COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Oil-rich Iraq, divided by the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, shares borders with
Iran, Turkey, Syria, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and Kuwait. The Euphrates valley is
fertile, but most of the country is desert or mountains. Iraq was the site of the
ancient civilization of Babylon. Today, it encompasses Shi'a Muslim holy shrines.
After the removal of the monarchy in 1958, it experienced domestic political turmoil.
Despite Iraq's defeat in the 1991 Gulf War, the current regime (in place since 1979)
retained power until April 2003, when a US led invasion ousted the Saddam Hussein
regime. |
|
Climate |
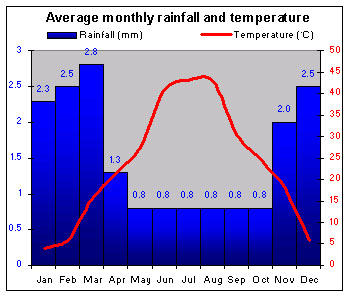 |
The weather is dry and rainfall is low and unreliable, except in the northeast. Iraq experiences a wide range of temperatures. The south has a desert climate, with hot, dry summers and mild winters. In mountainous Iranian and Turkish border regions winters can be harsh, with frost and heavy falls of snow. Sudden hot spells are a unique feature of winter in the center and north of the country. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Arabic, Kurdish, Armenian, Assyrian |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
In addition to the Arab and Kurdish populations, Iraq has a small number of minority
groups, such as Turks and Persians. Over 90% of the population are Muslim, while the rest
comprise a variety of Christian sects. Since the creation of Israel, most Iraqi Jews have
emigrated. The Arab Muslims are divided into Sunni and Shi'a sects. The Shi'a form the
largest single religious group; however, Shi'a divines do not have as intimate a connection
with the people as they do in Iran and their influence on government is
limited. Since the mid-1970s, many Iraqis have moved, or been forced to move, to the
cities, where some three-quarters of the population now live. In the marshes of the
extreme south, communities of mainly Shi'a Marsh Arabs survive. In the wake of the 1991
Gulf War, some of these attempted a rebellion against the state, which drained the marshes
in order to destroy both the people and their culture. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
20000
|
M |
GNP World rank |
64
|
|
| Inflation |
100 |
% |
Unemployment |
No data |
% |
|
StrengthsSecond-largest crude oil and natural gas reserves in OPEC. Large labor force. WeaknessesInability to sell oil on the international market; Iraq's GNP halved by UN sanctions. Once-thriving agricultural sector devastated by war. ProfileBefore 1990, Iraq was the world's third-largest oil supplier. Under sanctions, oil was produced only for domestic consumption. Limited oil exports under strict UN supervision were resumed for the first time in December 1996, and in 2000 the UN Security Council approved a resolution permitting Iraq to buy parts and equipment for the oil industry. The denial of Western assistance following the 1991 Gulf War has stifled Iraq's economy, although the resumption of some informal economic links and the revision of UN sanctions in 2002 may lead to some improvement. The once thriving agricultural sector was badly affected by the war. The manufacturing industry is at a standstill. The introduction of draconian penalties, including the death sentence, have failed to curb the black market or halt the sharp depreciation in the value of the dinar. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2000 |
Next election |
2004 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
Iraqi politics are in a state of transition following the successful US-led Invasion of Iraq in 2003, and the subsequent overthrow of Saddam Hussein's regime. Coalition forces are working to facilitate the establishment of a freely elected government. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Oil, natural gas, sulfur |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
112.5bn barrels |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
2.41m b/d |
|
Iraq has huge reserves of oil and gas. The oil industry is controlled by the Iraqi National Oil Company. Total gas reserves, many of which are associated with oil, are proven to be 3.11 trillion cu. m (110 trillion cu. ft.), with estimates of a further 4.25 trillion cu. m (150 trillion cu. ft.). Most electricity is generated from oil, although hydroelectric power also makes a small contribution. Reserves of phosphates, sulfur, gypsum, and salt are also exploited. Before the invasion of Kuwait and subsequent war, Iraq supplied 80% of the world's trade in dates. Production is now sharply down. Food is now produced simply for domestic consumption. Iraq has, however, achieved a degree of self-sufficiency in such crops as wheat, rice, and sugarcane. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
61 |
Life expect. World rank |
136 |
| Population per doctor |
2000 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
93 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Pneumonia, influenza, cancers, heart diseases |
|
An effect of UN sanctions has been to aggravate the shortage of medical supplies and equipment, and deaths among children and the elderly have spiraled sharply. The increase in the number of children born with birth defects since 1991 is attributed to the use of depleted uranium shells during the Gulf War. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
56 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
5 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
88 |
% |
Secondary |
20 |
% |
Tertiary |
13 |
% |
|
Education is free and universal, except in remote rural areas. Primary education has
been made compulsory in an effort to reduce illiteracy. There are six universities.
Academics authorized the organized plunder of antiquities and university equipment from
Kuwait during the 1990 occupation. University scientists worked closely with the regime on
weapons research programs. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
36 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
29 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
83 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Vulnerable sections of society have been particularly affected by UN sanctions. Middle-class citizens and traders are able to benefit from Iraq's open border with Jordan.
|
History |
Iraq became independent in 1932. In 1958, the Hashemite dynasty was overthrown when King
Faisal died in a coup led by the military under Brig. Kassem. He was initially supported by
the Iraqi Ba'ath Party. - 1961 Start of Kurdish rebellion. Iraq claims
sovereignty over Kuwait on the eve of Kuwait's independence.
- 1963 Kassem
overthrown. Col. Abd as-Salem Muhammad Aref takes power. Kuwait's sovereignty
recognized.
- 1964 Ayatollah Khomeini, future leader of Iran, takes refuge at
Najaf in Iraq.
- 1966 Aref is succeeded by his brother, Abd
ar-Rahman.
- 1968 Ba'athists under Ahmad Hassan al-Bakr take
power.
- 1970 Revolutionary Command Council agrees manifesto on Kurdish
autonomy.
- 1972 Nationalization of Western-controlled Iraq Petroleum
Company.
- 1978 Iraq and Syria form economic and political
union.
- 1979 Saddam Hussein replaces al-Bakr as
president.
- 1980 Outbreak of Iraq–Iran war.
- 1982 Shi'a
leader Mohammed Baqir al-Hakim, exiled in Tehran, forms Supreme Council of the Islamic
Revolution in Iraq.
- 1988 Iraq and Iran agree cease-fire. Iraqi chemical
weapons attack on Kurdish village of Halabja.
- 1990 British journalist Farzad
Bazoft hanged for spying. Iraq and Iran restore diplomatic relations. Iraq invades Kuwait.
UN imposes trade sanctions.
- 1991 Gulf War. US-led military coalition defeats
Iraq and liberates Kuwait. Iraqi regime suppresses Shi'a rebellion.
- 1992
Western powers proclaim air exclusion zone over southern Iraq.
- 1994 Outbreak
of Kurdish civil war. Iraq recognizes Kuwaiti sovereignty.
- 1995 Government
minister Gen. Hussein Kamil defects to Jordan, and is murdered on his return to Iraq in
January 1996.
- 1996 First legislative elections since 1989 are won by ruling
Ba'ath Party. UN supervises limited sales of Iraq oil to purchase humanitarian
supplies.
- 1998–1999 UN weapons inspection teams refused reentry into
Iraq; USA and UK mount punitive air strikes.
- 2003 US-led coalition invades
Iraq and topples Saddam Hussein's regime.
|
|