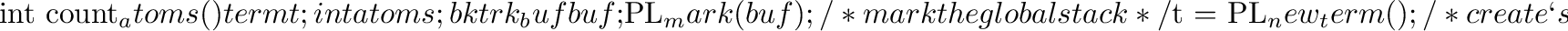
Modules are identified via a unique handle. The following functions are available to query and manipulate modules.
.BF .F module PL_context 0 Return the module identifier of the context module of the currently active foreign predicate. .F term PL_strip_module 2 term, module * Utility function. If term is a term, possibly holding the module construct module:rest this function will return rest and fill module * with module. For further nested module constructs the inner most module is returned via module *. If term is not a module construct term will simply be returned. If module * is NULL it will be set to the context module. Otherwise it will be left untouched. The following example shows how to obtain the plain term and module if the default module is the user module:
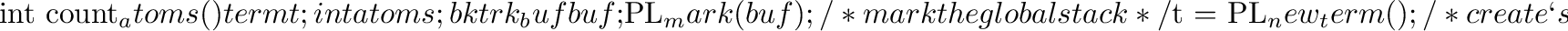
.F atomic PL_module_name 1 module Return the name of module as an atom. .F module PL_new_module 1 atomic Find an existing or create a new module with name specified by the atom atomic. .EF