡√≥Φσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ ). |
| FIN_WAIT_2 | εµΦΣαφΦσ τα∩≡ε±α φα ταΩ≡√≥Φσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ ±ε ±≥ε≡εφ√ ≈≤µεΘ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞√ TCP. |
| TIME_WAIT | εµΦΣαφΦσ ΩεπΣα Φ±≥σ≈σ≥ Σε±≥α≥ε≈φεσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε Γ≡σ∞σφΦ
Φ ∞εµφε ß√≥ⁿ ≤Γσ≡σφφ√∞, ≈≥ε ≈≤µα ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α TCP ∩εδ≤≈Φδα ∩εΣ≥Γσ≡µΣσφΦσ ±Γεσπε τα∩≡ε±α φα ταΩ≡√≥Φσ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ . |
|
|
NetBIOS |
∞εµφε ≤ΓΦΣσ≥ⁿ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ε ±ΓεΦ⌡ ±σ≥σΓ√⌡ Φφ≥σ≡⌠σΘ±α⌡, α
ταΣαΓ Φ∞ ∞α°Φφ√ (≥Φ∩α "123.23.21.12" ΦδΦ "www.uc.ru" ΦδΦ σ±δΦ ²≥ε ∞α°Φφα
Γ δεΩαδΩσ "vova_computer" ΦδΦ '*' Σδ ±ΓεσΘ ∞α°Φφ√) Φ
ΣΦα∩ατεφ φε∞σ≡εΓ Φφ≥σ≡⌠σΘ±εΓ (φα∩≡Φ∞σ≡ 0-9) ∞εµφε ∩εδ≤≈Φ≥ⁿ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■
±σ≥σΓ√⌡ Φφ≥σ≡⌠σΘ±α⌡ ≤ΣαδσφφεΘ ∞α°Φφ√ : MAC αΣ≡σ±, ≥αßδΦ÷≤ Φ∞σφ Φ ≥.Σ.
╨αßε≥ασ≥ σ±δΦ ≥σ±≥Φ≡≤σ∞α ±Φ±≥σ∞α ∩εΣΣσ≡µΦΓασ≥ NetBIOS ∩≡ε≥εΩεδ
|
|
NB Scanner |
∞εµφε ∩≡ε±ΩαφΦ≡εΓα≥ⁿ τα°α≡σφφ√σ ±σ≥σΓ√σ ≡σ±≤≡±√ ∞α°Φφ Φτ ταΣαφφεπε
ΣΦα∩ατεφα ΦδΦ ∩ε ταΣαφφε∞≤ ±∩Φ±Ω≤ αΣ≡σ±εΓ.
╨στ≤δⁿ≥α≥ ±ΩαφΦ≡εΓαφΦ ∞εµφε τα∩Φ±α≥ⁿ ∩≡Φ∞σ≡φε Γ ≥αΩ≤■ ≥αßδΦ≈Ω≤
(∩≤φΩ≥ "Save as HTML.." δεΩαδⁿφεπε ∞σφ■).
═α±≥≡εΘΩΦ ±Ωαφσ≡α Γ ΣΦαδεπσ "Options" φα ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ
"NB Scanner".
|
|
SNMP Scanner |
The Simple Network Management Protocol is the Internet standard protocol for exchanging management information
between management console applications and managed entities (hosts, routers, bridges, hubs).
SNMP Scanner allows you to scan a range or list of hosts performing Ping,
DNS and SNMP queries. For each SNMP responding device scanner displays following information:
| | Host | IP address and optionally name of the host. |
| | Status | Status of the probe. If IP-Tools was able to retrieve necessary information
from the host, this field shows reply time for SNMP request. Otherwise it will display error message briefly
describing the reason of request failure. |
| | System ID | Enterprise OID or type of the system (E.g. "Windows Workstation", "Windows Domain Controler" or "1.3.6.1.3.9999"). |
| | System description | Description of the system (this field may contain information about hardware and software running on the host). |
| | UpTime | Represents the time interval since last initialization (boot, start-up) of the host. |
| | Router | Shows "Yes" if host is a router (device that forwards IP packets). Otherwise shows "No". |
| | Interfaces | Number of network interfaces on the host. |
| | TCP Curr/Max | Shows current number of established TCP connections and maximum number of TCP connections the host can support. |
| | Community | Community string that has been used to communicate
with the host (you may setup a list of strings that will be used for communication with hosts; see
Community strings option). |
Optionally you may setup IP-Tools so that it will retrieve additional information, utility can request the value
of any counter(s) supported by SNMP agent. See "Request additional information"
option.
