COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Sandwiched between the Greater and Lesser Caucasus, Georgia is a mountainous country, with a Black Sea coastline running north–south from Abkhazia to Ajaria. Georgia was one of the first republics to demand independence from the Soviet Union, but has been plagued over recent years by civil war and ethnic disputes in Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Primarily agricultural, it is famous for its wine. |
|
Climate |
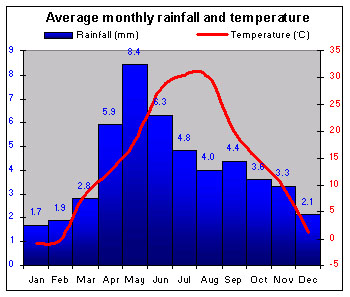 |
Georgia's climate is continental inland and subtropical along the coast, where grapes, citrus fruit, and tea are grown. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Georgian, Russian |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Georgia is a paternalistic society, with strong family and cultural traditions. Approximately 70% of the population is Georgian, with Armenian, Russian, Azeri, Ossetian, Greek, and Abkhaz minorities. More than 300,000 people were displaced by the internal conflicts of the 1990s. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
3183
|
M |
GNP World rank |
129
|
|
| Inflation |
19 |
% |
Unemployment |
15 |
% |
|
StrengthsGateway to West for Azeri oil through pipelines across Georgia to Black Sea and Mediterranean ports. Hyperinflation brought under control in mid-1990s. WeaknessesWar damage and severance of links with other ex-Soviet republics. Large black economy and influential Mafia. Drought and currency crisis in 1998. Serious budget deficit problems. Negative trade balance. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1999 |
Next election |
2003 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
The political situation remains volatile. Eduard Shevardnadze, reelected as president in 2000, has been the target of several assassination attempts. He came to power in 1992 amid civil war with the "Zviadists," supporters of ex-president Zviad Gamsakhurdia, who committed suicide while under fire in late 1993. Fighting raged simultaneously in Abkhazia, where ethnic Abkhazians attempted to secede; ethnic Georgians were expelled. Fighting still flares up sporadically. A UN-brokered peace process begun in mid-2000 soon stalled over the basic issue of the future status of Abkhazia. |
|
International Affairs |
| |
Relations with Russia are strained over regional security and oil pipelines; Georgia is a focus of the US "war on terrorism." |
|
Defence |
| Expenditure (US$) |
116 |
M |
Portion of GDP |
3 |
% |
|
| Army |
90 main battle tanks (T-55, T-72) |
| Navy |
11 patrol boats |
| Airforce |
7 combat aircraft (Su-25) |
| Nuclear capab. |
None |
|
The army's main focus remains Abkhazia. However, US concerns over the presence of Islamic terrorists prompted the arrival in 2002 of US forces to train the regular Georgian army; the security service is already CIA-trained. Russian troops, once numbering over 9000, have been steadily withdrawn since 2000. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Manganese, coal, oil, natural gas, zinc, cobalt, vanadium |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
37m barrels |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
2386 b/d |
|
Known oil reserves are as yet barely developed. Georgia is dependent on Russia for much of its energy supply, although a new US–Georgian oil refinery was opened in eastern Georgia in 1998. Georgia is a predominantly agricultural country, and food processing and wine production continue to be the major industries. Manganese and small quantities of zinc, cobalt, and vanadium are mined. |
|
Environment |
| Protected land |
3 |
% |
Part protected land |
No data |
% |
|
|
|
Radiation from materials left by departing Russian soldiers is a growing problem, as is Black Sea pollution and the protection of upland pastures. |
|
Communications |
| Main airport |
Novo Alexeyevka, Tblisi |
Passengers per year |
270011 |
|
| Motorways |
0
|
km |
Roads |
19354
|
km |
Railways |
1545
|
km |
|
Civil war has seriously disrupted transportation. A new rail route and oil pipeline from Baku to the Black Sea ports of Poti and Supsa was opened in 1999. |
|
International Aid |
| Donated (US$) |
Not applicable
|
M |
Received (US$) |
170
|
M |
|
As well as aid for infrastructure projects, Georgia receives Western support for institutional and financial sector reform. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
73 |
Life expect. World rank |
51 |
| Population per doctor |
227 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
17 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Circulatory and respiratory diseases, cancers, accidents |
|
The health system was limited under the Soviet Union. Internal strife and a lack of resources have prevented any recent investment. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
99 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
5 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
95 |
% |
Secondary |
79 |
% |
Tertiary |
34 |
% |
|
Since independence, education has stressed Georgian language and history. All levels of education are seriously underfunded. Tbilisi University was formerly of a high standard. |
|
Criminality |
| Crime rate trend |
Up 7% 1996–1998 |
|
|
|
| Murder |
5 |
per 100,000 population |
| Rape |
1 |
per 100,000 population |
| Theft |
82 |
per 100,000 population |
|
Organized crime under the control of Mafia-style groups has flourished since independence in 1991. The judicial system currently favors Shevardnadze and his supporters. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
49 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
139 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
474 |
per 1,000 population |
|
There is a small wealthy and extravagant elite, but most Georgians live in poverty. Wages and welfare are often in arrears. |
|
Media |
| Newspapers |
There are 3 daily newspapers, Rezonansi, published in Georgian, Georgian Messengerand Georgian Timesi published in English. |
| TV services |
2 services: 1 state-controlled, 1 independent |
| Radio services |
1 state-controlled service |
|
|
|
Tourism |
|
|
The volatile political situation has discouraged tourism, but numbers are rising again. Most tourists still come from former Soviet states. |
|
History |
A Russian protectorate from 1763, Georgia was absorbed into the Russian Empire in 1801. It was established as an independent state under a Menshevik socialist government in 1918. - 1920 Recognized by Soviet Russia as independent state.
- 1921 Soviet Red Army invades. Effectively part of USSR.
- 1922–1936 Incorporated into Transcaucasian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (TSFSR).
- 1989 Pro-independence riots in Tbilisi put down by Soviet troops.
- 1990 Declares sovereignty.
- 1991 Independence. Zviad Gamsakhurdia elected president.
- 1992 Gamsakhurdia flees Tbilisi. Shevardnadze elected chair of Supreme Soviet and State Council.
- 1992–1993 Abkhazia conflict.
- 1995 Shevardnadze narrowly survives assassination attempt, subsequently elected president.
- 1999 Opening of pipeline from Caspian to Black Sea.
- 2000 Shevardnadze reelected. Russian troop withdrawal begins.
|
|