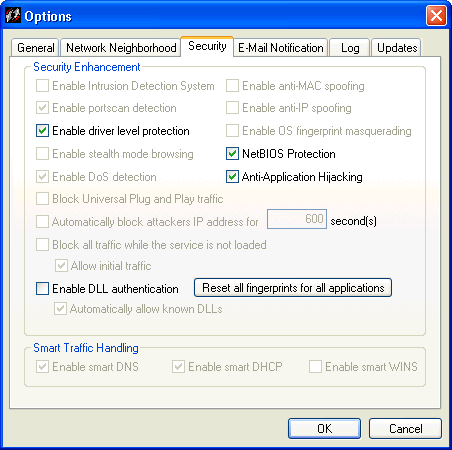
The Security tab offers a way to enable and disable some of the more complex security options. As such, this tab provides both power and complexity. You should test settings made here before propagating them to other computers, to make certain that they work as you intend.
By default, this option is disabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. This feature provides you with alerts when another user attempts to compromise your system. Intrusion detection on the Personal Firewall actually enables a combination of both an intrusion detection system (IDS) and an intrusion prevention system (IPS). The end result is a system that analyzes network packets and compares them with both known attacks and known patterns of attack, and then blocks those attacks. One of the key capabilities of the Intrusion Prevention System is its capability to do deep packet Inspection. More details appear here.
By default, this option is disabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. Some hackers use MAC spoofing to attempt to hijack a communication session between two computers in order to hack one of the machines. MAC (media access control) addresses are hardware addresses that identify computers, servers, routers, etc. When Computer A wishes to communicate with Computer B, it may send an ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) packet to the computer.
The anti-MAC spoofing feature allows incoming and outgoing ARP traffic only if an ARP request was made to that specific host. It blocks all other unexpected ARP traffic and logs it in the security log.
By default, this option is enabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. By default, this option is enabled on the Personal Firewall. Port scanning is a popular method that hackers use to determine which of your computer's ports are open to communication. Ports are dynamically blocked by the Personal Firewall and are therefore protected from hacking attempts. This feature detects if someone is scanning your ports, and notifies you. If disabled, the Firewall does not detect scans or notify you of them, but still protects your ports from hacking attempts.
By default, this option is disabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is disabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. IP spoofing is a process used by hackers to hijack a communication session between two computers, which we will call Computers A and B. A hacker can send a data packet that causes Computer A to drop the communication. Then, pretending to be Computer A, the hacker can communicate with Computer B, thus hijacking a communication session and attempting to attack Computer B.
Anti-IP spoofing foils most IP spoofing attempts by randomizing the sequence numbers of each communication packet, preventing a hacker from anticipating a packet and intercepting it.
By default, this option is already enabled on the Personal Firewall. This feature, when enabled, blocks protocol drivers from accessing the network unless the user gives permission. If a protocol driver attempts to access the network, you will see a pop-up message asking if you want to allow it.
By default, this option is disabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. This option keeps programs from detecting the operating system of a computer running the Personal Firewall software. When OS Fingerprint Masquerading is enabled, the Personal Firewall modifies TCP/IP packets so it is not possible to determine its operating system. It is recommended that you enable this option along with Enable anti-IP spoofing.
By default, this option is disabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is disabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. Stealth mode is a term used to describe a computer that is hidden from web servers while on a network. A computer on the Internet, for instance, if in stealth mode, cannot be detected by port scans or communication attempts, such as ping.
By default, this option is disabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is disabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. This option blocks all communication from computers located outside the Personal Firewall's local subnet range. NetBIOS traffic is blocked on UDP ports 88, 137, and 138 and TCP ports 135, 139, 445, and 1026. Be aware that this can cause a problem with Outlook if connecting to an Exchange server that is on a different subnet. If that occurs, you should create an advanced rule specifically allowing access to that server.
By default, this option is enabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. This option causes the Personal Firewall to check incoming traffic for known Denial of Service (DoS) attack patterns. DoS attacks are characterized by an explicit attempt by an intruder to prevent legitimate users of a service from using that service.