Of course scanner is multithreaded; it can check multiple hosts simultaneously. As usually, information obtained
by scanner could be saved into plain text file or as HTML report (use "Save as Text" or "Save as HTML" menu items).
All settings for this utility are located on "SNMP Scanner page in the
Options dialog.
|
|
Name Scanner |
±ΩαφΦ≡εΓαφΦσ ⌡ε≥ⁿ Γ±σπε Φφ≥σ≡φσ≥α τα ≡ατ Φτ∩εδⁿτ≤ GetHostByName (Γ√Σασ≥ Φ∞ ∞α°Φφ Φτ DNS)
∩ε ΣΦα∩ατεφ≤ αΣ≡σ±εΓ (φα∩≡Φ∞σ≡ 1.1.1.1 - 255.255.255.255) ΦδΦ ∩ε ±∩Φ±Ω≤
αΣ≡σ±εΓ. ╤∩Φ±εΩ αΣ≡σ±εΓ ε∩σ≡σΣσδ σ≥± Γ ΣΦαδεπσ "Options"
φα ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ "ScanList".
|
|
Port Scanner |
±ΩαφΦ≡εΓαφΦσ TCP ∩ε≡≥εΓ ⌡ε≥ⁿ Γ±σπε Φφ≥σ≡φσ≥α τα ≡ατ
∩ε ΣΦα∩ατεφ≤ αΣ≡σ±εΓ (φα∩≡Φ∞σ≡ 1.1.1.1 - 255.255.255.255)
ΦδΦ ∩ε ±∩Φ±Ω≤ αΣ≡σ±εΓ. ╧≡σµΣσ ≈σ∞ ±ΩαφΦ≡εΓα≥ⁿ ∩ε≡≥√ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α ∞εµσ≥ ∩ε∩√≥α≥±
≤τφα≥ⁿ Φ∞ ∞α°Φφ√ Φ ∩≡ε∩ΦφπεΓα≥ⁿ σσ, Ω≡ε∞σ ≥επε ∩≡Φ ±ΩαφΦ≡εΓαφΦΦ ∩ε≡≥εΓ
IP-Tools ∞εµσ≥ ∩ε±√δα≥ⁿ ταΣαφφ≤■ ±≥≡εΩ≤ φα ±ΩαφΦ≡≤σ∞√Θ ∩ε≡≥ Φ ∩εΩατ√Γα≥ⁿ
ε≥Γσ≥ ε≥ ±σ≡Γσ≡α.
╤∩Φ±εΩ ∩ε≡≥εΓ ταΣασ≥± Γ Γ ΣΦαδεπεΓε∞ εΩφσ "Options"
φα ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ "Ports", α ∩α≡α∞σ≥≡√ ±α∞επε
±ΩαφΦ≡εΓαφΦ φα ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ "Port Scanner".
What is a port?
The TCP port number identifies a process or application inside the computer.
Any application or process that uses TCP for its transport is assigned a
unique identification number called a TCP port. These ports are numbered
beginning with zero. Port numbers for client applications are dynamically
assigned by the operating system when there is a request for service. Port
numbers for server applications are preassigned by the IANA
(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) and do not change.
A server application or process that uses TCP as a transport has at least
one preassigned port number. For example, the preassigned port numbers for
FTP server services are 20 (data) and 21 (control).
|
|
UDP Scanner |
The UDP Scanner utility provides you with the ability to scan UDP based services (such as TFTP, SNTP, Daytime,
DNS, etc) over a range or list of IP addresses.
Here is a list of the features of the UDP Scanner utility:
supports a range of addresses to scan such as "126.128.12.1 - 126.128.15.254";
supports a list of addresses to scan (for more information refer to the section ScanList);
can resolve the IP address of the hosts into a host name before scanning its ports;
can ping the host before scanning its ports;
can display response from the remote system services.
Unlike TCP, UDP is connectionless protocol. It means that you cannot use some standard method to establish
connection between yours and remote systems and you cannot use exactly the same algorithm to check different
UDP services.
