COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Mostly undulating steppe country, Moldova is the smallest and most densely populated of the former Soviet republics. Once a part of Romania, it was incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1940. Independence in 1991 brought with it the expectation that Moldova would be reunited with Romania. In a 1994 plebiscite, however, Moldovans voted against the proposal. Most of its population is engaged in intensive agriculture. |
|
Climate |
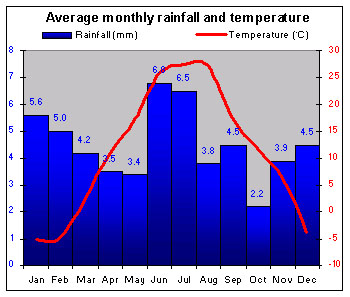 |
Warm summers, mild winters, and moderate rainfall give Moldova an ideal climate for cultivation. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Moldovan, Romanian, Russian |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Moldovans are ethnically identical to Romanians. There are 153,000 Gagauz (Orthodox Christian Turks) in the south, and a population of mixed Russian–Moldovan–Ukrainian parentage on the eastern bank of the Dniester. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
1428
|
M |
GNP World rank |
147
|
|
| Inflation |
31 |
% |
Unemployment |
11 |
% |
|
StrengthsAgriculture – notably wine, tobacco, and cotton – and food processing. Light manufacturing. WeaknessesDependent on Russia as source of raw materials and fuel, and main market for exports. Dramatic shrinking of economy since independence. Isolated location; weak transportation network. Slow pace of reform. Cumbersome bureaucracy. Strong black economy. Foreign debt – over 50% of GDP – costs 20% of export earnings to service. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2001 |
Next election |
2005 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
Moldova declared its independence in 1991. Reformist Petru Lucinschi was elected president in 1996 but faced stiff opposition from the increasingly powerful left: the revived CPM won most seats in the 1998 elections. Parliament ended direct presidential elections in 2000, but deadlock ensued over the appointment of Lucinschi's successor, forcing Parliament's dissolution in 2001. The new Parliament, with a big CPM majority, chose CPM leader Vladimir Voronin as president. However, the left's popularity has faltered, with mass discontent over its apparent eagerness to align Moldova with Russia rather than the West. Transdniestria (on the eastern bank of the river Dniester) and Gagauzia (in the south) declared themselves as republics in 1990. While Gagauzia accepted autonomous status as provided for in the 1994 constitution, Transdniestria still seeks independence. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Lignite, phosphates, gypsum, oil, natural gas |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Oil and gas reserves not exploited |
|
Moldova has few mineral resources. It has to import all its fuel and most of its electricity. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
67 |
Life expect. World rank |
116 |
| Population per doctor |
286 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
18 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Circulatory diseases, cancers, accidents |
|
The centralized health service is poor by regional standards. There are serious shortages of medical supplies. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
99 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
11 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
97 |
% |
Secondary |
81 |
% |
Tertiary |
27 |
% |
|
Education switched from a Soviet to a Romanian (French-inspired) system after 1991. Mass protests met plans in 2002 to make Russian compulsory in schools. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
54 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
133 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
297 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Former communist officials have been well placed to benefit from the sale of state-owned businesses. Car ownership is low but rising. However, pensions and wages are often months in arrears. In 1998 the benefits for low-income families and veterans were scrapped. Ethnic Gagauz (Orthodox Christian Turks) are the poorest group.
|
History |
Modern Moldova corresponds roughly to the eastern part of the Romanian principality of Moldavia, which existed for 500 years from 1359. Most of it was annexed by Russia in 1812 as Bessarabia. - 1918 Bessarabia joins Romania.
- 1924 Moldovan Autonomous Soviet Republic formed within USSR.
- 1940 Romania cedes Bessarabia to Ukrainian and Moldovan SSRs.
- 1941–1945 Bessarabia again under Romanian control.
- 1945 Returns to Soviet control.
- 1990 Declares sovereignty.
- 1991 Independence.
- 1993–1994 Pro-unification parties' election defeat; referendum rejects Romanian unification. Rejoins CIS.
- 1998 Communist revival at general election.
- 2001 CPM wins big majority. Voronin becomes president.
- 2002 Mass protests over education plans.
|
|