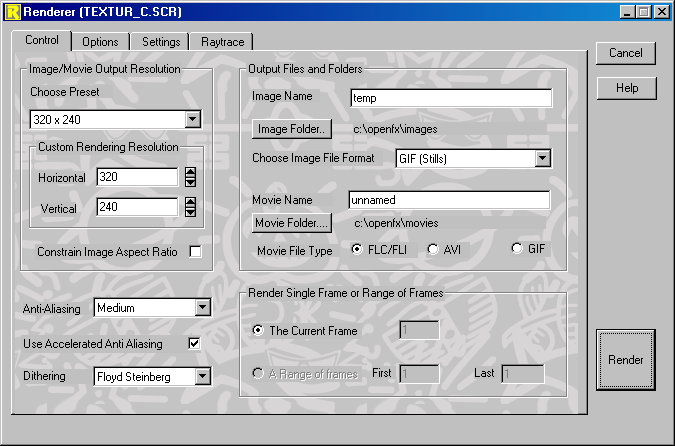
The Control page of the Renderer offers additional control parameters.

Resolution - Choose the resolution to which the image is rendered. Choose one of the presets or enter the number of horizontal and/or vertical pixels in the edit controls. The number of pixels in the image is horizontal resolution multiplied by the vertical resolution. The higher the resolution the longer it takes and the more memory it needs to render the image.
Anti-Aliasing - Choose the level of anti-aliasing. In low resolution modes the appearance of an image can be improved if it is anti-aliased. Basically, anti-aliasing smoothes out some of the 'jaggies' that are visible at the edges of colored regions in the image. Anti-Aliasing is very time consuming: it will take a little under 4 times as long to render a Good anti-aliased image than an image with no anti-aliasing. Using Best level of anti-aliasing, the image will take approximately 9 times longer to render than a non anti-aliased one.
Accelerated Anti-Aliasing - Accelerate the anti-aliasing process, with small quality reduction. Normally anti-aliasing an image increase the rendering time quite significantly, up to 9 or 10 times for a setting of Best. The main effect of anti-aliasing is seen near the edges of models or where faces with different colors join. Pixels in the interior of faces benefit very little from anti-aliasing. When this option is selected, anti-aliasing is applied near the edges of faces and not in the center. For most models this is as good as full anti-aliasing and it can be up to 3 times faster. Images with models that have image maps or shaders, where there is quite a bit of detail in the interior of faces, will not benefit as much from having their anti-aliasing accelerated.
Dithering - Choose the type of dithering. 24 bit images do not require dithering. Dithering is the process that reduces the banding effect evident on systems with a limited color palette. The standard 256 color VGA adapter is often insufficient to display an image without some degree of banding. A 24 bit display adapter is required for color resolution high enough to eliminate banding.
There are two methods of dithering. The Floyd-Steinberg error distribution procedure is very effective at removing the banding in single images. However, it is not always suitable for animations. Noise dithering, although not as high quality as Floyd-Steinberg, is consistent from one frame to the next, so it is more suitable for animation. Values of 10 to 30 usually give good results.
Image Format - Select the file format into which the image or images will be stored. This automatically determines the color resolution in the image. For an single image or multiple still images the GIF format uses an 8 bit palette, while the TGA and TIF formats are either High-Color or True-Color (16 bit or 24 bit).
Animation Type - Select whether animation type is a FLIC file, AVI file, or animated GIF file. Note FLC files will not be compressed if the resolution higher than 640x480 pixels.
Image Name - Name the image and the directory to which it is to be rendered. The default image directory is "Render".
Animation Name - Name the animation and the directory to which it is to be rendered and compressed. The default animation directory is "Movies".
Current Frame - Specify which frame of an animation is to be rendered.
Range - Specify a range of frames to be rendered.