Most of UDP scanners, those available in the Internet, attempt to identify opened UDP ports by sending a
bogus UDP packet and waiting for an ICMP message 'PORT UNREACHABLE'. If ICMP packet will not be received,
scanner assumes UDP port is in service. This method is simple but very unreliable:
| 1) | Not every OS sends an ICMP response to a client if there is an attempt to connect to a UDP port that has no application listening to on it. |
| 2) | Even if OS, in standard configuration, sends ICMP response, some antivirus/firewall software will change behavior of the system and will not send any response. |
| 3) | Even if remote system will send ICMP response, some routers and firewalls between yours and remote systems can drop this ICMP packet. |
That's why IP-Tools uses different way to check UDP services. For each UDP service you can specify data to
send and condition that describes what answer is correct reply from the service.
For example: to check TFTP service fill up parameters with following values:
- Port: 69
- Filter: any reply
- Packet to send: %00%01filename%00%00netascii%00
where filename is the name of the file on the server. We recommend to provide incorrect (fake) name of the file.
In this case server will not start file transfer and you will avoid unnecessary network traffic.
When you start utility IP-Tools will be sending UDP packets (using different data for different services) to each
host from the list and will display list of services the answers received from.
This allows:
| 1) | to check availability of the UDP services more reliable; |
| 2) | IP-Tools can display reply from the service (in text and hexadecimal modes) which is useful when you need to check whether service is working properly or not; |
| 3) | for different services you can apply different filter conditions. IP-Tools will check reply from the hosts and display only services which satisfy filter conditions. |
IP-Tools contains preconfigured list of the popular UDP services (Echo, Daytime, Chargen, Time, DNS, TFTP, NTP,
SNMP, etc). You can change parameters of the checks and add checks for other UDP services.
For more information about options of the UDP Scanner, see "Options
-> UDP Scanner" section of this documentation.
|
|
Ping Scanner |
Ping ≥εµσ ∞εµφα ±Σσδα≥ⁿ ∩ε ΣΦα∩ατεφ≤ αΣ≡σ±εΓ ΦδΦ ∩ε ±∩Φ±Ω≤ αΣ≡σ±εΓ.
═α±≥≡εΘΩΦ φα⌡εΣ ≥± Γ ΣΦαδεπεΓε∞ εΩφσ "Options"
φα ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ "Ping/Trace"
What is a Ping?
the ping command verifies connections to remote computer or computers, by
sending ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) echo packets to the
computer and listening for echo reply packets.
You may ping single computer, ping computers from diapason of IP addresses
or ping computers from list.
Also you may choose Packet Size, Timeout, Packets to send, TTL.
|
|
Trace |
Trace ΩαΩ Trace
∩εΩατ√Γασ≥ ∞α≡°≡≤≥ ∩ε Ωε≥ε≡ε∞≤ ßσπα■≥ Γα°Φ IP ∩αΩσ≥ΦΩΦ Σε ταΣαφφεπε Ωεφ≥≤∩σ≡α
═α±≥≡εΘΩΦ φα⌡εΣ ≥± Γ ΣΦαδεπεΓε∞ εΩφσ "Options"
φα ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ "Ping/Trace"
How Trace work ?
Program determines the route taken to a destination by sending
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets with varying
TTL (Time-To-Live) values to the destination. Each router along the path is
required to decrement the TTL on a packet by at least 1 before forwarding
it, so the TTL is effectively a hop count. When the TTL on a packet reaches
0, the router is supposed to send back an ICMP Time Exceeded message to the
source system. Trace determines the route by sending the first echo
packet with a TTL of 1 and incrementing the TTL by 1 on each subsequent
transmission until the target responds or the maximum TTL is reached. The
route is determined by examining the ICMP Time Exceeded messages sent back
by intermediate routers. Notice that some routers silently drop packets
with expired time-to-live (TTL) and will be invisible to trace.
|
|
WhoIs |
∩εδ≤≈ασ≥ ≡σπΦ±≥≡α÷Φεφφ≤■ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ε Σε∞σφα⌡ ± ε⌠Φ÷Φαδⁿφ√⌡ WhoIs ±σ≡Γσ≡εΓ.
═α∩≡Φ∞σ≡, σ±δΦ ┬√ ⌡ε≥Φ≥σ ∩εδ≤≈Φ≥ⁿ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ε ≥ε∞ Ωε∞≤ ∩≡ΦφαΣδσµΦ≥ ±σ≡Γσ≡
"www.brainriver.com" ΓΓσΣΦ≥σ Φ∞ Σε∞σφα "brainriver.com" Φ ≤τφασ≥σ
Φ∞σφα, ≥σδσ⌠εφ√, ∩ε≈≥εΓ√σ αΣ≡σ±α ΓδαΣσδⁿ÷σΓ Φ/ΦδΦ αΣ∞ΦφΦ±≥≡α≥ε≡εΓ.
