COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Bounded east and west by rivers, Suriname sits on the north coast of South America in the center of the "Guyana Plateau." The interior is rainforested highlands; most people live near the coast. In 1975, after almost 300 years of Dutch rule, Suriname became independent. The Netherlands is still its main aid supplier, and is home to one-third of Surinamese. Multiparty democracy was restored in 1991, after almost 11 years of military rule. |
|
Climate |
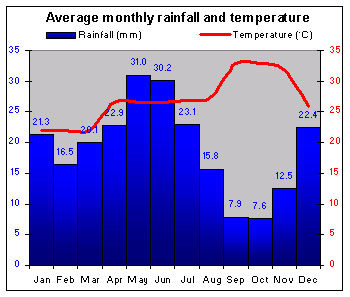 |
Suriname's tropical climate is cooled by the trade winds. Annual rainfall varies from 150 to 300 cm (60 to 120 in.) between coast and interior. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Sranan, Dutch, Javanese, Sarnami Hindi, Saramaccan, Chinese, Carib |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
About 250,000 Surinamese have emigrated since 1975. Of those who remain, 90% live near the coast, while the rest live in scattered rainforest communities. Tension between the Creole-dominated government, bosnegers (the descendants of runaway slaves), and Amerindians spilled over into armed rebellion in the 1980s. Many South Asians and Javanese work in farming. Christianity, Hinduism, and Islam are the dominant religions. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
788
|
M |
GNP World rank |
159
|
|
| Inflation |
64 |
% |
Unemployment |
11 |
% |
|
StrengthsBauxite. Gold. Timber potential. Oil. Agricultural exports: rice, bananas, citrus fruits. Shrimp exports. WeaknessesOverdependence on declining bauxite reserves and decreased foreign aid. Weak currency. Severe shortage of foreign exchange. Banana industry damaged by ending of preferential EU access. Net food importer. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2000 |
Next election |
2005 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
A coalition government representing Creoles, South Asians, and Javanese took power under Ronald Venetiaan in 1991. Five years later it was defeated by the NDP, controlled by Desi Bouterse, the military dictator from 1980 to 1988 and the man behind the 1990 coup which ended Suriname's first attempt to return to democracy. Between 1996 and 2000 President Jules Wijdenbosch of the NDP withstood the efforts of opponents in the National Assembly to replace him. In the 2000 legislative elections, however, the NDP was massively defeated by the opposition NF. The new Assembly went on to elect NF leader Venetiaan as president. |
|
International Affairs |
| |
Relations with the Netherlands and the USA, Suriname's key aid and trading partners, have been weakened over charges of official connivance in narcotics trafficking. Although ties with Suriname's immediate neighbors are damaged by border disputes, greater regional integration, particularly with the Caribbean, is a priority. |
|
Defence |
| Expenditure (US$) |
11 |
M |
Portion of GDP |
3 |
% |
|
| Army |
No main battle tanks |
| Navy |
3 patrol boats |
| Airforce |
7 combat aircraft |
| Nuclear capab. |
None |
|
The army was politically dominant in the 1980s under Lt. Col. Desi Bouterse. A six-year war with bosneger rebels ended in 1992. Aid and training have been provided in recent years by both the USA and China. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Bauxite, iron, gold, manganese, copper, nickel, platinum, oil |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
87m barrels |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
4972 b/d |
|
Suriname is a major exporter of aluminum and bauxite, but the minerals sector is affected by poor world prices, as is raw gold production. Oil consumption is almost double the level of oil production. Exploitation of the rainforests has begun. Rice and fruit are Suriname's key agricultural products. |
|
Environment |
| Protected land |
No data |
% |
Part protected land |
10 |
% |
|
|
|
In 1998 the government declared some 16,000 sq. km (6150 sq. miles) of rainforest – almost 10% of the country – to be a natural reserve barred to logging. Exploitation of the forest for economic gain remains of real concern to environmentalists. |
|
Communications |
| Main airport |
Johann Pengel International, Paramaribo |
Passengers per year |
175000 |
|
| Motorways |
0
|
km |
Roads |
1178
|
km |
Railways |
157
|
km |
|
Rivers provide the main north–south links, and the vast interior relies on water or air transportation. The road network runs east–west and focuses on the coast and its immediate hinterland. |
|
International Aid |
| Donated (US$) |
Not applicable
|
M |
Received (US$) |
34
|
M |
|
The Netherlands is the largest donor, but it has on occasion suspended aid amid deteriorating relations. The IDB and European Investment Bank have granted loans for agricultural and industrial development. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
71 |
Life expect. World rank |
72 |
| Population per doctor |
4000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
27 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Heart attacks, cancers, malaria, malnutrition, tuberculosis |
|
Urban medical facilities are relatively good; Paramaribo has several hospitals. Provision in the interior is basic. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
94 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
4 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
52 |
% |
Tertiary |
9 |
% |
|
Education is free and includes adult literacy programs. There is a long tradition of higher education, but most graduates now live in the Netherlands. |
|
Criminality |
| Crime rate trend |
Relatively high crime levels |
|
|
|
| Murder |
14 |
per 100,000 population |
| Rape |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
| Theft |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
|
Human rights abuses associated with the former military regime have largely ended. Rival armed factions remain in some interior regions. Drugs trafficking and money laundering are a problem, as is urban street crime. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
144 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
174 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
153 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Living standards have fallen since 1982, due to the effects of civil war and to aid and loan suspension. Urban Creoles dominate the rich elite. Amerindians and bosnegers are the poorest groups. |
|
Media |
| Newspapers |
There are 2 daily newspapers, De Ware Tijd and De West |
| TV services |
2 state-owned services |
| Radio services |
10 services: 1 state-owned, 9 independent |
|
|
|
Tourism |
|
|
Tourism is undeveloped. Travelers outside Paramaribo are advised to carry their own hammock and food. |
|
History |
Dutch rule began in 1667, after an Anglo-Dutch treaty whose terms included Britain ceding its colony in Suriname to the Dutch but gaining Nieuw Amsterdam (later New York). - 1975 Independence.
- 1980 Coup. Rule by Lt. Col. Desi Bouterse.
- 1982 Opponents executed. Dutch suspend aid for six years.
- 1986–1992 Bosneger rebel war.
- 1988–1991 Elections, coup, and new elections. Ronald Venetiaan elected president.
- 1992 Bouterse quits as army head.
- 1996 Pro-Bouterse NDP wins elections.
- 2000 Opposition NF defeats NDP. Venetiaan elected president again.
|
|