COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
The west African state of Sierra Leone was founded by the British in 1787 for Africans freed from slavery. The terrain rises from coastal lowlands to mountains in the northeast. A democratic government took office in 1996 against a background of bloody rebellion. Sierra Leone soon plunged into a savage civil war. Although a 1999 peace agreement was short-lived, an ECOWAS-brokered accord signed in late 2000 seemed to be holding. |
|
Climate |
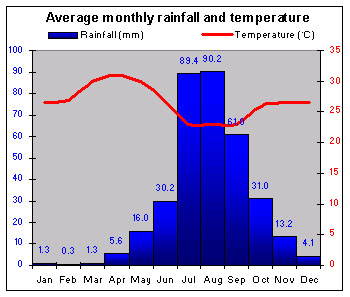 |
Coastal rainfall can be as high as 500 cm (197 in.) a year, making Sierra Leone one of the wettest places in coastal west Africa. Humidity is consistently high – about 80% – during the rainy season. The dusty, northeasterly harmattan wind often blows during the hotter dry season from November to April. The northeastern savannas are drier, with 190–250 cm (75–98 in.) of rain, and are one of the hottest areas. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Mende, Temne, Krio, English |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Freetown was founded as a settlement for people freed from slavery. Its citizens' British and North American origins account for Sierra Leone's strongly anglicized Creole culture. An estimated two million people were displaced by the civil war. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
647
|
M |
GNP World rank |
164
|
|
| Inflation |
-1 |
% |
Unemployment |
No data |
% |
|
StrengthsDiamonds, although much of the output is smuggled; official exports resumed in late 2000 under a UN certification scheme. Some bauxite and rutile production. WeaknessesYears of instability affected the most productive areas, including diamond fields, with severe disruption of agricultural and mining sectors. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2002 |
Next election |
2007 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
A rebellion by the Revolutionary United Front (RUF) in 1991 sparked a decade of particularly savage civil war. President Ahmad Kabbah was popularly elected at the head of a civilian government in 1996. A peace and power-sharing agreement, reached in 1999, collapsed in 2000. A large UN and British force helped to secure a new cease-fire later that year. The RUF, remodeled as a political party, failed to win a single seat in the 2002 elections, which resulted in a convincing victory for Kabbah and his SLPP. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Diamonds, rutile, bauxite, gold, titanium |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
The large diamond deposits need fresh investment as areas currently being mined become depleted. The southeast is the most fertile region. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
39 |
Life expect. World rank |
192 |
| Population per doctor |
10000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
154 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Communicable diseases, malaria, malnutrition |
|
Only traditional care is available outside the capital. WHO have ranked Sierra Leone's health care bottom in the world in terms of attainment and efficiency. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
36 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
1 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
57 |
% |
Secondary |
22 |
% |
Tertiary |
2 |
% |
|
Freetown has a long tradition of education, and its university, Fourahbay College, became affiliated with Durham University in the UK in 1876. In recent times, its students have often been active in political dissent. Educational provision has inevitably deteriorated over the past decade. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
2 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
4 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
13 |
per 1,000 population |
|
In terms of quality of life, the UN has repeatedly ranked Sierra Leoneans as the world's poorest people. Any wealth is associated with political power.
|
History |
Freetown was founded in 1787 and became a British colony in 1808; the interior was annexed in 1896. - 1961 Independence.
- 1978 Single-party republic.
- 1991 RUF rebellion starts.
- 1996 Civilian rule restored after 1992 army coup; Kabbah president.
- 1997 Coup ousts Kabbah for a year.
- 1999–2000 Attempt at power-sharing.
- 2001 RUF ends insurgency.
- 2002 Government and UN agree to set up war crimes court. Kabbah and SLPP reelected.
|
|