COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Occupying the horn of Africa, Italian Somaliland and British Somaliland joined in 1960 to form an independent Somalia. Except in the more fertile south, the land is semiarid. Years of clan-based civil war have resulted in the collapse of central government, the frustration of US and UN intervention initiatives aimed at easing a huge refugee crisis, and mass starvation. |
|
Climate |
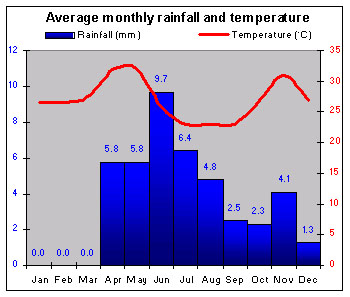 |
Somalia is very dry. The northern coast is very hot and humid, the eastern less so. The interior has some of the world's highest mean yearly temperatures. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Somali, Arabic, English, Italian |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
The clan system is fundamental to Somalia. Shifting allegiances characterize its structure – a tendency stifled by Siad Barre's dictatorship but revived after his fall in 1991. His undermining of the traditional brokers of justice, the elders, contributed to the power vacuum that resulted in civil war, and his persecution of the Issaqs led to Somaliland's declaration of secession in 1991. However, the entire population is ethnic Somali, and national identity remains strong, shown by widespread opposition to the UN peacekeeping force. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
835
|
M |
GNP World rank |
157
|
|
| Inflation |
No data |
% |
Unemployment |
No data |
% |
|
StrengthsVery few. Export of livestock to Arabian peninsula resumed in the north. Inflow of money from Somalis abroad. Growing market in stolen food aid. WeaknessesEvery commodity, except arms, in extremely short supply. Little economic potential in the south. Destruction by drought of livestock. Mogadishu port closed by civil unrest until October 2000. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1984 |
Next election |
Uncertain |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
Somalia has remained in anarchy since the former dictator President Siad Barre fled in 1991. The unified state dissolved amid conflict in the south and separatism in the north. The USA led a UN peacekeeping force to the south in 1992, but failed to loosen the grip of the warring factions. Throughout the 1990s rival warlords, including the powerful Gen. Aideed, contended for supreme power. A National Salvation Council sank without trace in 1997. A conference of businessmen and influential figures, held in neighboring Djibouti in 2000, established a transitional assembly and appointed former Barre minister Abdulkassim Salat Hassan as president. The new government, although warmly received in Mogadishu, was immediately rejected by most of the warlords and by the northern separatist authorities in "Somaliland" and "Puntland." |
|
International Affairs |
| |
The UN force withdrew in 1995, after which the international community appeared to abandon Somalia until giving support to the transitional parliament from 2000. Relations with Ethiopia are particularly tense. The government accuses Addis Ababa of sending troops to assist opposition warlords. The USA's belief in the existence of terrorist training camps in Somalia has eroded relations since 11 September 2001. |
|
Defence |
| Expenditure (US$) |
39 |
M |
Portion of GDP |
5 |
% |
|
| Army |
No data |
| Navy |
No data |
| Airforce |
No data |
| Nuclear capab. |
None |
|
Former soldiers have been urged to reenlist. Efforts to demobilize the estimated 75,000 militia began in 2000. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Salt, tin, zinc, copper, gypsum, manganese, uranium, iron |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Commercially exploitable minerals remain untapped. An oil exploration agreement was signed with a French oil group in February 2001. |
|
Environment |
| Protected land |
0 |
% |
Part protected land |
No data |
% |
|
|
|
Human deprivation and starvation caused by the effects of drought and war on land and livestock outweigh all other ecological considerations. |
|
Communications |
| Main airport |
Mogadishu International |
Passengers per year |
No data |
|
| Motorways |
0
|
km |
Roads |
2608
|
km |
Railways |
0
|
km |
|
About 50% of Somalis are nomads for whom the camel is the principal means of transportation. In 1990, the IDA agreed to repair the road network, but work on the seven-year project has not yet begun. |
|
International Aid |
| Donated (US$) |
Not applicable
|
M |
Received (US$) |
104
|
M |
|
Mass starvation among the Somali population in 1991 finally prompted the UN to launch a large-scale humanitarian aid effort. In this the UN was largely effective, averting widescale starvation and restoring food security. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
48 |
Life expect. World rank |
167 |
| Population per doctor |
20000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
117 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Diarrheal, communicable, and parasitic diseases |
|
The state-run system has collapsed entirely. A few very rudimentary facilities are run by foreign workers. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
24 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
0 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
14 |
% |
Secondary |
8 |
% |
Tertiary |
2 |
% |
|
The system collapsed during the civil war. There were reports of improvised open-air schools starting up again in urban areas in 1993. Somali has been a written language only since 1972. |
|
Criminality |
| Crime rate trend |
Widespread breakdown in law and order since 1991 |
|
| Prison population |
No data |
|
| Murder |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
| Rape |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
| Theft |
No data |
per 100,000 population |
|
Armed clan factions (some, in remoter regions, engaged in family feuds rather than the war) and bandits rule large areas. In Mogadishu a "national" police force has been established, and possession of firearms outlawed. Sharia (Islamic law), now the de facto system, is run in a makeshift fashion by elders. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
1 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
2 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
14 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Bandits and warlords gained rich pickings. Money sent by relatives living overseas is the main income for some people. |
|
Media |
| Newspapers |
There are 5 daily newspapers, including Jamhuuriya, Qaran, and Xiddigta Oktobar |
| TV services |
2 services: limited to the Mogadishu area |
| Radio services |
11 services: mostly political or religious |
|
|
|
Tourism |
|
|
Aid workers and foreign journalists are the only visitors. Land mines are a major hazard. |
|
History |
The lands of the Somalis became UK and Italian colonies in the 1880s. - 1960 Unification at independence.
- 1964–1987 Conflict with Ethiopia over Ogaden region.
- 1969 Gen. Siad Barre takes power.
- 1991 Siad Barre ousted. Civil war and clan chaos. Mass starvation. Somaliland declares secession.
- 1992 Abortive US intervention.
- 1995 UN force withdrawn.
- 1997 Accord signed by 26 clan factions.
- 2000 National reconciliation conference appoints government; warlords dispute its authority.
- 2001 Somali Reconciliation and Restoration Council set up, with support from southern clan leaders.
|
|