COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYRM) is landlocked in southeastern Europe. Despite the signing of an accord in 1995, Greece remains suspicious that it harbors ambitions about absorbing northern Greece – also called Macedonia – in a "Greater Macedonia." A militant movement among ethnic Albanians erupted into violent conflict in March–September 2001, but a peace agreement was reached after the involvement of a NATO force. |
|
Climate |
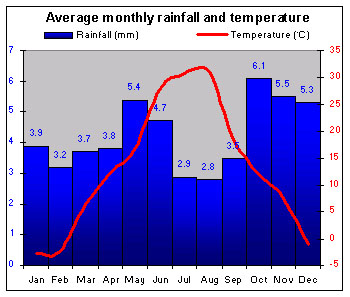 |
The FYRM has a continental climate. Winter snow supports skiing. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Macedonian, Albanian, Serbo-Croat |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Slav Macedonians, speaking a language akin to Bulgarian, are in the majority. The large Albanian minority claims to amount to over one-third of the population. They maintain strong links with Albanians in neighboring states. Months of violent conflict sparked by ethnic Albanian insurgents seeking greater rights resulted in a new constitution in 2001 guaranteeing equality. Macedonians are mostly Orthodox Christians, but there are a substantial number of Slavic Muslims (Pomaks), whose ancestors converted during the Ottoman occupation. Ethnic Albanians are mostly Muslim. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
3696
|
M |
GNP World rank |
124
|
|
| Inflation |
-1 |
% |
Unemployment |
32 |
% |
|
StrengthsGrowth in private sector and foreign investment. Mineral resources. WeaknessesPoorest of former Yugoslav republics. Loss of trade in mid-1990s due to Greek embargo and sanctions on Yugoslavia. Dependence on oil, gas, and machinery imports. Disruption caused by Kosovo conflict and 2001 violence. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1998 |
Next election |
2002 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
Political parties are largely fragmented along nationalist lines. The right-wing VMRO–DPMNE and the DPA are the relatively moderate representatives of the ethnic Slav and Albanian communities respectively. VMRO–DPMNE Prime Minister Ljubco Georgievski led a pan-ethnic coalition, including the DPA, after the defeat of reformed communist parties in 1998. Although hounded by the opposition, this government survived into 2001, when an insurrection by Albanian rebels (UCK) prompted the creation of a government of "national unity." The fragile grouping survived long enough to conclude a peace deal in August with the UCK, drafting a new, more equal constitution and guaranteeing Albanian rights. However, once peace was secured at the end of 2001, the coalition fractured. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Coal, copper, bauxite, iron, antimony, chromium, lead, zinc |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Minerals remain underexploited. South-facing fertile plains produce early fruit and vegetables for EU markets. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
73 |
Life expect. World rank |
51 |
| Population per doctor |
455 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
14 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Cerebrovascular and heart diseases, cancers |
|
In theory, the state guarantees universal health care, but effective and speedy treatment is increasingly only available in the private sector. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
94 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
5 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
83 |
% |
Tertiary |
22 |
% |
|
A new university at Tetovo, with teaching in Albanian as well as Macedonian, officially opened in 2001. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
139 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
255 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
282 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Incomes have fallen by more than two-thirds since 1990, although smuggling and organized crime have made a few people conspicuously wealthy.
|
History |
The end of Ottoman rule saw historic Macedonia divided between Serbia, Bulgaria, and Greece in 1912–1913. What is now FYRM was incorporated into Serbia. - 1944 Tito establishes republic, stressing Macedonian identity.
- 1989–1990 Multiparty elections.
- 1991 Independence declared. EU recognition delayed by Greeks.
- 1995 Accord with Greece.
- 1998–1999 Right-wing VMRO– DPMNE coalition wins elections.
- 1999 Upheaval over Kosovo conflict.
- 2001 Peace agreement and new constitution after NATO involvement to end conflict with ethnic Albanian militants.
|
|