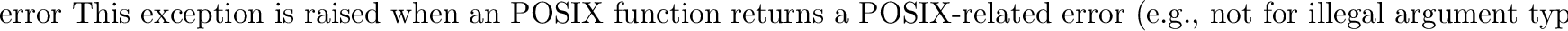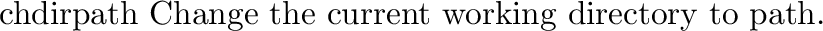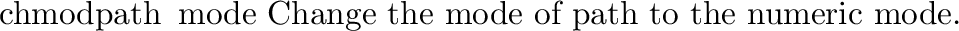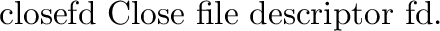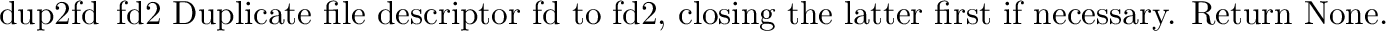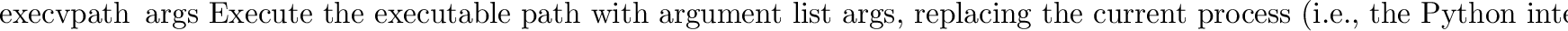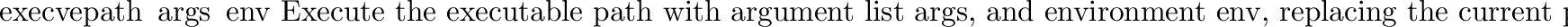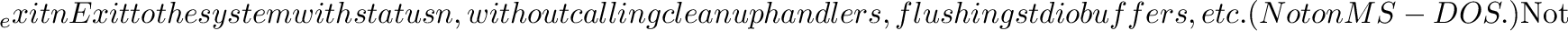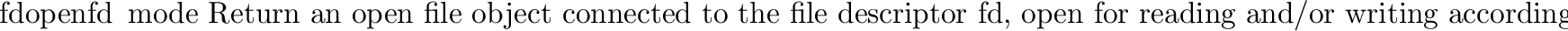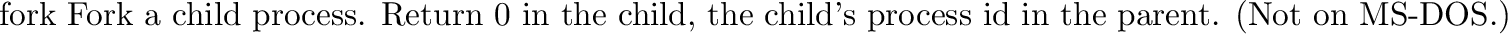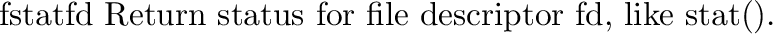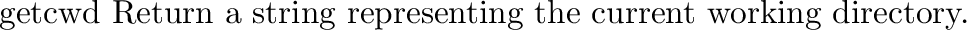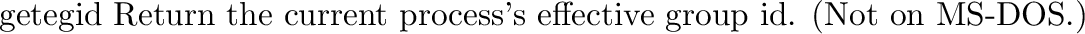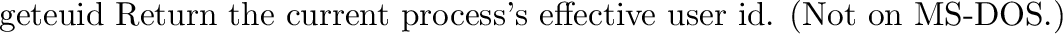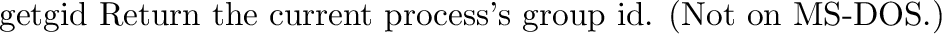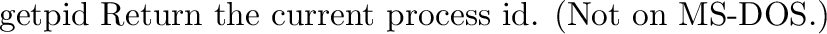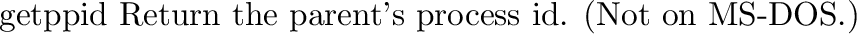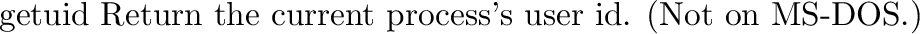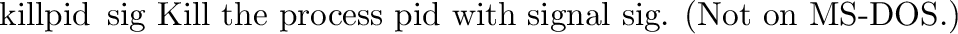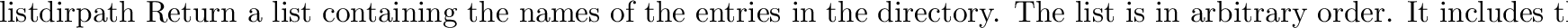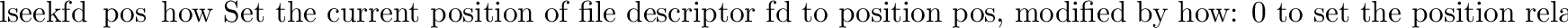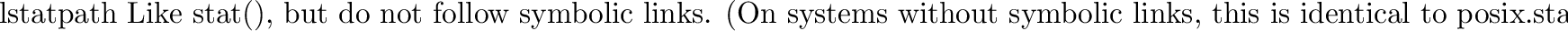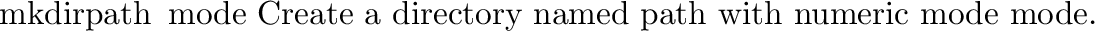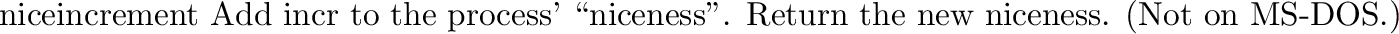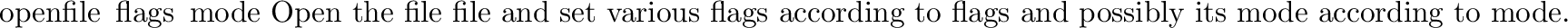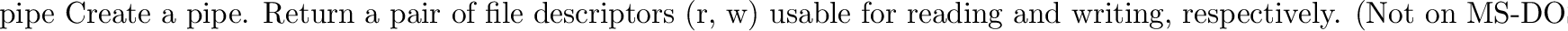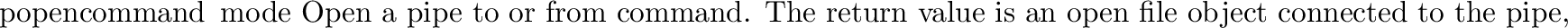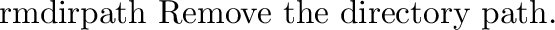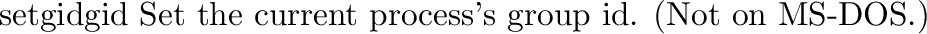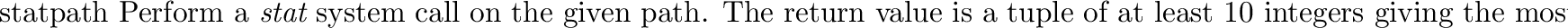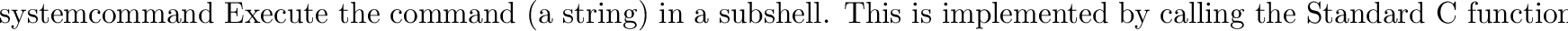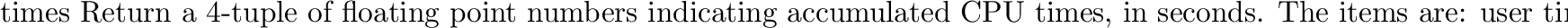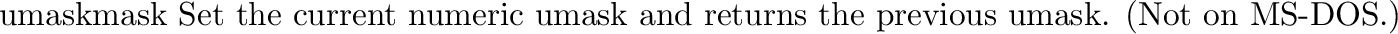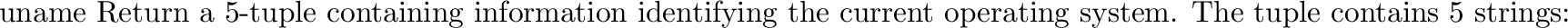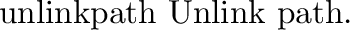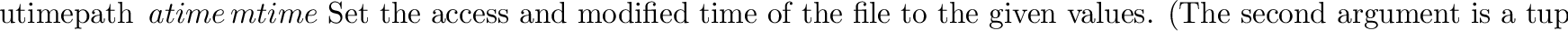posix
This module provides access to operating system functionality that is standardized by the C Standard and the POSIX standard (a thinly diguised interface). It is available in all Python versions except on the Macintosh; the MS-DOS version does not support certain functions. The descriptions below are very terse; refer to the corresponding manual entry for more information.
Errors are reported as exceptions; the usual exceptions are given for type errors, while errors reported by the system calls raise posix.error, described below.
Module posix defines the following data items:

It defines the following functions: