COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Landlocked Rwanda lies just south of the equator in east central Africa. Since independence in 1962, ethnic tensions have dominated politics. In 1994, the violent death of the president led to appalling political and ethnic violence. Over half of the surviving population were displaced. The perpetrators of the genocide held sway in desperately overcrowded refugee camps in adjacent countries, greatly complicating the process of eventual repatriation and reintegration. |
|
Climate |
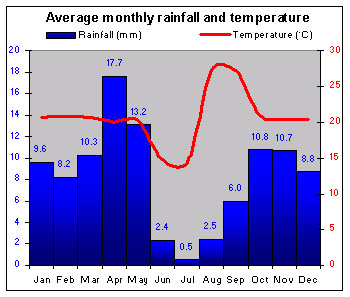 |
Rwanda's climate is tropical, tempered by altitude. Two wet seasons allow for two harvests each year. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Kinyarwanda, French, Kiswahili, English |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
The Hutu and Tutsi are the main groups; few of the Twa pygmies, the original inhabitants, remain. For over 500 years, the cattle-owning Tutsi were politically dominant, oppressing the land-owning Hutu majority. In 1959, violent revolt led to a reversal of the roles. The two groups have since been waging a spasmodic war. It is estimated that 800,000 people were killed in the violence of the mid-1990s, the majority of them Tutsi victims massacred by Hutus. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
1988
|
M |
GNP World rank |
138
|
|
| Inflation |
4 |
% |
Unemployment |
No data |
% |
|
StrengthsCurrently none. Assuming stability, Rwanda could produce coffee and tea. Possible oil and gas reserves. Tourism potential. WeaknessesEconomic activity completely disrupted by 1994 violence. Lengthy journey to Kenyan and Tanzanian ports means high transportation costs. Few resources. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1988 |
Next election |
2003 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
In 1993 a peace accord to end the rebellion launched in 1990 by the Tutsi-dominated Rwandan Patriotic Front (FPR) was signed. However, the fragile peace process was halted in 1994 by the death of the president in a plane crash. Genocidal violence was unleashed between the mainly Hutu supporters of the old regime and its mainly, but not exclusively, Tutsi opponents. An estimated 800,000 died and millions fled the conflict, in which the FPR eventually gained control. Hutu were allocated key government posts, including the presidency, but when, in March 2000, the balance was shifted to increased Tutsi representation, President Pasteur Bizimungu resigned. Vice President Paul Kagame, the regime's dominant figure and the FPR leader, was formally elected president in April. Presidential and parliamentary elections are planned for end-2003, following the approval of a constitution. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Tin, tungsten, gold, columbo-tantalite, methane gas |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Gas deposits in Lake Kivu are likely to be explored with the DRC. Only 20% of urban homes are on the national power grid. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
40 |
Life expect. World rank |
189 |
| Population per doctor |
20000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
123 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Malaria, measles, diarrheal diseases, violence |
|
Rwanda has a network of 34 hospitals and 188 health centers. 11% of the population are estimated to be HIV-positive. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
67 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
2 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
9 |
% |
Tertiary |
1 |
% |
|
Schools are run by the state and by Christian missions. Primary education is officially compulsory, but only 78% of children attended in 1997; just 8% go on to secondary schooling. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
2 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
2 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
0 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Wealth is limited to the country's political elite. Most Rwandans are poor farmers; Twa pygmies and refugees are poorer still.
|
History |
The Hutu majority began to arrive in the 14th century, the warrior Tutsi in the 15th. From 1890, German and then Belgian colonizers acted to reinforce Tutsi dominance. - 1962 Independence. Hutu-led government.
- 1960s Tutsi revolt; massacres by Hutu; thousands of Tutsi in exile.
- 1973 Coup by Gen. Habyarimana.
- 1994 Habyarimana dies in plane crash. Genocidal violence unleashed by Hutu extremist regime, ousted by Tutsi-led FPR. Hutu refugee exodus.
- 1995 Start of war crimes tribunal.
- 1997 Refugees forcibly repatriated.
- 2000 Prominent Hutus leave office.
- 2001 Limited troop withdrawal from DRC.
|
|