COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Landlocked in north central Africa, Chad has had a turbulent history since independence from France in 1960. Intermittent periods of civil war, involving French and Libyan troops, followed a military coup in 1975. Following a coup in 1990, an interim government commenced the transition to multipartyism, now enshrined in a new constitution. The discovery of large oil reserves could eventually have a dramatic impact on the economy. The tropical, cotton-producing south is the most populous region. |
|
Climate |
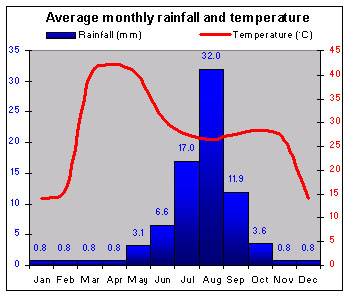 |
There are three distinct zones: the tropical south, the central semiarid Sahelian belt, and the desert north. |
|
People |
| Languages |
French, Sara, Arabic, Maba |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
About half the population, mainly the Sara-speaking and related peoples, is concentrated in the south in one-fifth of the national territory. Most of the rest are located in the central sultanates. The northern third of Chad has a population of only 100,000 people, mainly nomadic Muslim Toubou. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
1541
|
M |
GNP World rank |
143
|
|
| Inflation |
4 |
% |
Unemployment |
No data |
% |
|
StrengthsDiscovery of large oil deposits and building of Chad–Cameroon pipeline could transform economy. Cotton industry; potential for other agriculture in south. Strategic trading location in heart of Africa. Natron and uranium deposits. WeaknessesUnderdevelopment and poverty. Lack of transportation infrastructure. Political instability. Frequent droughts. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2002 |
Next election |
2006 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
Idriss Déby overthrew President Hissène Habré in 1990 after an armed invasion from Sudan. He promised multipartyism, and in 1992 political parties were legalized for the first time since the early 1960s. After many delays, the transitional process led to a successful referendum in 1996 on a new constitution based on the French model. President Déby was confirmed in office in elections in 1996 and again in 2001. His ruling MPS just achieved an overall majority in the 1997 elections, and expanded its share of seats further in 2002. A shaky Libyan-brokered peace deal in 2002 failed to end the rebellion in the north which had begun in 1999. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Natron, uranium, oil, kaolin, soda, rock salt |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Reserves currently unexploited |
|
A consortium of Exxon, Shell, and Elf has discovered large oil reserves in the south, mostly near Doba, which could make Chad a major African producer. Natron, found north of Lake Chad, is the only mineral currently exploited. There is uranium in the Aozou strip. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
46 |
Life expect. World rank |
173 |
| Population per doctor |
20000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
101 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Diarrheal, parasitic, and communicable diseases |
|
There are few city hospitals and under 300 smaller health centers. One in five children die before the age of five. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
43 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
2 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
67 |
% |
Secondary |
11 |
% |
Tertiary |
1 |
% |
|
Education is based on the French model, although there are Koranic schools in the north. Primary schooling is officially compulsory, but enrollment is only 46%. Recently, World Bank aid has been directed at elementary schooling. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
2 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
1 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
1 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Poverty is almost universal in Chad; the middle class is very small. There are few wealthy individuals. Habré looted the treasury when he was overthrown in 1990.
|
History |
France extended its domination of the area now known as Chad after ousting the last Arab ruler in 1900. - 1960 Independence. One-party state.
- 1973 Libyans seize Aozou strip.
- 1975 Coup by Gen. Félix Malloum.
- 1979–1982 North–south civil war.
- 1980 Goukouni Oueddei in power.
- 1982 Hissène Habré (northerner) defeats Oueddei.
- 1990 Idriss Déby overthrows Habré, who flees to Senegal.
- 1994 Libya relinquishes Aozou strip.
- 1996 National cease-fire; new constitution.
- 1997 Déby's MPS wins elections.
- 1999 Rebellion in north.
- 2001 Déby reelected.
- 2002 MPS expands its majority.
|
|