COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Spanning the Central American isthmus and wedged between Nicaragua and Panama, Costa Rica was under Spanish rule until 1821 and gained full independence in 1838. From 1948 until the end of the 1980s, it had the most developed welfare state in Central America. Costa Rica is nominally a multiparty democracy, but two parties dominate. Its army was abolished in 1948; the 1949 constitution then forbade national armies. |
|
Climate |
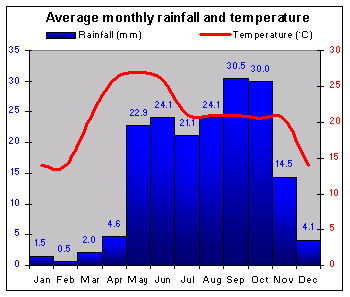 |
The Caribbean coast has heavy rainfall, while the Pacific coast is much drier. The central uplands are temperate. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Spanish, English Creole, Bribri, Cabecar |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
The majority of the population is mestizo, of partly Spanish origin. One-third of people in the Limón area are black and often English-speaking. There are only about 5000 indigenous Indians. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
14510
|
M |
GNP World rank |
76
|
|
| Inflation |
11 |
% |
Unemployment |
5 |
% |
|
StrengthsMajor coffee, beef, and banana exports. Expanding tourism also fueling construction. Strong inward investment. Favorable WTO ruling on banana access to EU market. WeaknessesCoffee, beef, and bananas all vulnerable to falling prices. History of high inflation. Dependence on imported oil. Large domestic debt. Competitiveness hindered by insufficient investment in infrastructure. State monopolies have deterred investment in energy, telecommunications, and insurance sectors. Inefficient management. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2002 |
Next election |
2006 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
Politics has long been dominated by the PUSC and PLN, both of which have close ties to major banana- and coffee-growing families. Historically the USA has exercised a very powerful influence on politics. The PLN in 1994 promised reforms to its previous austerity policies, but soon came under pressure from international financial organizations to reduce the budget deficit. Harsh structural adjustment measures proved highly unpopular. In 1998 the PUSC regained power. President Miguel Angel Rodríguez launched a three-year plan to reduce inflation and poverty, create thousands of jobs, and stimulate foreign investment in state companies. His chosen successor, Abel Pacheco, needed an unprecedented second run-off to clinch the presidency in 2002, when voter turnout hit an all-time low. |
|
International Affairs |
| |
Trade ties with the USA and protection of prices for coffee and bananas are priorities. Trade ties have been agreed with Canada and Chile. Tensions with Nicaragua over their mutual border were resolved in 2000, but illegal immigrants remain an issue. |
|
Defence |
| Expenditure (US$) |
84 |
M |
Portion of GDP |
1 |
% |
|
| Army |
None |
| Navy |
None |
| Airforce |
None |
| Nuclear capab. |
None |
|
Costa Rica emerged from the 1948 civil war as a neutral, demilitarized modern state. A 4400-strong Civil Guard is complemented by a largely military-trained police force. Spending on security has long been the lowest in the region. Lack of a common command structure hinders the influence of the security forces but also renders them less open to public control. Right-wing paramilitary groups exist. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Bauxite, gold, silver, manganese, mercury |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Costa Rica has large bauxite deposits in the south – aluminum smelting is an important industry. Small quantities of gold, silver, manganese, and mercury are also mined. Self-sufficiency in energy is being pursued through the development of hydroelectric power. Forests cover 34% of the country. |
|
Environment |
| Protected land |
14 |
% |
Part protected land |
3 |
% |
|
|
|
Despite good environmental regulation, reckless economic development has contributed to extensive deforestation. Pasture land now covers some 45% of the territory and pesticide abuse by agribusiness has poisoned rivers and threatened species. Urban sprawl has degraded the fertile central valley. |
|
Communications |
| Main airport |
Juan Santamar&299;a, San Jos&275; |
Passengers per year |
988000 |
|
| Motorways |
663
|
km |
Roads |
7827
|
km |
Railways |
471
|
km |
|
San José is the hub of a well-used bus network. Railroads, badly damaged by an earthquake in 1991, are being reconstructed. |
|
International Aid |
| Donated (US$) |
Not applicable
|
M |
Received (US$) |
12
|
M |
|
During the 1980s Costa Rica was a large recipient of US aid designed to inoculate it against left-wing insurgencies such as those in El Salvador, Guatemala, and neighboring Nicaragua. Peace in the region has led to a sharp decline in such aid, especially given the country's relatively high per capita income. World Bank aid will help modernize Juan Santamaría international airport. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
76 |
Life expect. World rank |
33 |
| Population per doctor |
1111 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
10 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Heart diseases, accidents, cancers, perinatal deaths |
|
The public health system is one of the most developed in Latin America. Health was allocated 29.3% of total public spending in 1999. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
96 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
6 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
52 |
% |
Tertiary |
31 |
% |
|
Costa Rica has the highest literacy rate in the isthmus, and is home to the University of Central America. |
|
Criminality |
| Crime rate trend |
Up 71% 1989–1994 |
|
|
|
| Murder |
10 |
per 100,000 population |
| Rape |
8 |
per 100,000 population |
| Theft |
626 |
per 100,000 population |
|
Costa Rica is the least violent Central American country. Attacks on and kidnappings of tourists are rare but have dented its image as a safe haven. Drug cartels use the country to transfer cocaine to the USA and Europe. Police show hostility toward immigrants from neighboring countries. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
88 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
249 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
231 |
per 1,000 population |
|
The plantation-owning families are the wealthiest group; official figures give one-fifth of the population as living in poverty. |
|
Media |
| Newspapers |
There are 8 daily newspapers, including La Nación, La República, La Prensa Libre, and Diario Extra |
| TV services |
8 stations: 1 state-owned, 7 independent |
| Radio services |
State-owned and independent stations |
|
|
|
Tourism |
| Visitors per year |
1088000 |
|
Tourism brought in $1 billion in 1999 and is expanding, with the help of both domestic and foreign investment. A new 154-room hotel in San José and a comparable one on the Pacific coast attract wealthy visitors. |
|
History |
Costa Rica, ruled since the 16th century by Spain, became an independent state in 1838. - 1948 Disputed elections lead to civil war; ended by Social Democratic Party (later the PLN) forming provisional government under José Ferrer. Army abolished.
- 1949 New constitution promulgated.
- 1987 Central American Peace Plan initiated by President Arias.
- 1998 PUSC returns to power.
|
|