COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Lying on the northern edge of South America, Guyana stretches 600 km (375 miles) from dense tropical rainforests deep in the interior, through broad savanna and mountains dotted with waterfalls, to the narrow Atlantic coastal plain which is home to most of the population. A British colony from 1814 until independence in 1966, Guyana has closer cultural and diplomatic ties with the mostly anglophone Caribbean than with its Spanish-, Dutch-, and Portuguese-speaking neighbors. |
|
Climate |
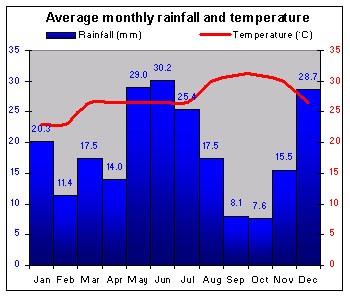 |
The lowlands are very humid with a constant temperature. The highlands are a little cooler, especially at night. |
|
People |
| Languages |
English Creole, Hindi, Tamil, Amerindian languages, English |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Tension exists between the Afro-Guyanese, descended from Africans brought over in the 17th to 19th centuries, and the Indo-Guyanese, descendants of south Asian laborers brought from India in the 19th century. This is currently displayed in the hostility existing between the opposition PNC, representing Afro-Guyanese, and the ruling PPP, traditionally representing the Indo-Guyanese. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
652
|
M |
GNP World rank |
163
|
|
| Inflation |
6 |
% |
Unemployment |
12 |
% |
|
StrengthsGold, rice, sugar, diamonds, bauxite, and timber production. Good tourism potential. Debt reduction plan agreed with multilateral agencies. WeaknessesHigh per capita foreign debt. Political instability dents investor confidence. Currency vulnerable to exchange rate pressure. Main exports vulnerable to fluctuations in international commodity prices. Weak manufacturing base. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
2001 |
Next election |
2006 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
The success of the PPP in the 1992 elections, widely seen as the first fair poll since independence, ended the dominance of the pro-Afro-Guyanese PNC. Veteran PPP leader Cheddi Jagan, a Marxist before adopting free-market policies, died in office in 1997. The PNC violently contested the succession of his wife Janet. A Caricom-brokered peace restored calm, though tension flared in early 2001 when the High Court condemned the 1997 poll. Violence erupted once again when elections in 2001 confirmed Janet Jagan's successor, Bharrat Jagdeo, as president. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Bauxite, gold, diamonds, gemstones, oil, manganese, uranium |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
No data |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
Not an oil producer |
|
Gold, bauxite, diamonds, and timber are major resources. Offshore and onshore prospecting for oil has not reduced the need for petroleum imports for electricity generation. More hydroelectric power plants are being constructed. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
63 |
Life expect. World rank |
130 |
| Population per doctor |
5556 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
54 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Heart diseases, violence, accidents, cancers |
|
Nearly all of the population have access to Guyana's mainly state-run health service. The referral system is relatively good. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
98 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
5 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
96 |
% |
Secondary |
75 |
% |
Tertiary |
11 |
% |
|
Education is based on the British system. Entry to high schools is by 11-plus examination. There is a state-financed university, though many students go to the USA or the UK. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
13 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
79 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
55 |
per 1,000 population |
|
Significant urban and rural poverty in Guyana has forced the government to make provision in the budget for poverty alleviation. Redundancies in the public sector exacerbate the problem. The poorest group in society are Amerindian subsistence farmers. There are a few very affluent urban families who derive their wealth not only from business but also from farming interests.
|
History |
During the 17th and 18th centuries, the Dutch founded three colonies, Essequibo, Demerara, and Berbice, in the region. In 1814, these came under British control, and were later combined to form British Guiana. - 1953 First universal elections won by PPP under Cheddi Jagan; parliament later suspended by UK.
- 1966 Independence from UK.
- 1973 PPP boycotts parliament, accusing PNC of electoral fraud.
- 1992 Fair elections won by PPP. Jagan president.
- 1997–1998 Jagan dies in office; PNC rejects his widow Janet's election victory. Political crisis.
- 1999 Caricom-brokered peace deal. Janet Jagan resigns due to illness. Bharrat Jagdeo takes over as president.
- 2001 Jagdeo and PPP reelected. Political violence flares again.
|
|