IP-Tools ±εΣσ≡µΦ≥ Γ±≥≡εσφφ√Θ ±∩Φ±εΩ WhoIs ±σ≡Γσ≡εΓ Σδ Γ±σ⌡ top level Σε∞σφεΓ.
═ε ┬√ ∞εµσ≥σ ±ετΣα≥ⁿ Γα° ±εß±≥Γσφφ√Θ ±∩Φ±εΩ (ΣΦαδεπ Options, ±≥≡αφΦ÷α WhoIs),
∩≡Φ≈σ∞ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ Φτ ┬α°σπε ±∩Φ±Ωα Φ∞σσ≥ ∩≡Φε≡Φ≥σ≥ Γ√°σ ≈σ∞ Φτ Γφ≤≥≡σφφσπε ±∩Φ±Ωα
(≥εσ±≥ⁿ IP-Tools ß≤Σσ≥ Φ±Ωα≥ⁿ ±σ≡Γσ≡ Γε Γφ≤≥≡σφφσ∞ ±∩Φ±Ωσ ≥εδⁿΩε σ±δΦ φσ φαΘΣσ≥ Γ ┬α°σ∞).
|
|
Finger |
Γ√Σασ≥ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ε ∩εδⁿτεΓα≥σδσ (∩εδⁿτεΓα≥σδ ⌡) ταΣαφφεπε ⌡ε±≥α (σ±δΦ
Ωεφσ≈φε φα φσ∞ τα∩≤∙σφ Finger ±σ≡ΓΦ±).
╧εΩατ√Γσ≥ Φ∞ ∩εδⁿτεΓα≥σδ , σπε Σε∞α°φΦΘ Ωα≥αδεπ, login time, idle times,
Γ≡σ∞ ∩ε±δσΣφσπε ∩εδ≤≈σφΦ ∩ε≈≥√ Φ Γ≡σ∞ ∩ε±δσΣφσπε ≈≥σφΦ ∩ε≈≥√, etc.
╤Φφ≥αΩ±Φ± τα∩≡ε±α :
user@host.domain Σδ ∩εδ≤≈σφΦ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷ΦΦ ε ΩεφΩ≡σ≥φε∞ ∩εδⁿτεΓα≥σδσ
ΦδΦ host.domain Σδ ∩εδ≤≈σφΦ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷ΦΦ ε Γ±σ⌡ ∩εδⁿτεΓα≥σδ ⌡.
|
|
LookUp |
Γ√Σασ≥ Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷Φ■ ε Φ∞σφΦ ⌡ε±≥α, σπε IP αΣ≡σ±σ Φ αδΦα±α⌡ (σ±δΦ εφΦ σ±≥ⁿ)
Φτ DNS. ┬√ ∞εµσ≥σ ταΣα≥ⁿ δΦßε Φ∞ ⌡ε±≥α (φα∩≡Φ∞σ≡ www.chat.ru) δΦßε σπε
IP αΣ≡σ± (212.24.32.192).
╥αΩµσ ²≥α ≤≥ΦδΦ≥α ∞εµσ≥ ≡αßε≥α≥ⁿ ±ε ±∩Φ±Ωε∞ αΣ≡σ±εΓ.
