COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
The smallest and most densely populated Central American republic, El Salvador won full independence in 1841. Located on the Pacific coast, it lies within a zone of seismic activity. Between 1979 and 1991, El Salvador was engulfed in a civil war between US-backed right-wing government forces and left-wing FMLN guerrillas. Since the UN-brokered peace agreement, the country has been concentrating on rebuilding its shattered economy. |
|
Climate |
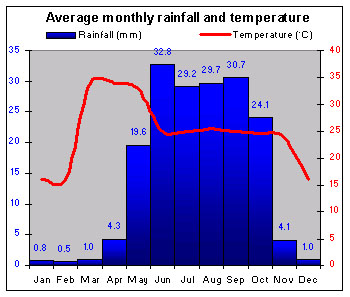 |
The tropical coastal tierra caliente is very hot, with seasonal rains. The low hills are cooler at night; the higher tierra templada is drier and also cooler. |
|
People |
|
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Salvadorans are largely mestizo (mixed race); there are few ethnic tensions. The civil war was fought over gross economic disparities, which still exist. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
12569
|
M |
GNP World rank |
78
|
|
| Inflation |
2 |
% |
Unemployment |
10 |
% |
|
StrengthsCoffee. Foreign investment in maquila assembly plants. Sizable family remittances from USA. WeaknessesExports uncompetitive. High tax evasion and unemployment. Low savings. Vast reconstruction needed after earthquakes in 2001. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2000 |
Next election |
2003 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
El Salvador had traditionally been dominated by the centrist PDC and right-wing ARENA. The latter, however, now faces greater opposition from the FMLN, the leftist former guerrillas, who in 1997 won the mayorship of San Salvador and half the state capitals. In the 1999 presidential election the FMLN, split between center-left pragmatists and hard-liners, came a poor second to ARENA's Francisco Flores, who promised reduced poverty and income redistribution. By March 2000, however, with the economy in difficulties, voters punished ARENA by returning the FMLN as the largest party in parliament. |
|
International Affairs |
| |
El Salvador was an international pariah in the 1980s because of the human rights abuses committed by military death squads. Today it cooperates with its neighbors in pressing the USA on key issues such as trade and immigration. It relied heavily on US aid in 2001 after three devastating earthquakes. In 2000 it co-signed a free trade treaty with Guatemala, Honduras, and Mexico. The final issue arising from a territorial dispute with Honduras was settled in 1998, when those affected were permitted to choose between Honduran and Salvadoran citizenship. |
|
Defence |
| Expenditure (US$) |
168 |
M |
Portion of GDP |
2 |
% |
|
| Army |
No main battle tanks |
| Navy |
5 patrol boats |
| Airforce |
23 combat aircraft (5 A-37B, 4 OA-37B, 9 O2A, 1 Ouragan) |
| Nuclear capab. |
None |
|
Between 1979 and 1991, the role of the US-backed military was to fight an unrestricted war against the FMLN. Human rights were in effect suspended and governments that opposed the military were overthrown. Under the peace accords the military agreed to withdraw from politics and internal security matters, but it remains a potent force. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Salt, limestone, gypsum |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
No significant resources. Several volcanoes facilitate abundant and relatively cheap geothermal energy. |
|
Environment |
| Protected land |
0 |
% |
Part protected land |
0 |
% |
|
|
|
Deforestation has led to erosion and desertification – worsening landslides during the earthquakes of 2001. Overuse of pesticides is a major problem. |
|
Communications |
| Main airport |
Cuscatlan, San Salvador |
Passengers per year |
1341705 |
|
| Motorways |
327
|
km |
Roads |
1986
|
km |
Railways |
674
|
km |
|
Earthquakes in 2001 further damaged the already war-ravaged road and rail networks. Reconstruction will take many years. |
|
International Aid |
| Donated (US$) |
Not applicable
|
M |
Received (US$) |
180
|
M |
|
Post-civil war aid focused on efforts to secure peace and achieve national reconciliation by funding rebuilding and refugee resettlement programs. Now the emphasis has shifted to support for growth. The UN received a slow international response in 2001 to its appeal for $34.8 million in emergency housing, medicine, and disaster prevention programs after devastating earthquakes. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
70 |
Life expect. World rank |
83 |
| Population per doctor |
909 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
29 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Accidents, violence, circulatory diseases, infections |
|
Health spending, almost halved during the civil war, has been slow to recover. The wealthy go to the USA for surgery. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
79 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
3 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
50 |
% |
Tertiary |
18 |
% |
|
Education is based on the US system and is limited in rural areas. During the civil war, state universities were closed by the military and replaced by private universities which continue to thrive despite their low standards. A 1995 reform bill tried to address the negative impact of deregulation. |
|
Criminality |
| Crime rate trend |
Falling, but still high by regional standards |
|
|
|
| Murder |
37 |
per 100,000 population |
| Rape |
10 |
per 100,000 population |
| Theft |
158 |
per 100,000 population |
|
A corrupt judiciary and police force have failed to stem a postwar crime wave fueled by readily available arms; armed robberies, kidnappings, and murders deter investment and tourism. Uncompleted elements of the peace accords, particularly land transfers, often lead to violence. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
30 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
100 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
201 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Gross wealth disparities see 20% of the population owning 70% of national wealth. Land distribution remains highly skewed, and some three million – nearly half the population – live in poverty. |
|
Media |
| Newspapers |
There are 8 daily newspapers. El Diario de Hoy has the highest circulation |
| TV services |
10 channels: 2 state-owned, 8 independent |
| Radio services |
66 stations: 1 state-owned, 65 independent |
|
|
|
Tourism |
|
|
Peace has brought visitors back to the unspoiled beach resorts. However, high prices for rooms and air travel, along with crime, hinder tourist expansion. |
|
History |
El Salvador was Spanish until 1821. Part of the United Provinces of Central America in 1823–1839, it became fully independent in 1841. - 1932 Army crushes popular insurrection led by Farabundo Martí.
- 1944–1979 Army rules through PCN.
- 1979 Reformist officers overthrow PCN government.
- 1981 Left-wing Farabundo Martí National Liberation Movement (FMLN) launches civil war.
- 1991 UN-brokered peace. FMLN recognized as a political party.
- 1997 Leftist wins San Salvador mayoralty.
- 2001 Devastating earthquakes kill hundreds; dollarization of economy.
|
|