Model object
A model object is a type of object that contains the data of an application, provides access to that data, and implements logic to manipulate the data. Model objects play one of the three roles defined by the Model-View-Controller design pattern. (The other two roles are played by view and controller objects.) Any data that is part of the persistent state of the application (whether that persistent state is stored in files or databases) should reside in the model objects after the data is loaded into the application.
Because model objects represent knowledge and expertise related to a specific problem domain, they can be reused when that problem domain is in effect. Ideally, a model object should have no explicit connection to the view objects that present its data and allow users to edit that data—in other words, it should not be concerned with user-interface and presentation issues.
A Well-Designed Model Class
A model class—that is, a class that produces model objects—is typically a subclass of NSObject or, if you are taking advantage of the Core Data technology, a subclass of NSManagedObject. To create a model object, define it as you would a basic class and observe the Cocoa naming conventions. For example, begin the names of instance variables, declared properties, and declared methods with a lowercase letter and capitalize the first letter of embedded words.
When you implement your model subclass, you should consider the following aspects of class design:
Instance variables. You declare instance variables to hold the encapsulated data of an application. Instance variables can be objects, scalar values, or structures such as
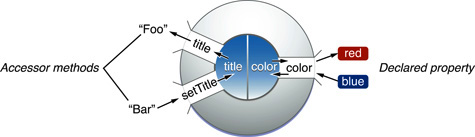
NSRange. There are tradeoffs to using object versus nonobject types, and object mutability is a consideration.Accessor methods and declared properties. Accessor methods and declared properties provide ways to preserve encapsulation because they mediate access to an object’s instance data. Accessor methods typically get and set the values of instance variables (and are colloquially known as getter and setter methods). Declared properties are a language-level convenience that allow the runtime to synthesize accessor methods for a class. An important role of accessor methods and declared properties is to manage object memory. For this reason, there are recommended forms for implementing getter methods and setter methods.
Key-value coding. Key-value coding is a mechanism that lets clients access an object's property using the property name as a key. It is used by Core Data and elsewhere in Cocoa. The naming of accessor methods (and, implicitly, declared properties) is a factor in this mechanism.
Initialization and deallocation. In most cases, a model class implements an initializer method to set its instance variables to reasonable initial values. It should follow the standard form for initializer methods. It should also ensure that it releases any instance variables holding object values in its
deallocmethod.Object encoding. If you expect objects of your model class to be archived, make sure that the class encodes and decodes the instance variables of its objects.
Object copying. If you expect clients to copy your model objects, your class should implement object copying.
Last updated: 2010-08-03