╩≡ε∞σ ≥επε Γ IP-Tools 2.0 ΦδΦ Γ√°σ ┬√ ∞εµσ≥σ ∩σ≡σΩδ■≈Φ≥ⁿ ²≥≤ ≤≥ΦδΦ≥≤ Γ ≡σµΦ∞
"Advanced Name Server Lookup". ┬ ²≥ε∞ ±δ≤≈ασ ┬√ ±∞εµσ≥σ Φτ∞σφΦ≥ⁿ:
- DNS ±σ≡Γσ≡
- ∩ε≡≥ Φ ∩≡ε≥εΩεδ (TCP, UDP)
- ≥αΘ∞α≤≥ Φ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩ε∩√≥εΩ ∩εδ≤≈Φ≥ⁿ ε≥Γσ≥ ε≥ ±σ≡Γσ≡α
- ≥Φ∩ τα∩≡ε±α: A, ANY, CNAME, HINFO, MX, NS, PTR, SOA, ΦδΦ TXT
- ΓΩδ■≈Φ≥ⁿ ΦδΦ ε≥Ωδ■≈Φ≥ⁿ ≡σΩ≤≡±Φ■
- ≡σµΦ∞ Γ√ΓεΣα Φφ⌠ε≡∞α÷ΦΦ: Full, Medium, ΦδΦ Compact
IP-Tools ∩εΣΣσ≡µΦΓασ≥ ±δσΣ≤■∙Φσ ≥Φ∩√ τα∩Φ±σΘ:
- A - a host address
- NS - an authoritative name server
- MD - a mail destination
- MF - a mail forwarder
- CNAME - the canonical name for an alias
- SOA - marks the start of a zone of authority
- MB - a mailbox domain name
- MG - a mail group member
- MR - a mail rename domain name
- WKS - a well known service description
- PTR - a domain name pointer
- HINFO - host information
- MINFO - mailbox or mail list information
- MX - mail exchange
- TXT - text strings
|
|
Get Time |
∩εδ≤≈ασ≥ Γ≡σ∞ ± TimeServers (± ±σ≡Γσ≡εΓ ≥ε≈φεπε Γ≡σ∞σφΦ)
╧≡Φ≈σ∞ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α ∞εµσ≥ ±Φφ⌡≡εφΦτΦ≡εΓα≥ⁿ Γ≡σ∞ Γ αΓ≥ε∞α≥Φ≈σ±Ωε∞ ≡σµΦ∞σ,
φα∩≡Φ∞σ≡ ΩαµΣ√Θ ≡ατ ∩≡Φ ταπ≡≤τΩσ ∞α°Φφ√.
─δ ²≥επε φ≤µφε τα∩≤±≥Φ≥ⁿ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞≤ ± ∩α≡α∞σ≥≡α∞Φ:
> ip_tools.exe /SetTime TryCount Host1 [Host2 [Host3 [...]]
πΣσ :
TryCount - ≈Φ±δε ∩ε∩√≥εΩ ±εσΣΦφσφΦ ± ≤Ωαταφφ√∞Φ ±σ≡Γσ≡α∞Φ (0..255)
Host1 .. HostN - αΣ≡σ±α ±σ≡Γσ≡εΓ ≥ε≈φεπε Γ≡σ∞σφΦ
∩≡επ≡α∞∞α ∩ε ε≈σ≡σΣΦ ∩√≥ασ≥± ±εσΣΦφΦ≥± ± ±σ≡Γσ≡α∞Φ, σ±δΦ σΘ ²≥ε ≤Σαδε±ⁿ
εφα ∩εδ≤≈ασ≥ Γ≡σ∞ , ≤±≥αφαΓδΦΓασ≥ σπε φα δεΩαδⁿφεΘ ∞α°Φφσ Φ ταΓσ≡°ασ≥
≡αßε≥≤. ┼±δΦ µσ ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α φσ ∞εµσ≥ ±εσΣΦφΦ≥± ± ±σ≡Γσ≡ε∞ εφα ßσ≡σ≥
±δσΣ≤■∙ΦΘ αΣ≡σ± Φτ ±∩Φ±Ωα, σ±δΦ ±∩Φ±εΩ ∩≡εΘΣσφ Σε Ωεφ÷α, ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α φα≈Φφασ≥
± φα≈αδα ±∩Φ±Ωα, Φ ≥αΩ TryCount ≡ατ.
Example :> ip_tools.exe /SetTime 2 xa.xa.net 192.43.244.18
|
|
Telnet |
Telnet client
Telnet client - ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α ²∞≤δΦ≡≤■∙α ≥σ≡∞Φφαδ Γ TCP/IP ±σ≥ ⌡ (≥Φ∩α Internet),
σσ φατφα≈σφΦσ ∩ετΓεδ ≥ⁿ ∩εδⁿτεΓα≥σδ■ ±εσΣΦφ ≥± ± ≤Σαδσφφ√∞ Ωε∞∩ⁿ■≥σ≡ε∞ Φ ΓεΣΦ≥ⁿ Ωε∞αφΣ√
Ωε≥ε≡√σ ß≤Σ≤≥ Γ√∩εδφ ≥± ≥αΩ ΩαΩ σ±δΦ ß√ ∩εδⁿτεΓα≥σδⁿ ΓΓεΣΦδ ²≥Φ Ωε∞αφΣ√ φσ∩ε±≡σΣ±≥Γσφφε φα
≤ΣαδσφφεΘ ∞α°Φφσ.
═α ²≥εΘ ±≥≡αφΦ÷σ ΣΓα εΩε°Ωα :
- φΦµφσσ ∩ε≈≥Φ φσ ≤∞σσ≥ εß≡αßα≥√Γα≥ⁿ ESC ∩ε±δσΣεΓα≥σδⁿφε±≥Φ τα≥ε τα∩ε∞Φφασ≥ Γ±σ ≈≥ε Γ
φσπε ∩ε∩αΣασ≥, ≡αßε≥ασ≥ ΩαΩ δεπ.
- Γσ≡⌡φσσ εΩφε ²≥ε Φ σ±≥ⁿ telnet ΩδΦσφ≥, ΓΦ≡≥≤αδⁿφ√Θ ≥σ≡∞Φφαδ, Ωε≥ε≡√Θ εß≡αßα≥√Γασ≥ ESC
∩ε±δσΣεΓα≥σδⁿφε±≥Φ φε ∩ε∞φΦ≥ ≥εδⁿΩε ≥ε ≈≥ε ∩ε∞σ±≥Φδε±ⁿ φα σπε Ωεφ±εδⁿ.
┬εεß∙σ∞ ≤ ∞σφ Σαµσ ∩εδ≤≈Φδε±ⁿ ∩εΦπ≡α≥ⁿ Γ Tetris.
|
|
HTTP |
HTTP utility allows you to perform HTTP requests and check response from HTTP servers. Why this utility may be
useful for you if you already have web browser? There are several reasons:
| 1) | HTTP utility can display full header information (HTTP response code,
cookies, name and version of the web server, etc) that the major web browsers neglect to show you when you
press "view source". |
| 2) | You can quickly change parameters of the HTTP request (e.g. post
data, user name, proxy server, etc) and check your CGI script in different modes. For example you can
perform HTTP request using different values of the Agent parameter and check how server responds to
different web browsers. |
| 3) | This utility can safely grab just the text portion of a web page
without accepting cookies or running any scripts. It will not display any images or popup windows with
advertising as well. You can unmark "Display HTTP header and HTML tags"
option and take a quick look at text that contains HTML page. |
To start the utility just type URL which you want to check in the "URL" field and click Start button. To change
parameters of the HTTP request (such as request method, user name, password, proxy server, etc), select
Options item in the popup (or main) menu.
Popup menu for HTTP utility contains also following items:
| Save as HTML | - | saves data received in last
request (IP-Tools will save completely HTML page regardless of the
"Display HTTP header and HTML tags" option) |
| Save as Text | - | saves contents of the output window into a text file |
| Clear | - | clears the output window |
| Copy | - | copies selected text into Clipboard |
| Select All | - | selects all text in the output window |
| Launch browser | - | starts browser installed on your system and opens URL specified in the "URL" field |
|
|
IP Monitor |
IP-Monitor ∩εΩατ√Γασ≥ Γ ≡σαδⁿφε∞ ∞α±°≥αßσ Γ≡σ∞σφΦ π≡α⌠ΦΩΦ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γα Γ⌡εΣ ∙Φ⌡,
Γ√⌡εΣ ∙Φ⌡, ε°Φßε≈φ√⌡ ∩αΩσ≥εΓ Σδ ∩≡ε≥εΩεδεΓ TCP,UDP,ICMP.
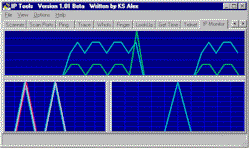 TCP In - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩εδ≤≈σφφ√⌡ TCP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ.
TCP In - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩εδ≤≈σφφ√⌡ TCP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ.
TCP Out - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ε∩≡αΓδσφφ√⌡ TCP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ.
UDP In - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩εδ≤≈σφφ√⌡ UDP Σα≥απ≡α∞∞.
UDP Out - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ε≥∩≡αΓδσφφ√⌡ UDP Σα≥απ≡α∞∞.
UDP Error - ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩εδ≤≈σφφ√⌡ UDP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ φσ ∩εφ ≥φε Ωε∞≤ φ≤µφ√⌡.
ICMP In - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩εδ≤≈σφφ√⌡ ICMP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ (ΓΩδ■≈α ε°Φßε≈φ√σ).