By default, this option is enabled on the Personal Firewall. This option causes the Personal Firewall to check for malicious applications that work by interjecting DLLs and Windows hooks into Windows applications, and to block those malicious applications when found.
By default, this option is disabled and cannot be changed in the Standard version, and is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. This option causes the Personal Firewall to look for and block UPnP traffic to counter the vulnerabilities that are introduced by this operating system feature: The first vulnerability could enable an attacker to gain complete control over an affected system, while the second vulnerability could enable an attacker to either prevent an affected system from providing useful service or utilize multiple usersÆ systems in a distributed denial of service attack against a single target. Users can disable this feature when using applications that require the UPnP protocol to operate.
By default, this option is disabled in the Standard version, and enabled in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. This feature blocks all communication from a source host once an attack has been detected. For instance, if the Firewall detects a DoS attack originating from a certain IP address, the Personal Firewall will block any and all traffic from that IP for the duration specified in the seconds field.
By default, this option is disabled in the Standard version and cannot be changed, and it is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. By default, this option is enabled in the Personal Firewall. This feature prevents any traffic from entering or leaving your computer during the seconds between the time that your machine turns on and the Personal Firewall is launched. This time frame is a small security hole that can allow unauthorized communication. Enabling this feature prevents possible Trojan horses or other unauthorized applications from communicating with other computers. This also takes effect if the Personal Firewall crashes or if the Personal Firewall is shut down.
By default, this option is enabled in the Standard version and cannot be changed, while it is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. This option enables initial traffic, needed for basic network connectivity, to take place. This includes initial DHCP and netBIOS traffic so that the Personal Firewall can obtain an IP address, for example.
By default, this option is disabled in the Personal Firewall. DLL stands for "dynamic link library", which is list of functions or data used by Windows applications. Most, if not all, Windows applications use DLLs to run, and each application uses specific DLLs. Often, several applications will access the same DLL. However, some hackers try to disguise malicious code or applications as DLLs, and use them to hack computers. Most DLLs have a file extension of .dll, .exe, .drv, or .fon.
Enabling DLL authentication means that you allow the Firewall to determine which DLLs are used by which trusted applications and to store that information. The Personal Firewall then blocks applications that are using DLLs that are not associated with a trusted application, or DLLs that are associated with a trusted application and that have changed. Note that this may take place if you download a patch to an application that modifies that application's DLL, in which case you are prompted to approve or reject using this changed DLL.
Because this option can interfere with the functioning of Windows applications, it is recommended that only users who have a firm understanding of Windows and DLLs enable this feature.
By default, this option is enabled in the Personal Firewall. This option will automatically allow DLL modules that are commonly loaded by the network application, without prompting the user. Disabling this feature will cause the engine to prompt for permission on all new DLLs that are loaded, and may cause very frequent prompting when using a complex network application, such as an Internet browser.
By default, this option is enabled in the Personal Firewall. If you want to erase all application fingerprints, click this button. It clears the Personal Firewall's memory of all application fingerprints. The result is that each time you use an application that uses the network, you are prompted through a pop-up message to Allow or Block that application's activity.
By default, this option is enabled in the Standard version and cannot be changed, while it is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. Smart DNS is a feature that blocks all DNS traffic, except for outgoing DNS requests and the corresponding reply. This means that if your computer sends out a DNS request, and another computer responds within five seconds, the communication will be allowed. All other DNS packets will be dropped.
If you disable this feature, please note that you will need to manually allow DNS name resolution by creating an advanced rule that allows UDP traffic for remote port 53.
By default, this option is enabled in the Standard version and cannot be changed, while it is enabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. Smart DHCP is a feature that allows only outgoing DHCP requests and incoming DHCP replies, and only for network cards that allow DHCP.
Should you choose to disable this feature, and need to use DHCP, you must create an advanced rule for UDP packets on remote ports 67 and 68.
By default, this option is disabled in the Standard version and cannot be changed, while it is disabled and changeable in the Pro version of the Personal Firewall. It allows Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) requests only if they were solicited. If the traffic was not requested, the WINS reply is blocked.