COUNTRY INFORMATION |
Introduction |
Once part of the Inca heartland, Ecuador lies on the western coast of South America. It was ruled by Spain from 1533, when the last Inca emperor was executed, until independence in 1830. Most Ecuadorans live either in the lowland coastal region or in the Andean Sierra. The Amazonian Amerindians are now pressing for their land rights to be recognized. Oil exports have boosted the economy. |
|
Climate |
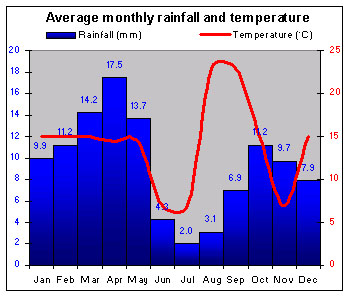 |
Climate varies from hot equatorial in the Amazon forests, to dry heat in the south and "perpetual spring" in Quito. |
|
People |
| Languages |
Spanish, Quechua, other Amerindian languages |
|
| URBAN/RURAL POPULATION DIVIDE |
|
|
|
Over half of the population is of Indian–Spanish extraction (mestizo). Black communities exist on the coast. The Amerindians, who make up about one-quarter of the population, are pressing for Ecuador to be described as a plurinational state, within which the different indigenous communities are recognized as distinct nationalities. The strong and largely unified Amerindian movement is at the forefront of social protests. |
|
Economy |
| GNP (US$) |
15256
|
M |
GNP World rank |
74
|
|
| Inflation |
96 |
% |
Unemployment |
13 |
% |
|
StrengthsNet oil exporter. World's biggest banana producer. Fishing industry. WeaknessesPoor infrastructure and land productivity. Energy crises. High inflation. Financial instability. Confusion over adoption of US dollar as official currency in 2000. |
|
Politics |
| Lower house |
Last election |
1998 |
Next election |
2002 |
| Upper house |
Last election |
Not applicable |
Next election |
Not applicable |
|
After the instability and corruption of the late 1990s, a new broad-based alliance was formed in 1999. Severe austerity reforms provoked widespread protests; the army intervened and Vice President Gustavo Noboa took over the presidency in 2000. The dollarization of the economy in 2000 led to popular protest, which resurfaced more widely and violently in response to IMF-backed austerity in 2001. |
|
Resources |
| Minerals |
Oil, natural gas, gold, silver, copper, zinc |
|
| Oil reserves (barrels) |
2.1bn barrels |
Oil production (barrels/day) |
416,000 b/d |
|
The government is encouraging faster oil exploration and higher output. Ecuador left OPEC in 1992. Overfishing is threatening mackerel and squid stocks. |
|
Health |
| Life expectancy |
70 |
Life expect. World rank |
83 |
| Population per doctor |
588 |
Infant mortality (per 1000 births) |
28 |
|
|
|
| Principal causes of death |
Malnutrition, intestinal infectious diseases, pneumonia, accidents |
|
Health care is seriously underfunded. Some services exist in poor urban districts but are still unavailable in many rural areas. Severe budget cuts mean that any improvement will depend on more outside aid. |
|
Education |
| Literacy |
91 |
% |
Expend. % GNP |
4 |
%
|
|
| PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION IN FULL TIME EDUCATION |
|
| Primary |
100 |
% |
Secondary |
56 |
% |
Tertiary |
20 |
% |
|
Some 20% of Ecuadorans in the relevant age group receive higher education at 16 universities. Programs have been launched to combat high levels of adult illiteracy in rural areas. Secondary schools are badly underfunded. |
|
Wealth |
| Cars |
41 |
per 1,000 population |
| Telephones |
100 |
per 1,000 population |
| Televisions |
218 |
per 1,000 population |
|
An estimated 60% of the population live in poverty, but disparity between rich and poor is not as great as in other South American countries.
|
History |
Alternating republican and military governments ruled Ecuador from independence in 1830 to 1978. - 1941–1942 Loss of mineral-rich El Oro region to Peru.
- 1948–1960 Prosperity from bananas.
- 1972 Oil production starts.
- 1979 Return to democracy.
- 1992 Amerindians win land in Amazonia.
- 1996–1997 Abdalá Bucarám Ortíz removed from presidency on grounds of mental incapacity.
- 1998–1999 Jamil Mahuad of DP wins elections; forms new majority alliance. Economic crisis.
- 2000 Army sides with Amerindian protestors. Vice President Gustavo Noboa replaces Mahuad.
|
|