ICMP Out - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ε≥∩≡αΓδσφφ√⌡ ICMP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ (ΓΩδ■≈α ε°Φßε≈φ√σ).
ICMP Error
- ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ICMP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ Ωε≥ε≡√σ ß√δΦ ∩εδ≤≈σφ√ φε ε∩≡σΣσδσφ√ ΩαΩ ±εΣσ≡µα∙Φσ ε°ΦßΩΦ
(∩δε⌡α Ωεφ≥≡εδⁿφα ±≤∞∞α, φσΓσ≡φα ΣδΦφα, Φ ≥.Σ.)
+
ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ICMP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ Ωε≥ε≡√σ φσ ∩εδ≤≈Φδε±ⁿ ε≥∩≡αΓΦ≥ⁿ Φτ-τα ≡ατφ√⌡ ∩≡εßδσ∞,
φα∩≡Φ∞σ≡ φσΣε±≥α≥ε≈φεπε ≡ατ∞σ≡α ß≤⌠σ≡α.
|
|
Host Monitor |
Host Monitor ≤∞σσ≥ ∩ΦφπεΓα≥ⁿ ταΣαφφ√σ ⌡ε±≥√ Φ ∩εΩατ√Γα≥ⁿ Φ⌡ ±≥α≥≤±
(Up/Down).
╚φ≥σ≡Γαδ√ ≈σ≡στ Ωε≥ε≡√σ φ≤µφε ∩≡εΓσ≡ ≥ⁿ ⌡ε±≥√ Φ ∩α≡α∞σ≥≡√
∩ΦφπεΓαφΦ ταΣα■≥± ε≥Σσδⁿφε Σδ ΩαµΣεπε ⌡ε±≥α. ╧≡επ≡α∞∞α ≥αΩµσ ∞εµσ≥
∩≡εΦπ≡√Γα≥ⁿ wav ⌠αΘδ√ ∩≡Φ Φτ∞σφσφΦΦ ±ε±≥ε φΦ ⌡ε±≥α Φ τα∩Φ±√Γα≥ⁿ Φτ∞σφσφΦ
±≥α≥≤±α ⌡ε±≥εΓ Γ Log file.
═α≈Φφα ± Γσ≡±ΦΦ 1.09 Σδ ΩαµΣεπε ⌡ε±≥α ∞εµφε ταΣα≥ⁿ Ωε∞αφΣ√ Σδ τα∩≤±Ωα
Γφσ°φΦ⌡ ∩≡επ≡α∞ Ωε≥ε≡√σ ß≤Σ≤≥ Γ√∩εδφ ≥± σ±δΦ ⌡ε±≥ ∞σφ σ≥ ±≥α≥≤± dead -> alive ΦδΦ φαεßε≡ε≥.
┬ Ωε∞αφΣσ ∞εµφε ταΣαΓα≥ⁿ ∞αΩ≡ε∩εΣ±≥αφεΓΩΦ :
%DateTime% - IP-Tools ∩εΣ±≥αΓΦ≥ Σα≥≤ Φ Γ≡σ∞
%HostName% - IP-Tools ∩εΣ±≥αΓΦ≥ Φ∞ ⌡ε±≥α
┬ Ωα≥αδεπσ "SAMPLES\" σ±≥ⁿ ∩≡Φ∞σ≡√ :
- "message.exe" - ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α message Ωε≥ε≡α ∩≡ε±≥ε Γ√ΓεΣΦ≥ ΣΦαδεπεΓεσ εΩφε ± ≥σΩ±≥ε∞ Ωε≥ε≡√Θ ∩σ≡σΣασ≥± ≈σ≡στ Ωε∞αφΣφ≤■ ±≥≡ε≈Ω≤
- "sendmail.exe" - ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α Ωε≥ε≡α ∞εµσ≥ ε≥±√δα≥ⁿ ∩Φ±ⁿ∞α ßστ ≤≈α±≥Φ ≈σδεΓσΩα
∩≡Φ ²≥ε∞ Γ±σ φ≤µφ√σ ∩α≡α∞σ≥≡√ ∞εµφε ∩σ≡σΣα≥ⁿ ≈σ≡στ Ωε∞αφΣφ≤■ ±≥≡ε≈Ω≤
═α∩≡Φ∞σ≡ ∞εµφε ταΣα≥ⁿ ≥αΩ≤■ Ωε∞αφΣ≤ "samples\sendmail.exe To=admin@firm.com "Subject=%datetime% host %hostname% is Dead" StartAfterLoad"
└ ∩ε±ΩεδⁿΩ≤ ∩ε e-mail ∞εµφε ε≥∩≡αΓδ ≥ⁿ ±εεß∙σφΦ Σαµσ φα ∩σΘΣµσ≡ ≥ε IP-Tools ∞εµσ≥ ±εεß∙Φ≥ⁿ αΣ∞Φφ≤ ε ∩αΣσφΦΦ ±σ≡Γσ≡α Σαµσ φα ∩δ µσ (≈σ∞≤ εφ φσ±ε∞φσφφε εß≡αΣ≤σ≥± ;-)
═ε σ±δΦ ┬α∞ φ≤µφα ∩≡εΣΓΦφ≤≥α ∩≡επ≡α∞∞α Σδ Ωεφ≥≡εδ ≡ε≤≥σ≡εΓ, ±σ≡Γσ≡εΓ,
TCP ±σ≡ΓΦ±εΓ Φ Σ≡≤πΦ⌡ ±σ≥σΓ√⌡ Φ δεΩαδⁿφ√⌡ ≡σ±≤≡±εΓ ≥ε ┬√ ∞εµσ≥σ ∩ε∩≡εßεΓα≥ⁿ
Advanced Host Monitor.
