COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Founded in 1847 by freed slaves from the USA, Liberia today is struggling to recover from a civil war which reduced it to anarchy in the 1990s. Facing the Atlantic in equatorial west Africa, most of its coastline is characterized by lagoons and mangrove swamps. Inland, a grassland plateau supports the limited agriculture (just 1% of land is arable). Liberia has the world's largest flag of convenience merchant fleet. |
|
Climate |
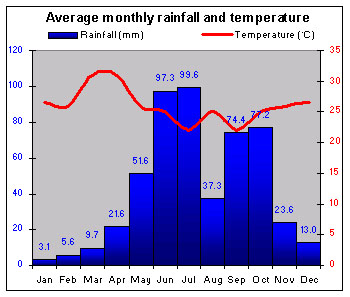 |
There is one long rainy season from May to October, except in the southeast which has two separate rainy seasons. Temperatures are consistently high. During the dry season, when the dust-laden harmattan wind blows, they rise even higher inland. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Kpelle, Vai, Bassa, Kru, Grebo, Kissi, Gola, Loma, English |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
A key distinction in Liberia has been between Americo-Liberians, the descendants of those freed from slavery (known as "civilized persons"), and the majority indigenous "tribals." The latter were long held in contempt by the Americos, but intermarriage and political assimilation since 1944 have softened attitudes. Intertribal tension in Liberia is now a more serious problem, and was the main cause of the civil war which erupted in 1990. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
1029
|
M |
GNP World rank |
153
|
|
| Inflation |
5 |
% |
Unemployment |
70 |
% |
|
StrengthsPotential for reviving the Firestone rubber plantation and huge LAMCO iron ore mine. Tropical timber, but reserves declining. WeaknessesLittle commercial activity, and low confidence. Political instability. UN sanctions on diamond trade from 2001. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1997 |
Next election |
2003 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
1997 |
Next election |
2006 |
|
Liberian politics collapsed after 1990 into a chaotic, bloody, and many-sided conflict. A peace agreement finally signed in 1996 provided for presidential and legislative elections in 1997, won by Charles Taylor and his NPP, formerly the National Patriotic Front of Liberia (NPFL), the predominant armed faction. Some 700,000 refugees began returning, but instability continued, and intense fighting broke out in the north in mid-2000 following the formation of a new rebel faction, Liberians United for Reconciliation and Democracy. Thousands of civilians fled the area in 2001 and 2002 as fighting escalated. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Iron ore, diamonds, gold, barytes, kyanite, columbite, manganese |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Liberia has an estimated billion tonnes of iron ore reserves at Mount Nimba, but even when peaceful conditions return, the current state of world demand would barely justify exploitation. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
47 |
Life expect. World rank |
171 |
| Population per doctor |
20000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
111 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Communicable, diarrheal, parasitic, and heart diseases |
|
Very few people have access to basic health care. The infant mortality rate remains among the highest in the world. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
54 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
6 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
83 |
% |
Secondary |
24 |
% |
Tertiary |
7 |
% |
|
Originally based on the US model, the education system effectively collapsed during the civil war. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
3 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
2 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
25 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Power and wealth have a very direct connection in Liberia. Both the Americo-Liberian regimes and the Doe regime which replaced them, saw the state as a source of plunder in the form of well-paid jobs and kick-backs from contracts. The factions in the 1990–1996 civil war sought similar power. Most ordinary Liberians live in rural poverty.
|
History |
Between 1816 and 1892, 22,000 liberated slaves, most from the USA, settled in Liberia, established as a republic in 1847. - 1980 Coup. President assassinated by Samuel Doe.
- 1990 Outbreak of civil war.
- 1991 Doe assassinated.
- 1996 Second peace agreement.
- 1997 Charles Taylor president.
- 2001 Borders with Guinea and Sierra Leone closed. Conflict with rebels escalates.
- 2002 State of emergency declared.
|
|