COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Latvia is one of the three Baltic states (with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south) which regained independence from Soviet rule in 1991. It lies on a low plain, which nowhere rises above 300 meters (975 ft.). Almost one-third of the population lives in the capital, Riga. Defense-related industries and agriculture play an important role in the economy. Only just over half of the population are ethnic Latvians. |
|
Climate |
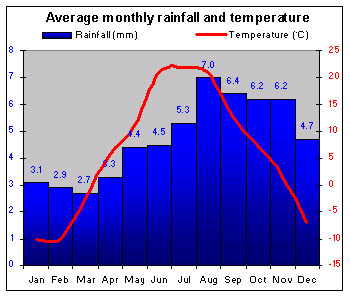 |
Latvia's coastal position means that the climate is temperate, with cold winters and cool summers. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Latvian, Russian |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Latvians make up just over half the population, but are a minority in Riga. Naturalization procedures were simplified in 1998, easing tension with the country's large minority population of ethnic Russians, but a restrictive language law reopened controversy. In mid-2000 Latvian was proclaimed the only official language for the public and private sectors. The divorce rate is high. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
6925
|
M |
GNP World rank |
97
|
|
| Inflation |
3 |
% |
Unemployment |
8 |
% |
|
StrengthsIndustrial production improving after slump. Service sector now providing more than half of GDP. Inflation under control. Foreign investment rising. WeaknessesDependence on imported oil and natural gas for energy. Lack of raw materials. Farming technically backward after dismantling of collective farms. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1998 |
Next election |
2002 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
The 1998 general election boosted center-right parties, all in favor of EU membership and continuing market reforms. The largest single party was the recently formed TP, led by former premier Andris Skele, whose 1995–1997 government prepared the way for economic recovery. The TP was excluded from the new government, but this coalition was short-lived, the populist Skele taking over again in 1999. In May 2000, however, Riga's high-profile mayor, Andris Berzins, was appointed as prime minister as Skele's coalition disintegrated. |
|
International Affairs |
| |
Latvia is one of six "second wave" candidates for admission to the EU which began membership negotiations in 2000. It also has US backing for entry to NATO. Discrimination against Russian-speakers, exemplified by laws passed in 2000 making Latvian the only official language, have strained relations with Russia. |
|
Defence |
| Expenditure (US$) |
70 |
M |
Portion of GDP |
1 |
% |
|
| Army |
3 main battle tanks (T-55) |
| Navy |
4 patrol boats |
| Airforce |
No combat aircraft |
| Nuclear capab. |
None |
|
Building up the military is a priority, and there is now US backing for entry into NATO. Latvia has been participating in NATO's Partnership for Peace program. In February 2000, Russian forces finished dismantling their last military installation in Latvia, the Skrunda radar station. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Amber, dolomite, gravel, gypsum, limestone, peat, sand |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Latvia has very limited natural resources, and is dependent on imports (mainly from Russia) to meet its energy needs. Peat is still burned for energy. Electricity comes chiefly from hydroelectric power and imports from Lithuania and Estonia. Offshore oil exploration is planned. Ventspils deepwater port is being promoted as an oil terminal. |
|
Environment |
| Protected land |
13 |
% |
Part protected land |
No data |
% |
|
|
|
Peat extraction has damaged valuable bog habitat. Pollution of the Baltic Sea and air and water quality in industrial centers are also of concern. Environmental issues featured in pre-independence protests and have retained a high profile. |
|
Communications |
| Main airport |
Riga International |
Passengers per year |
574870 |
|
| Motorways |
0
|
km |
Roads |
22843
|
km |
Railways |
2413
|
km |
|
Riga has the busiest container port in the Baltic. The EU-backed Via Baltica highway, linking Poland and Finland, runs north–south through Latvia. An east–west link of similar standard is a priority. |
|
International Aid |
| Donated (US$) |
Not applicable
|
M |
Received (US$) |
91
|
M |
|
Aid to Latvia comes mainly from the World Bank, the IMF, and the EU. Most goes toward improving the country's infrastructure. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
70 |
Life expect. World rank |
83 |
| Population per doctor |
357 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
10 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Heart diseases, cancers, accidents, respiratory diseases |
|
The state-run system suffers shortages of medicines and equipment. Some improvements have been made, but it is still seriously underfunded. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
99 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
7 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
87 |
% |
Tertiary |
51 |
% |
|
Schools have opened for many minority ethnic groups. There are more than 50,000 students in higher education. |
|
Criminality |
| Crime rate trend |
Up 41% in 1999 |
|
|
|
| Murder |
9 |
per 100,000 population |
| Rape |
5 |
per 100,000 population |
| Theft |
1216 |
per 100,000 population |
|
Organized crime is a growing problem, but general crime levels are lower than in other former Soviet states. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
218 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
303 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
789 |
per 1,000 population |
|
The old bureaucracy has retained its privileged status and contacts, and remains the wealthiest group. Farmers are among the poorest. |
|
Media |
| Newspapers |
There are 23 daily newspapers, including Diena and Neatkariga Rita Avize |
| TV services |
2 services: 1 state-owned, 1 independent |
| Radio services |
16 services: 1 state-owned, 15 independent |
|
|
|
Tourism |
|
|
Riga is the main tourist destination, with many hotels and restaurants. Its medieval center is being restored. |
|
History |
Latvia was dominated by Germany and, briefly, Sweden before Russia completed its conquest in 1795. - 1917 Opposes Russian Bolshevik revolution. Declares independence.
- 1918–1920 Invaded by Bolsheviks and Germany.
- 1920 Gains independence.
- 1944 Incorporated into USSR.
- 1989 Popular Front wins elections; declares independence.
- 1991 Independence recognized.
- 1995 TP-led coalition formed.
- 1998 Elections; LC-led coalition. Naturalization procedure eased.
- 1999 First woman president. Andris Skele of TP returns as premier.
- 2000 Skele resigns; replaced by Andris Berzins.
|
|