Earth


Earth Facts
- Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the fifth largest:
- distance from Sun: 149,600,000 km (1.00 AU)
- diameter: 12,756.3 km
- mass: 5.976e24 kg
- Earth is the only planet whose English name does not derive
from Greek/Roman mythology.
The name derives from Old English and Germanic. There are, of course, hundreds
of other names for the planet in other languages.
- It was not until the time of Copernicus (the
sixteenth century) that it
was understood that the Earth is just another planet.
- Earth, of course, can be studied without the aid of spacecraft. Nevertheless
it was not
until the twentieth century that we had maps
(picture 5) of the entire planet. And
pictures of the planet taken from space are of considerable importance; for
example, they
are an enormous help in weather prediction and especially in tracking and
predicting hurricanes.
And they are extraordinarily beautiful, to this critic
at least (picture 20).
- The Earth is divided into several layers which have distinct chemical
and seismic properties (depths in km):
0- 40 Crust
10- 400 Upper mantle
400- 650 Transition region
650-2700 Lower mantle
2700-2890 D'' layer (sometimes included in the lower mantle)
2890-5150 Outer core
5150-6378 Inner core
The crust is thinner under the oceans, thicker under the continents. The inner
core and crust are solid; the outer core and mantle layers are fluid.
- The core is probably composed mostly of iron (or nickel/iron) though
it is possible that some lighter elements may be present, too.
Temperatures at the center of the
core may be as high as 7500 K, hotter than the surface of the
Sun.
The lower mantle is probably mostly silicon, magnesium and oxygen with some
iron, calcium and aluminum.
The upper mantle is mostly olivene and pyroxene
(iron,magnesium silicates),
calcium and aluminum.
We know most of this only from seismic techniques; samples from the upper mantle
arrive at the surface as lava from volcanoes but the majority of the Earth is
inaccessible.
The crust is primarily quartz (silicon dioxide) and other
silicates like feldspar. Taken as a whole, the Earth's chemical composition
(by mass) is:
34.6% Iron
29.5% Oxygen
15.2% Silicon
12.7% Magnesium
2.4% Nickel
1.9% Sulfur
0.05% Titanium
- The Earth is the densest major body in the
solar system.
- The other terrestrial planets
probably have similar structures and compositions with some differences: the
Moon has at most a small core;
Mercury has an extra large core
(relative to its diameter); the mantles of
Mars and the Moon are much thicker;
the Moon and Mercury may not have chemically
distinct crusts; Earth may be the only one with distinct inner and outer cores.
Note, however, that our knowledge of planetary interiors is mostly theoretical
even for the Earth.
- Unlike the other terrestrial planets,
Earth's crust is divided into several separate solid
plates which float around independently on top of the hot mantle below.
This is known as plate tectonics.
It is characterized by two major processes: spreading and subduction. Spreading
occurs when two plates move away from each other and new crust is created by
upwelling magma from below. Subduction occurs when
two plates collide and the edge of one dives
beneath the other and ends up being destroyed in the mantle.
There is also transverse motion at some plate boundaries (i.e. the San Andreas
Fault in California) and collisions between continental plates
(i.e. India/Eurasia).
There are (at present) eight major plates (picture 23):
- North American Plate - North America, western North Atlantic and Greenland
- South American Plate - South America and western South Atlantic
- Antarctic Plate - Antarctica and the "Southern Ocean"
- Eurasian Plate - eastern North Atlantic, Europe and Asia except for India
- African Plate - Africa, eastern South Atlantic and western Indian Ocean
- Indian-Austrailian Plate - India, Austrailia, New Zealand and
most of Indian Ocean
- Nazca Plate - eastern Pacific Ocean adjacent to South America
- Pacific Plate - most of the Pacific Ocean (and the southern coast of
California!)
There are also twenty or more small plates such as the Arabian, Cocos, and
Philippine Plates.
- The Earth's surface is very young.
In the relatively
short (by astronomical standards) period of 500,000,000 years or so
erosion and tectonic processes
destroy and recreate most of the Earth's
surface and thereby eliminate almost all traces of earlier
geologic surface history (such as impact craters).
Thus the very early history of the Earth has been erased.
The Earth is 4.5 to 4.6 billion years old,
but the oldest known rocks are less than
4 billion years old and rocks older than 3 billion years are rare.
The oldest fossils of living organisms are less than 3.9 billion years old.
There is no record of the critical period when life was first getting started.
- 71% of the Earth's surface is covered with water.
Earth is the only planet on which water can exist in liquid form on the surface
(though there may be liquid ethane or methane on
Titan's surface).
This is, of course, essential for life as we know it.
The heat capacity of the oceans is also very important in keeping the Earth's
temperature relatively stable. Liquid water is also reponsible for most of the
erosion and weathering of the Earth's continents, a process unique in the solar
system today (though it may have occurred on Mars in the past).
- The Earth's atmosphere is 77% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, with traces of
