COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Togo is sandwiched between Ghana and Benin in west Africa. A central forested region is bounded by savanna lands to the north and south. The port of Lomé is an important entrepôt for west African trade. The president, General Gnassingbé Eyadéma, has been in power since 1967. |
|
Climate |
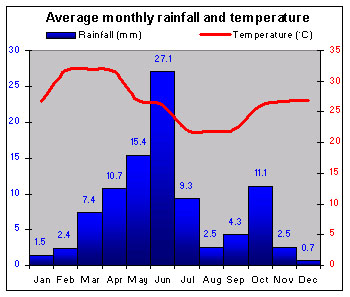 |
Togo has a typical Gulf of Guinea climate – very hot and humid on the coast, and drier inland. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Ewe, Kabye, Gurma, French |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
A bitter divide has existed between north and south since before independence. Most southern resentment is directed toward a northern minority, the Kabye people from the Kabye plateau, because of their domination of the military. The Kabye and other northerners in turn resent their own underdevelopment in contrast to the high development, especially educationally, of all southerners. The dominant southern group is the Ewe, who make up more than 40% of the population. As elsewhere in Africa, the extended family is important and tribalism and nepotism are key factors in everyday life. Some Togolese ethnic groups, such as the Mina, have matriarchal societies. The "Nana Benz," the market-women of Lomé, control the retail trade and have considerable private money. Politics, however, remains a male preserve. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
1318
|
M |
GNP World rank |
149
|
|
| Inflation |
2 |
% |
Unemployment |
No data |
% |
|
StrengthsEfficient civil service. Ideal location for role as entrepôt, based on Lomé port. Resourceful entrepreneurs, notably market-women. Proceeds of widespread smuggling. Phosphate deposits have the world's highest mineral content. Self-sufficient in basic foodstuffs. WeaknessesPolitical pariah status led to aid reductions in the 1990s. Low world prices for phosphates. Hydropower generation is vulnerable to drought. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1999 |
Next election |
2002 (postponed) |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
Politics has been dominated for three decades by General Gnassingbé Eyadéma, who took power at the head of a military government in 1967, and is Africa's longest-serving leader. A democracy movement has been gathering momentum since 1990. Multiparty presidential elections held in 1993 were won by Eyadéma, although some opposition candidates boycotted the poll over the exclusion of Gilchrist Olympio, son of a former president. Eyadéma claimed victory over Olympio in presidential elections in 1998, amid accusations of malpractice and of the killing of hundreds of opposition supporters immediately afterward in the runup to the 1999 Assembly election. (Serious human rights violations were later confirmed by a UN/OAU report.) During subsequent negotiations, the opposition accepted the election results, Eyadéma stated that he would not stand for reelection in 2003, and an accord provided for a new independent electoral body and a political code of conduct. New Assemby elections, set for October 2001, were repeatedly postponed, however, as the deadlock between Eyadéma and the opposition continued. |
|
International Affairs |
| |
The priority is maintaining traditional links, especially with France. President Eyadéma became chairman in 1998 of ECOWAS, in which capacity he acted as mediator in the Guinea-Bissau conflict and hosted talks in Sierra Leone. He was also president of the OAU for 2000/2001. |
|
Defence |
| Expenditure (US$) |
30 |
M |
Portion of GDP |
2 |
% |
|
| Army |
2 main battle tanks (T-54/55) |
| Navy |
2 patrol boats |
| Airforce |
16 combat aircraft (5 Alpha Jet, 4 EMB-326G) |
| Nuclear capab. |
None |
|
The military has an important role in Togo, and spending on defense is quite high. The army's senior ranks are dominated by loyalists from President Eyadéma's northern Kabré tribe. France guarantees Togo's security through a defense accord, and supplies most military equipment and training. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Phosphates, iron, chromite, bauxite, marble, dolomite |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Phosphates are Togo's most important resource. Offshore oil and gas deposits were found in 1999. The Nangbeto dam, constructed jointly with Benin and opened in 1988, has reduced dependence on Ghana for energy. |
|
Environment |
| Protected land |
8 |
% |
Part protected land |
No data |
% |
|
|
|
Ecologists have been critical of the transformation of nature reserves into hunting grounds for the military elite. Other problems include coastal erosion around Aneho and desertification. |
|
Communications |
| Main airport |
Tokoin, Lomé |
Passengers per year |
232578 |
|
| Motorways |
0
|
km |
Roads |
2376
|
km |
Railways |
517
|
km |
|
Improving the already good road network and Lomé's port facilities are priorities, given Togo's role as an entrepôt. Air and rail links to the interior, however, are limited. |
|
International Aid |
| Donated (US$) |
Not applicable
|
M |
Received (US$) |
70
|
M |
|
Development projects and the health of the economy overall have suffered from aid suspensions in 1998 by donors including the USA and the EU. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
52 |
Life expect. World rank |
155 |
| Population per doctor |
10000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
75 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Malaria, diarrheal, infectious, and parasitic diseases |
|
Health care suffers from a lack of resources. More than 5% of adults were HIV positive by 2000. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
57 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
5 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
33 |
% |
Tertiary |
4 |
% |
|
Schooling is based on the French model. The University of Bénin in Lomé has more than 4000 students. |
|
Criminality |
| Crime rate trend |
Theft on increase in the capital |
|
|
|
| Murder |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
| Rape |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
| Theft |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
|
Togo is normally relatively peaceable, but urban crime generally increased during the 1990s, particularly during periods of political unrest in the capital. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
19 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
9 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
32 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Considerable wealth disparities exist between those who work the land and the country's political and business classes. The urban class has been hit by an economic downturn in the late 1990s. |
|
Media |
| Newspapers |
There are 2 daily newspapers, Togo Presse, published by the government, and Les Echos du Demain |
| TV services |
1 state-owned service |
| Radio services |
3 services: 1 state-owned, 2 independent |
|
|
|
Tourism |
|
|
There is some package tourism, mainly French and German, to coastal tourist villages and hotels built during the expansion program of the 1980s. Tourists have been deterred by the political uncertainty since 1990. |
|
History |
After colonization by Germany in 1894, Togoland was divided between France and the UK in 1922. - 1960 French sector independent as Togo (UK part joined to Ghana).
- 1967 Eyadéma takes power.
- 1991–1992 General strike; repression.
- 1993 Eyadéma elected president.
- 1998 Eyadéma claims victory in disputed election.
|
|