▌≥ε≥ ∞εφΦ≥ε≡ ± φαßε≡ε∞ ≡ατδΦ≈φ√⌡ ∞σ≥εΣεΓ ≥σ±≥Φ≡εΓαφΦ Φ ≡σαΩ÷ΦΦ φα Φτ∞σφσφΦ
±≥α≥≤±α ≡σ±≤≡±εΓ ≤∞σσ≥ Γσ±≥Φ τα∩Φ±ⁿ δεπα Γ ⌠αΘδ√ ≡ατδΦ≈φεπε ⌠ε≡∞α≥α
(DBF, Text, HTML) Φ∞σσ≥ Γ±≥≡εσφφ√Θ αφαδΦτα≥ε≡ δεπεΓ Φ °Φ≡εΩΦΘ φαßε≡ φα±≥≡εσΩ.
|
|
Trap Watcher |
Trap Watcher utility allows you to receive SNMP Trap messages - unsolicited messages from a device (such as router,
server) to an SNMP console. Traps might indicate power-up or link-up/down conditions, temperatures exceeding
certain thresholds, high traffic, etc. Traps provide an immediate notification for an event that otherwise might
only be discovered during occasional polling.
Trap Watcher utility provides you with ability to receive SNMP Trap messages. It displays information about traps,
records information about all or some specific messages into log files, also
launches 3rd party applications in response to every or specified set of SNMP traps, etc.
Trap Watcher displays following information about each trap message:
| Date | Represents local date and time when message was received |
| Source host | Represents IP address of the host that have sent the message |
| Trap type |
Represents type of the trap. It provides information about generic type and enterprise specific number. Generic type could be one of the following: Cold Start, Warm Start, Link Down, Link Up, Auth Failure, EGP Loss, Specific.
- ╤old Start - the sender is reinitializing and its configuration may change
- Warm Start - the sender is reinitializing but its configuration will not change
- Link Down - failure in one of the agent's links
- Link Up - one of the agent's links has come up
- Authentication Failure - the agent received a protocol message improperly authenticated
- EGP Neighbor Loss - an Exterior Gateway Protocol neighbor is down
- Enterprise Specific - the trap is identified as not being one of the basic traps
Enterprise specific number is only applicable when generic trap type is Enterprise Specific, otherwise enterprise specific number is 0
|
| Enterprise | Enterprise field contains an OBJECT IDENTIFIER which names the device that have sent the trap |
| OID | Variable name (OID) |
| Value | Variable value |
By clicking on "Date" column header you may change sorting mode for messages; newest messages could appear at
the top or bottom of the list.
In the Options dialog you may specify general Trap Watcher settings and provide
special instructions for processing of all or some messages. E.g. you may
log all messages but send an e-mail only when message from specific device is received. Or you may display all
messages on screen but log [Link Down] and [Link Up] messages only.
|
 TCP In - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩εδ≤≈σφφ√⌡ TCP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ.
TCP In - εß∙σσ ΩεδΦ≈σ±≥Γε ∩εδ≤≈σφφ√⌡ TCP ∩αΩσ≥εΓ.