argon, carbon dioxide and water.
There was probably a very much larger amount of carbon dioxide in the
Earth's atmosphere when the Earth was first formed, but it has since been
almost all incorporated into carbonate
rocks and to a lesser extent dissolved
into the oceans and consumed by living plants. Plate tectonics and biological
processes now
maintain a continual flow of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to these
various "sinks" and back again. The tiny amount of carbon
dioxide resident in the atmosphere at any time is extremely
important to the maintenance of the Earth's surface temperature via the
greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect raises the average surface temperature
about 35 degrees C above what it would otherwise be
(from a frigid -21 C to a comfortable +14 C); without it the oceans
would freeze and life as we know it would be impossible.
- The presence of free oxygen is quite remarkable from a chemical point of view.
Oxygen is a very reactive gas and under "normal" circumstances would quickly
combine with other elements.
The oxygen in Earth's atmosphere is produced and maintained by
biological processes. Without life there would be no free oxygen.
- The interaction of the Earth and the Moon
slows the Earth's rotation. Current research indicates that there were 481
days in a year 900 million years ago.
- Earth has a modest magnetic field produced by electric currents in the core.
The interaction of the solar wind,
the Earth's magnetic field
and the Earth's upper atmosphere causes the
auroras
(see the Interplanetary Medium).
Pictures
- (above) Africa
404k gif
 Galileo image of South America 1st flyby
224k gif
Galileo image of South America 1st flyby
224k gif
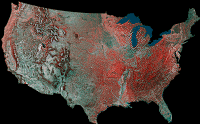 AVHRR mosaic
545k gif;
8811k gif;
html
AVHRR mosaic
545k gif;
8811k gif;
html
 section of Earth from Clementine
82k gif
section of Earth from Clementine
82k gif
- Map projected image of Earth
123k gif
- Gibbous Earth with SW North America visible
127k gif
- Mosiac of the Andes mountains in South America taken from Galileo
94k gif
- Americas by GOES (9/21/86)
391k gif;
583k jpg
- NOAA satellite's view of USA
322k gif
- The easternhalf USA viewed by GOES satellite
306k gif
- The great lakes of USA viewed by satellite
342k gif
- The southeastern USA viewed by NOAA satellite
226k gif
 Simpson desert in Austrailia
129k gif;
69k jpg
Simpson desert in Austrailia
129k gif;
69k jpg
- Pseudo color full disk image of pacific
316k gif
- Image of the Gulf of Mexico
122k gif;
227k gif
 Strait of Gibraltar
157k gif
Strait of Gibraltar
157k gif
- Earth-Moon together from Galileo 2nd flyby
79K gif
 San Francisco Bay infra-red from Shuttle
294k gif;
83k jpg
San Francisco Bay infra-red from Shuttle
294k gif;
83k jpg
 Space Station Mir over the Earth
111k gif
Space Station Mir over the Earth
111k gif
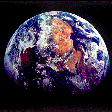 Earth from Apollo 11
52k gif;
32k jpg
Earth from Apollo 11
52k gif;
32k jpg
- USA at night
67k gif
- Current weather maps html
- Plate boundaries
171k gif
- Earth Viewer html
- AVHRR image browser html
- Shuttle image browser html
- ... more Earth images
Movies
- Earth-Moon animation
382K fli;
373K pics;
140K quicktime
- Clouds over West Europe, North Africa
379k mpeg
610k mpeg
- Aurora Video
1300k AVI
- Earth/Venus Rotation Movie
1000k AVI
- Galileo Earth Encounter
14000k AVI
- Clip 1 of Earth the Movie - Animation of Clouds
13000k AVI
- Rotating relief globe of Earth
2200k MPEG
Earth's Satellite
Earth has only one natural satellite, the Moon:
Distance Radius Mass
Satellite (000 km) (km) (kg)
--------- -------- ------ -------
Moon 384 1738 7.35e22
Thousands of small artificial satellites have also been placed in orbit
around the Earth. (Lilith doesn't exist but it's an
interesting story.)
More about Earth and the Moon
Open Issues
- Our knowledge of the interior of the Earth is derived almost entirely from
highly indirect evidence. How can we get more information?
- Despite substantial increases in the
solar "constant" the average temperature
on the surface of the Earth has remained very stable for several billion years.
The best theory is that this has been accomplished by varying the amount of
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to regulate the
greenhouse effect.
But just how is this done?
The Gaia Hypothesis asserts that the
biosphere actively regulates it. More detailed information about Venus and Mars
may provide clues.
- How much more carbon dioxide can we dump
into the Earth's atmosphere before it ends up like Venus?
 ... Sun
... Venus
... Earth
... Moon
... Mars
...
... Sun
... Venus
... Earth
... Moon
... Mars
... 

Bill Arnett; last updated:
1996 July 16
 Galileo image of South America 1st flyby
224k gif
Galileo image of South America 1st flyby
224k gif
 AVHRR mosaic
545k gif;
8811k gif;
html
AVHRR mosaic
545k gif;
8811k gif;
html
 section of Earth from Clementine
82k gif
section of Earth from Clementine
82k gif
 Simpson desert in Austrailia
129k gif;
69k jpg
Simpson desert in Austrailia
129k gif;
69k jpg
 Strait of Gibraltar
157k gif
Strait of Gibraltar
157k gif
 San Francisco Bay infra-red from Shuttle
294k gif;
83k jpg
San Francisco Bay infra-red from Shuttle
294k gif;
83k jpg
 Space Station Mir over the Earth
111k gif
Space Station Mir over the Earth
111k gif Earth from Apollo 11
52k gif;
32k jpg
Earth from Apollo 11
52k gif;
32k jpg


 ... Sun
... Venus
... Earth
... Moon
... Mars
...
... Sun
... Venus
... Earth
... Moon
... Mars
... 
