 |
|||
|
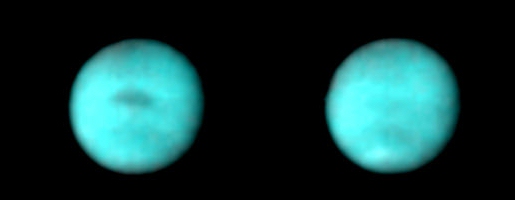
Voyager
images of Neptune taken five hours apart reveal a dynamic atmosphere.
|
|||
| THE MAGNETIC FIELD OF NEPTUNE | |||
| Neptune's magnetic field pattern is the same as would appear if a giant bar magnet were embedded in the planet. The field is dipolar, like Earth's, which means that it has a north and south pole, with field lines which exit at one pole (N) and enter at the other (S). In most respects it is quite like Uranus' field, but less complex and weaker. Neptune's field is certainly not as complex as Jupiter's. | |||
| Neptune's field axis is tilted 47o to the planet's axis of rotation and is offset from the centre (like Uranus'). The other planets have a field centred on their axis of rotation. The weird configuration is ascribed to the currents in the upper layers of the planet which create the field. | |||
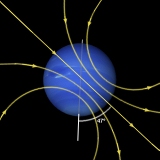 Neptune's magnetic field. |
|||
| Within the field are gaps, where charged particles trapped in the field lines, if they are aligned with the orbit of a satellite, are swept up. Voyager detected far fewer charged particles, electrons and protons, in Neptune's magnetosphere than at Uranus. | |||
|
|
|||